Consider the year 1971. If you were reading an article back then, you were likely reading it on paper, in a printed magazine, or a newspaper. You’re probably reading it on a desktop computer, laptop, or even your smartphone. In recent years, innovation has been so fast that it’s difficult to say which advancements have had the maximum impact on business and culture. In the 50 years since then, technology has advanced dramatically. One might assert that it has steadily improved our lives by trying to connect us to more data, leisure, and one another. Here are 20 significant breakthroughs that changed the world.
1. Apple iPhone
With the introduction of the iPhone in 2007, Apple brought a revolution. If social media, messaging, and the mobile internet hadn’t been freed from the restrictions of the desktop computer and optimized for the iPhone, they wouldn’t be nearly as powerful or universal. Cameras, dashboard GPS components, video recorders, PDAs, and music players died in the mobile revolution. And now we use mobile phones to shop, make video calls, and many more.

2. Wi-Fi
Without wireless systems such as Wi-Fi, the smartphones and the web we are using today would not exist. Wi-Fi was invented and made available to consumers in 1997. We may disconnect from the wired network and roam the house or office while trying to remain online with the modem and a dongle for our laptops. Wi-Fi is now so prevalent in our personal and professional relationships that it’s almost unimaginable to be without it in public space or home.

3. Voice Assistant
A voice assistant, such as Amazon’s Alexa, Google’s Assistant, or Apple’s Siri, is at the heart of many consumers’ homes. Their connected speakers will inform you of the weather, read you the headlines, and play music from numerous streaming platforms, among thousands of skills you use to control devices in your home.

4. Bluetooth
When first introduced to consumers in 1999, Bluetooth connected a cell device to a hands-free headset, enabling users to hold discussions while keeping their hands free for other tasks, such as driving. Activity trackers transmit messages to smartphones, and PCs can connect wirelessly to keyboards and mice.
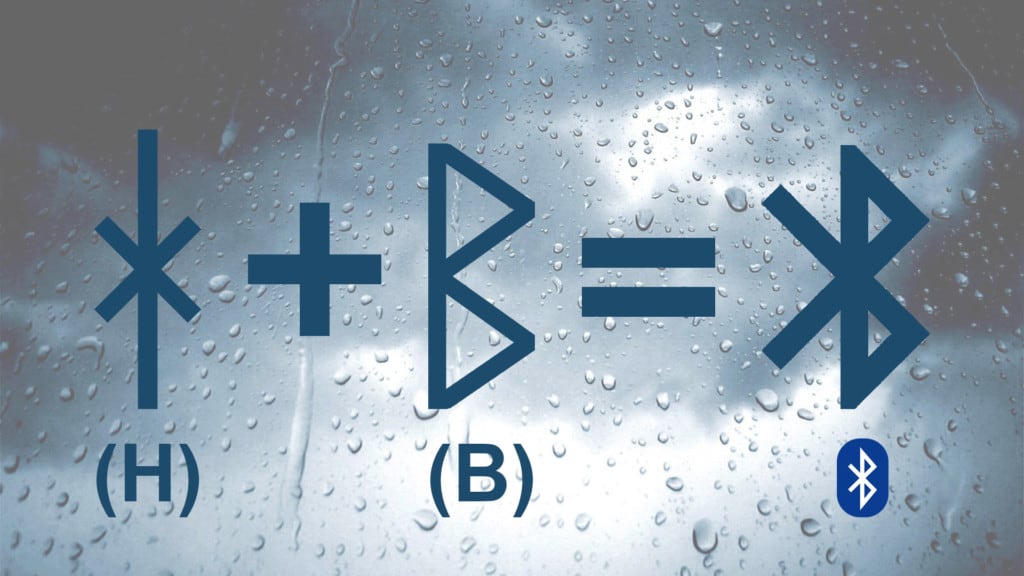
5. VPN
Both individuals and businesses discover that the VPN is an encoded tunnel for trying to transfer data over the internet and find it extremely useful. The technology, which first evolved in 1996, was almost exclusively used by businesses to enable employees to access the business’s internal network.

6. Bitcoin
Another technology made by anonymity, Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that made the news a few years ago for its rapid rise in value and then equally stunning decrease. Technology, currency, math, economics, and social dynamics are in the decentralized currency. Bitcoin attaches sellers and buyers via data encryption instead of using names, tax IDs, or Social Security numbers.

7. Blockchains
Blockchains perform as a secure digital ledger, and startups are working to integrate this technology into voting, lotteries, ID cards, identity verification, graphics rendering, welfare payments, job searching, and insurance payments. It also has the potential to be a big deal. According to Gartner, by 2025, blockchain will be worth $176 billion to businesses, and by 2030, it will be worth $3.1 trillion.

8. MP3 & MP4
The invention of MP3 and MP4 compression technologies has made entertainment much more portable in the last quarter-century. In the 1970s, the search for high-quality, low-bit-rate coding began. The goal was to compress audio into a digital file with negligible or no quality loss. The current MP3 player used by many was in the early 1990s, but customers didn’t get their hands on the first mobile MP3 player until 1998 when South Korean company Saehan published the MPMan, a flash-based player that might carry about 12 songs.
9. Facial Recognition
Facial recognition is a new technology, becoming progressively more prevalent in daily life. It’s a type of biometric verification that verifies your identity by using facial characteristics. Even though innovation enables firms to try to unlock devices and sort pictures in digital albums, advertising often becomes its primary application.

10. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is human intelligence processed by machines. Moreover, it has cracked into the real world in recent decades, becoming the most important technology of our time. Everything from voice recognition to spam detection is on the internet. Warner Bros. even aims to use AI to identify possible films and determine which ones to develop.

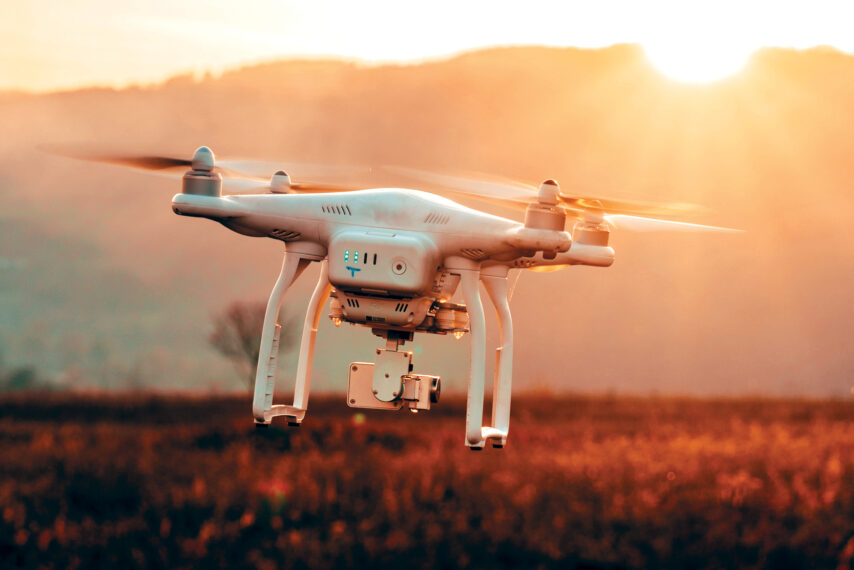
11. Drones
Drones have erupted in popularity over the years. Aircraft have transformed industries by shooting movie scenes, delivering to difficult-to-reach places, surveying construction sites, and spraying pesticides over crops to protect farms. Customs and Border Protection utilizes $16 million in military-style surveillance drones on the US-Mexico border that can fly up to 9 miles and equip with radar strong enough to identify traces in the sand.

12. DNA Testing Kits
Today, DNA aids in identifying suspects at crime scenes and allows crime labs to solve crimes that have been unsolved for decades. Investigators can use DNA to decide paternity, which can help with child support. People can learn about their genetic profile, lineage, and general health risks by using a DNA test kit.

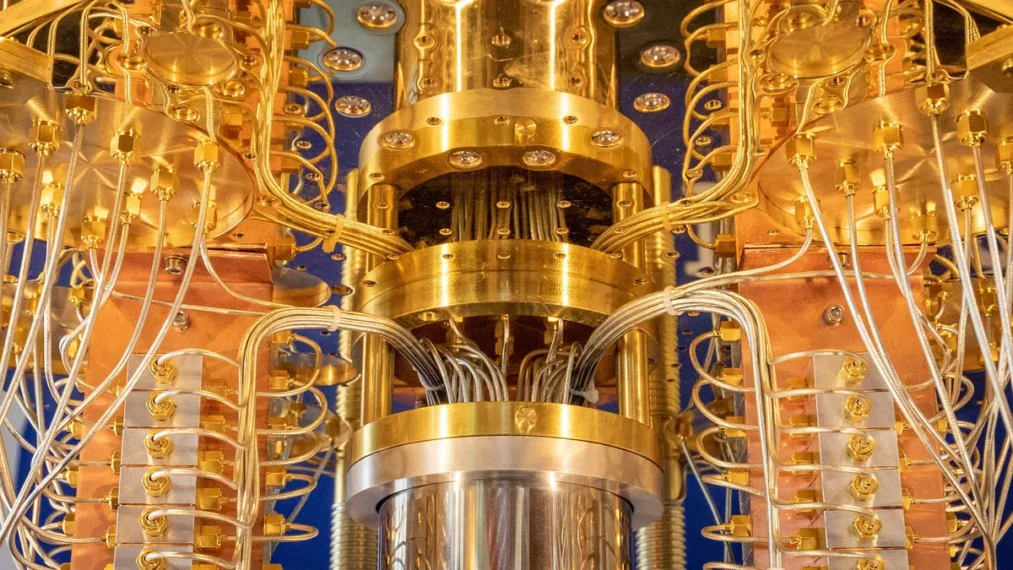
13. Quantum Computing
Billions and billions of dollars are being invested in quantum computing research and innovation by companies and the government. They believe this will pay off by letting them acquire new skills in science, transportation, raw material layout, financial services, machine intelligence, and other fields. Honeywell, which used to sell massive computer systems, predicts quantum computers will increase by ten each year for the next five years, creating them 100,000 times faster in 2025.

14. 3D Printing
Another technology that is getting closer to becoming mainstream every year is 3D printing, which is a way of forming a three-dimensional object. Manufacturers can now produce plastic parts softer than iron alternatives and with extraordinary shapes that are impossible to achieve using traditional injection molding techniques.

15. Apps
Mobile applications provide headlines, online streaming, text messaging, and social media apps. Mobile applications have changed the way we consume news and communicate. They’ve also altered how we go about our everyday lives, enabling us to discover on-demand vehicles, short-term and long-term leases, and have groceries brought to our home, to mention some of the numerous advantages.

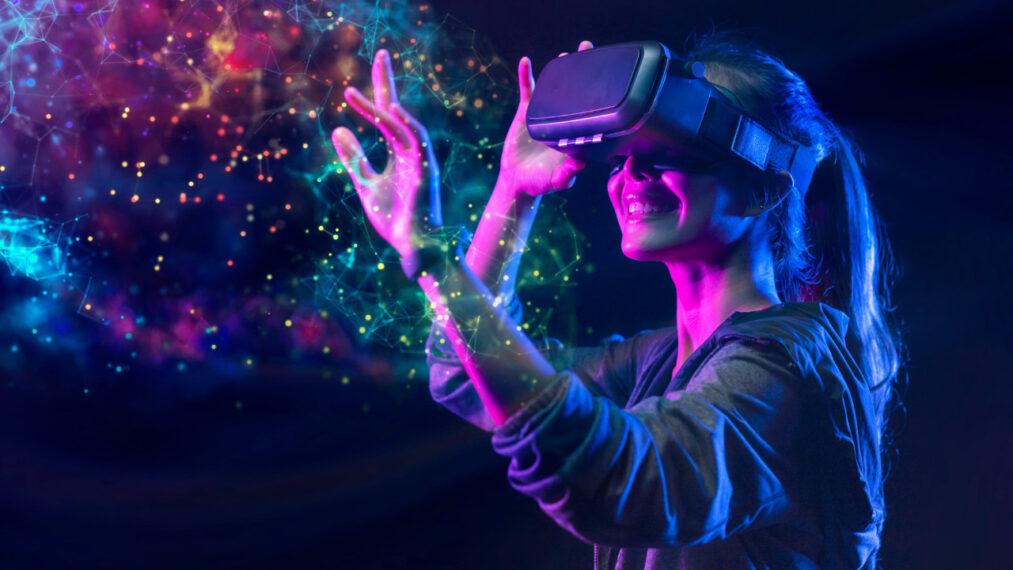
16. Virtual Reality
Virtual reality, which transfers consumers to a machine world, is becoming popular among large and small businesses. Virtual reality has enhanced the computer game company’s revenue. The technology sector sees other uses for technological innovations, such as schooling, universal healthcare, architectural style, and entertainment.

17. Ransomware
Ransomware locks a victim’s computer until they pay a ransom. Data suppression is a significant threat managed by hackers. It spreads either through email attachments or unsecured links, like other malware. Ransomware attacks hit nearly more than 1,000 government agencies, academic institutions, and healthcare providers in the United States in 2019, amounting to £7.5 billion.

18. Social Networking
Friendster, the platform that opened in 2002 and enabled people to fill out an online dating profile and connect with people they knew in real life, can be recalled by social networkers of a certain age. Two years later, Mark Zuckerberg initiated Facebook, a social networking website for university students. It became available to the public in 2006, quickly surpassing Friendster and MySpace.

19. Video Streaming
Since Netflix introduced its streaming services, its users can watch movies and TV shows over the internet. Consumers fell in love with the comfort of the programming, likely resulting in the “cutting the cord” phenomenon. Consumers began canceling cable and satellite subscriptions as more streaming services such as Amazon Prime had become accessible, and renting services such as Blockbuster closed up shop.

20. Music Streaming
Streaming now accounts for 88 percent of all music consumption in the US, up 7.6% from 2018. In 2019, on-demand audio broadcast consumption surpassed 705 billion streams, a 32 percent increase over the previous year.

So which technologies have impacted the world most? Do tell us in the comments.




















