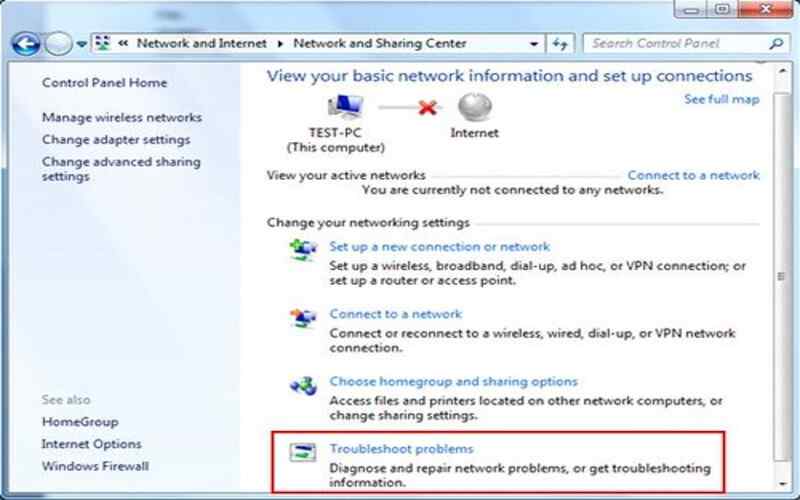
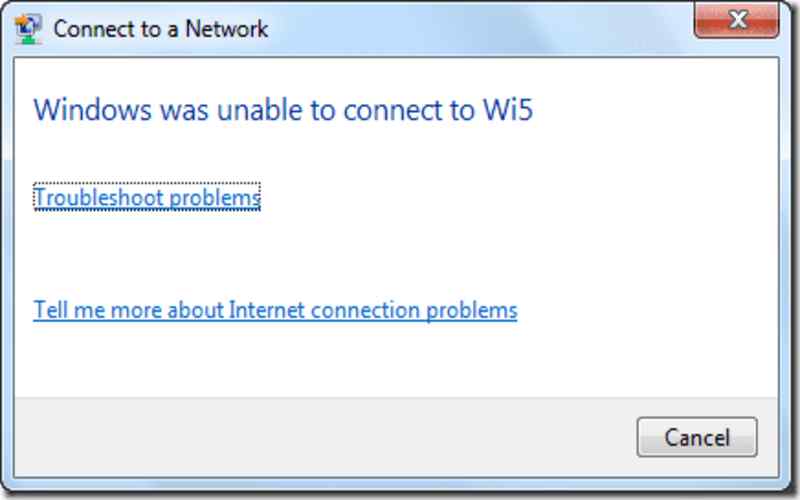
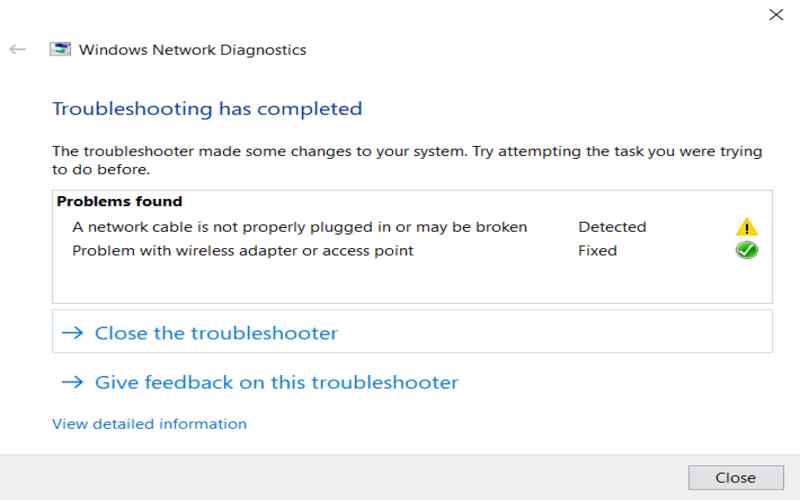
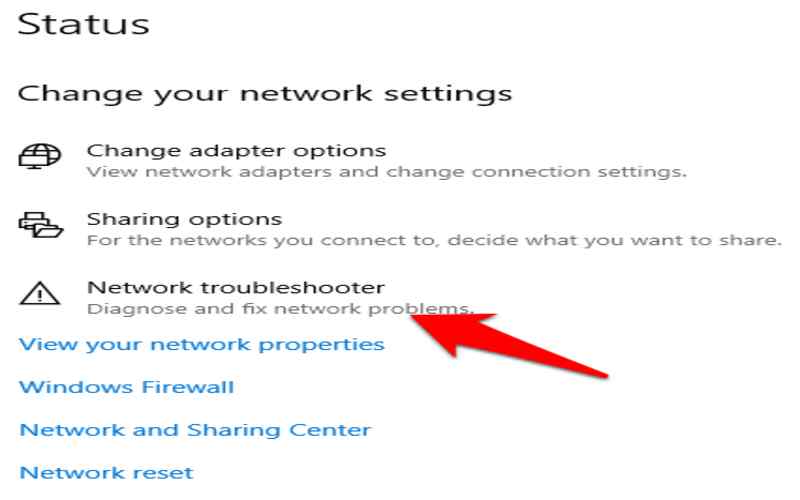
It might help to have a set of commands while troubleshooting Windows PC network connectivity issues. Users and network administrators may use these 20 Windows network troubleshooting commands to find and repair network issues.
1. IP Config
This command provides information about the IP configuration for all network interfaces on your Windows computer. It includes details such as the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server assignments for each interface. It is handy for resolving problems related to IP configuration and connectivity.
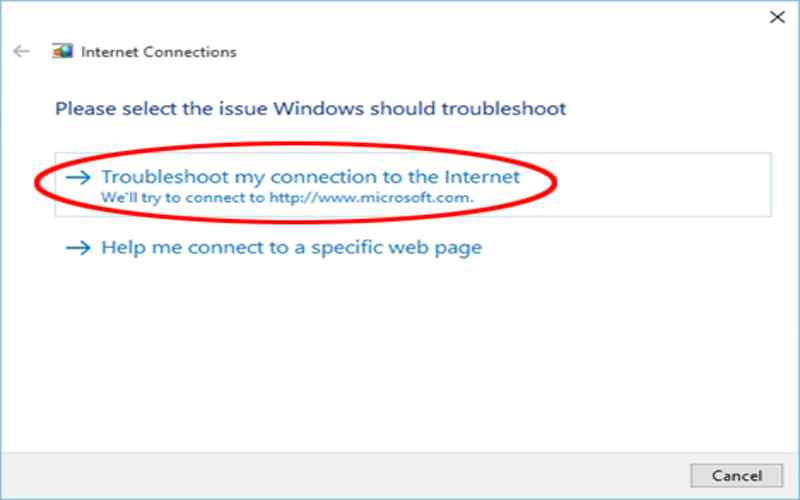
2. Ping
The ping command is in network troubleshooting. It tests the connection between two network devices by sending ICMP echo requests and receiving ICMP echo replies. It helps determine if a remote device is reachable and measures the time it takes for data to travel back and forth.
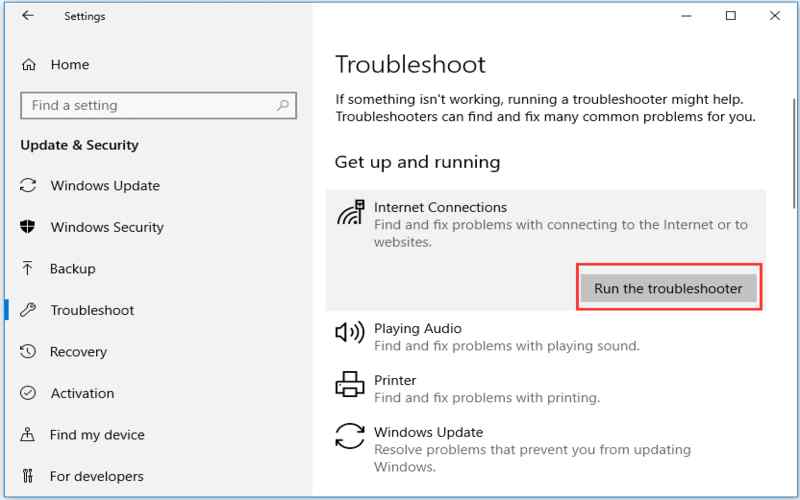
3. Tracers
This command traces the path that packets take to reach a specific destination IP address. It displays a list of routers. It hopes that the packets go through before reaching their destination. It can assist in identifying bottlenecks in the network and diagnosing latency issues.

4. NS Lookup
The ns lookup command performs DNS lookups to retrieve the IP address associated with a given hostname or domain name. It serves as a tool when troubleshooting issues with DNS, like resolving hostnames or verifying DNS server responses.
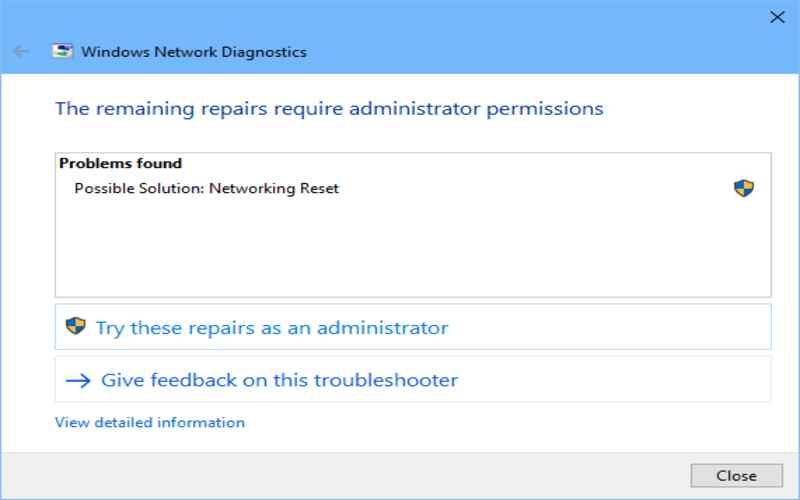
5. Net Stat
On a Windows computer, the net stat command shows network connections and ports being listened to. It provides valuable information about the local IP addresses, remote IP addresses, and network protocols for connection. It helps identify open network connections and potential security risks.
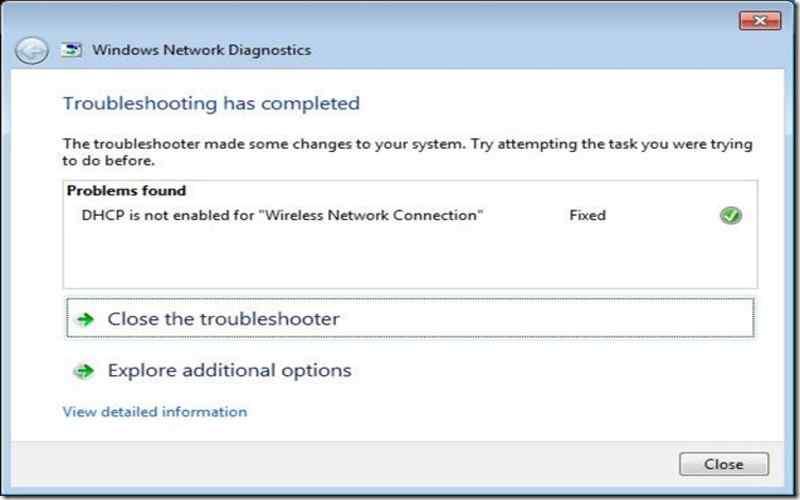
6. Route Command
The route command to view and modify the IP routing table. It provides information about the routing entries, including destination IP addresses, subnet masks, and gateway addresses for network interfaces. This command comes in handy when troubleshooting routing and connectivity problems.
7. ARP Command
The ARP command is the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache. It allows you to check and modify the IP-to-MAC address mapping for devices connected to your network. It helps resolve any issues related to cache entries. It is handy for resolving problems related to IP configuration and connectivity. It helps determine if a remote device is reachable and measures the time it takes for data to travel back and forth. It serves as a tool when troubleshooting issues with DNS, like resolving hostnames or verifying DNS server responses.
8. NetBIOS
You may use the net stat command to obtain NetBIOS information via TCP/IP, such as sessions, the NetBIOS name cache, and the NetBIOS scope ID. It proves handy in troubleshooting NetBIOS-related problems and verifying NetBIOS name resolution.
9. TCP Dump Command
TCP dump command is a tool for precisely capturing and analyzing network packets on a Windows machine. Network administrators often use this command to diagnose network issues by examining packet information.
10. Telnet Command
The Telnet command is your best bet if you need to connect to a network device using Telnet to log in and conduct network-based communication. You can create telnet connections with it. Use the telnet command to determine whether a remote device is accessible and ready to receive telnet connections.
11. Netsh
It’s a Windows command-line tool that lets you set up and view network settings. It offers options for managing network interfaces and other network-related configurations. It is for fixing issues with connection and IP settings. It monitors the time it takes for data to move back and forth and determines if a remote device is accessible. It is a tool for DNS troubleshooting, such as hostname resolution and DNS server response verification.
12. Use Command
The “use” command is to connect a Windows machine from a network resource that is shared. You may easily map network drives or access shared folders on a PC.
13. View Command
If you want to see a list of shared resources on a network, the “view” command is quite helpful. It provides information about computers on the network and the shared resources they offer. This command comes in handy when troubleshooting issues related to accessing shared network resources.
14. Net Statistics Command
For TCP/IP protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections, you can rely on the “command along with parameters. It offers insights into network performance. It helps monitor connections for any potential issues.
15. IP Config /Renew
To renew the configuration for all network interfaces on a Windows computer, you can employ the “IP config /renew” command. By using this command, you release your IP configuration. Request a new IP address lease from the DHCP server on your network.
16. IP Config /Release
On the other hand, if you wish to release the configuration for all network interfaces on your Windows computer, freeing up your IP address for use by other devices on the network, then executing the “IP config /release” command will do just that.
17. Winsock Reset
To fix problems with your network connection caused by corrupted or misconfigured Winsock settings, you can use the command “Winsock reset.” This command resets the Winsock catalog back to its default state.
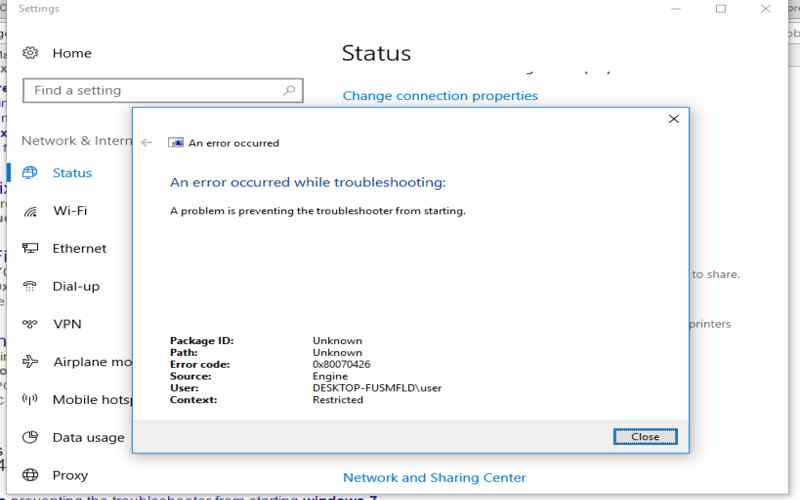
18. Netsh Int Ip Reset
To reset TCP/IP settings to their default values, you can use the command ” int ip reset.” This command comes in handy when dealing with issues related to TCP/IP configurations and helps restore the network stack to a stable state.
19. Interface Ipv4 Show Subinterfaces
If you need to check the settings on a Windows computer, you can utilize the command ” interface ipv4 show subinterfaces.” It provides a list of these subinterfaces along with their configurations. This information is valuable for troubleshooting network interface issues. It Identifies any discrepancies in settings.
20. Show Profiles
To view all profiles stored on a Windows computer, use the command ” show profiles.” it helps When troubleshooting Wi-Fi connectivity issues and confirming SSID and security settings for networks. It comes in useful while troubleshooting connection and IP setup issues. It calculates the duration of data transmission between two locations and assists in determining if a distant device is reachable. It is for debugging DNS-related problems, such as resolving hostnames and confirming DNS server replies.
Summary
In summary, these 20 commands serve as tools for resolving network connectivity problems on a Windows computer. Familiarizing yourself with these commands and understanding how they operate will significantly expedite the process of troubleshooting network issues.