Network protocols are a collection of defined guidelines that secure, dependably, and conveniently regulate the exchange of information. These rule sets are available for a variety of purposes. For example, wired networking (like Ethernet), wireless networking (like WLANs), and Internet communication are well-known examples of protocols. Numerous protocols make up the Internet protocol suite, which broadcasts and transfers data across the Internet.
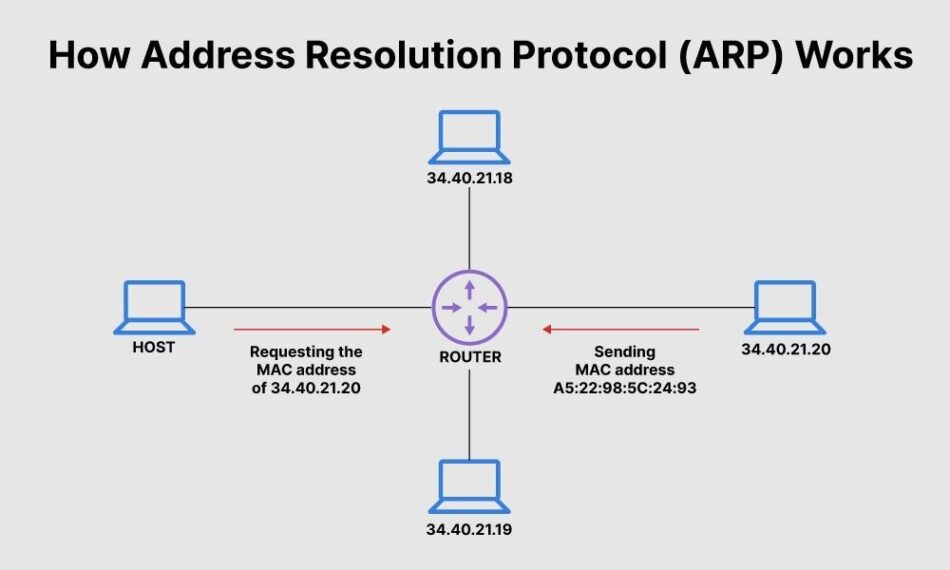
1. Protocol for Address Resolution (ARP)
A communication layer protocol is used to determine a media access control (MAC) address given an IP address (a mapping procedure between the data link layer and network layer). In a peer-to-peer network, the host cannot know where the network packet originated. This is a flaw that can lead to ARP spoofing. For example, if the attacker is on the same LAN as the victim or employs a compromised workstation connected to the same network, they may be able to take advantage of this. The attacker is supposed to link his MAC address to the target’s IP address so that any traffic intended for the target will instead be received by the attacker.
2. Domain Name System (DNS)
Because they are in numerical format, Domain Name System (DNS) IP addresses are complex for humans to read or remember. These IP addresses are transformed into human-readable hostnames using the hierarchical DNS system. Cache poisoning is the most frequent vulnerability in the DNS. In this case, the attacker uses a different IP address to direct the target audience to nefarious websites. For example, on a DNS server that allows recursive lookups, DNS amplification is used to boost the power of the attack.

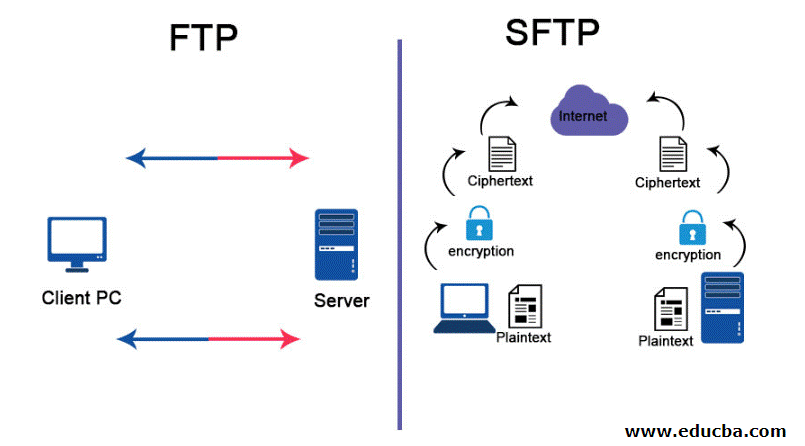
3. File Transfer Protocol/Secure (FTP/S)
It is a network protocol that allows for file transfers between clients and servers on a computer network based on the client and server model architecture. Most FTP assaults involve cross-site scripting, which occurs when an attacker sends a user’s browser malicious code in the form of a script (or cookies) via a web application. Data encryption and connection management are not features of the remote File Transfer Protocol (FTP). Instead, the usernames and passwords are sent in clear text, making them vulnerable to being captured by network sniffers or potentially used in man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM).
4. HyperText Transfer Protocol/Secure (HTTP/S)
On a computer network, it is utilized for safe communication. Its key features are website authentication, privacy and data integrity protection, and data exchange security. The Drown attack is a significant HTTPS flaw that allows attackers to bypass encryption and acquire passwords and credit card numbers. Another major bug is the Heartbleed issue, which permits the theft of data secured by the TLS/SSL encryption used to safeguard the Internet. Other flaws include Compressing Ratio Info-leak Made Easy and Factoring RSA export keys.
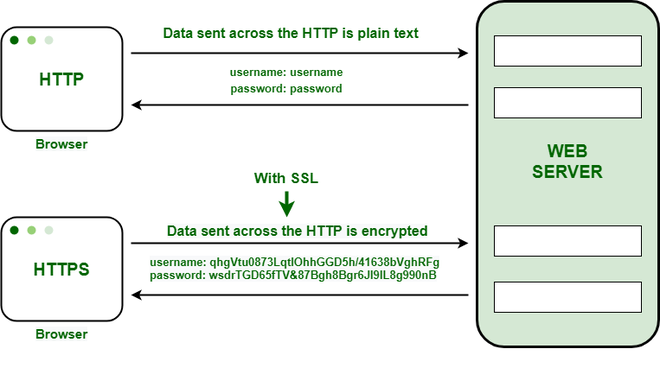
5. Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
With this Internet email protocol, emails are saved on the mail server but may still be retrieved, viewed, and handled as if they were kept locally on the user’s devices. In the first place, emails sent online go across insecure communication channels. Passwords, usernames, and messages themselves can all be intercepted. The mail server may also be the target of a Denial of Service (DoS) attack, which prevents emails from being sent or received. Additionally, malware can be inserted into the email server, which can then be delivered to customers via infected attachments.
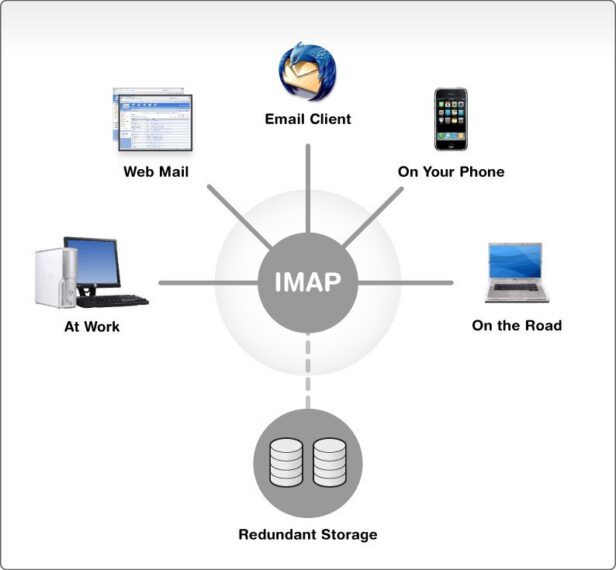
6. Post Office Protocol (POP3)
Emails are retrieved using an application-layer Internet protocol and delivered to the client’s local system. Even when you are offline, you can still use it to view messages. For example, a Firewire direct memory access, or DMS, an attack that exploits direct hardware access to read or write directly to the main memory without any operating system interaction or supervision, is one of the vulnerabilities that target mailbox storage. Login procedures enable the user to connect via unencrypted channels, resulting in the plain text transmission of login credentials across the network.
7. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
Microsoft created a protocol that enables users to connect to another computer via a graphical network connection. For example, one user uses RDP client software, and another uses RDP server software. Malware like ransomware may spread through unprotected computers due to a bug called BlueKeep. Attackers can connect to RDP services thanks to BlueKeep. Following that, they can give orders to steal or alter data, install harmful malware, and possibly engage in other criminal acts. Unfortunately, the user’s authentication is not necessary to exploit the vulnerability. Therefore, the user does not even have to click anything for it to work.
8. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
This signaling system can start, maintain, change, and terminate real-time sessions. These sessions may involve phone, video, messaging, and other communication applications and services between two or more endpoints on IP networks. Security risks like buffer overflow, injection attacks, hijacking, etc., can affect it. Unfortunately, these foes are simple to mount and incur the fewest charges, if any, for the attacker. Flooding attacks occur when an attacker delivers a large volume of traffic that overwhelms the target system’s resources and prevents it from providing services to genuine customers. Since signaling and data transfer channels are not separate, flooding in the SIP network infrastructure is easily possible.
9. Server Message Block (SMB)
It is a network communication protocol that allows network nodes to exchange access to files, printers, and serial ports. Additionally, it provides a framework for approved and authenticated inter-process communication. For example, the SMB Relay attack, which is used to deliver Man-in-the-Middle assaults, is a vulnerability in SMB. The EternalBlue attack is an additional attack. For example, a remote attacker can run arbitrary code on the target computer by sending specially crafted packets mismanaged by the SMBv1server in different versions of Microsoft Windows.
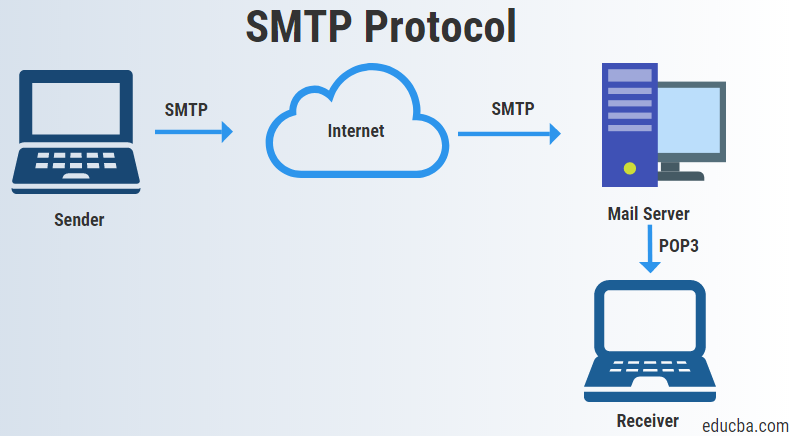
10. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Emails are sent using this application layer protocol for communication. Under the guise of the unaware owner of the open relay, spammers and hackers can utilize an email server to deliver spam or malicious software via email. A directory harvest attack is another technique hackers use to collect legitimate email addresses from a server or domain. Buffer overflow assaults, Trojan horse attacks, shell script attacks, etc., are vulnerabilities.