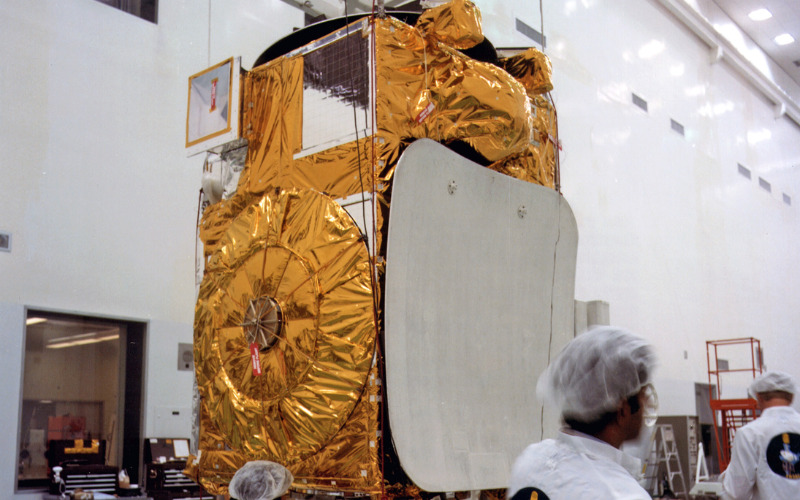
Objects that orbit celestial bodies like planets or moons are known as satellites. They can be man-made and launched by people, or they can be natural, like the Moon. Artificial satellites are essential in many areas, including communication, navigation, weather forecasting, and scientific research. Communication Internet access, television broadcasts, satellite phones, and telephone conversations are all made possible by the usage of satellites. GPS (Global Positioning System) navigation satellites provide these services. In order to accomplish their goals, satellites are built with a variety of sensors and equipment that are tailored to their respective missions. Here are some well-known satellites:
1. Aryabhata
Aryabhata became India’s first satellite, named after the Indian astronomer and mathematician. It was launched into space on April 19, 1975, by the Soviet Union. It is a 360 kg satellite designed to conduct scientific space experiments. Its goal is to observe X-ray astronomy and solar physics. It played a major role in data collection on cosmic X-ray sources and contributed to space science.
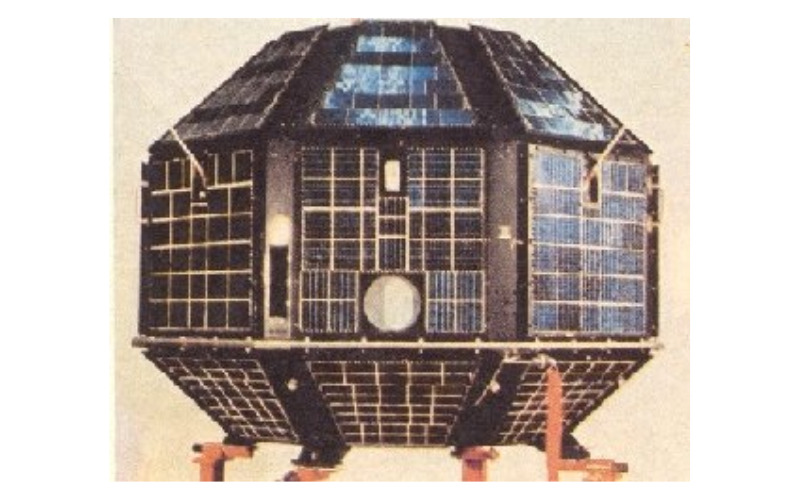
2. Chandrayaan-1
Chandrayaan-1, India’s first lunar exploration mission, was launched into orbit on October 22, 2008. It is used by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to perform in-depth research on our moon. It examines its mineral content, maps its whole surface, and searches for water molecule traces.
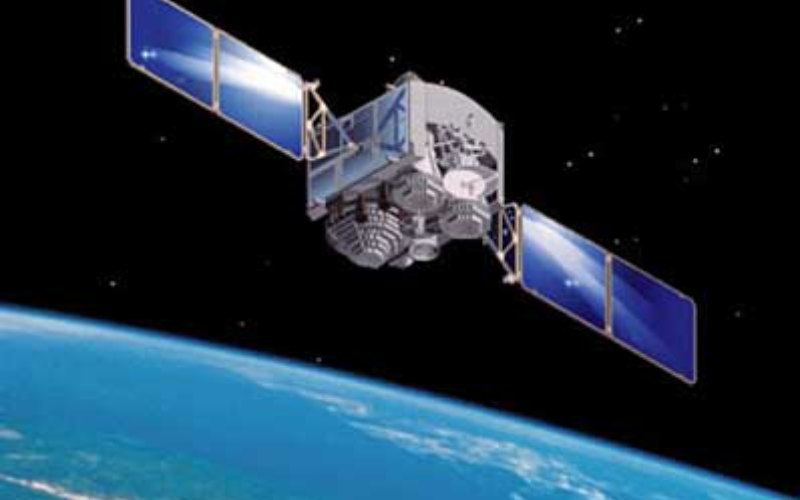

3. INSAT-3D
A weather satellite known as INSAT-3D was launched by ISRO on July 26, 2013. It is utilized for weather monitoring and forecasting and is a part of the Indian National Satellite System. In addition to taking pictures, it gathers statistics on land and ocean surface temperatures, atmospheric variables and weather patterns.
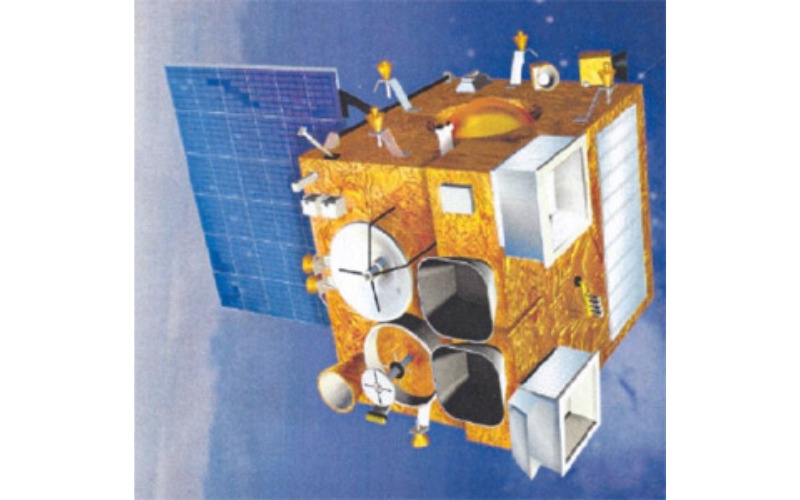

4. Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) Or Mangalyaan
The Mars Orbiter Mission, popularly known as Mangalyaan, was released with the aid of ISRO on November 5, 2013, making it India’s first interplanetary undertaking. It examines the environment, topography, and mineral content of Mars and looks for evidence of water and viable habitability. India is the first to go to Mars on its first try, which changed into a noteworthy accomplishment. This project contributed to our knowledge of Mars’ environment by imparting useful information on the ecosystem of Mars and its interactions with the solar wind.

5. INSAT-3DR
INSAT-3DR is a meteorological satellite launched by ISRO on September 8, 2016. It is designed to offer climate monitoring and forecasting abilities. This includes devices to capture high-decision images of the Earth’s surface and collect information on several atmospheric parameters. It performs an important role in catastrophe management, weather forecasting and cyclone tracking. It offers real-time facts on cloud cover, sea surface temperature, and other meteorological variables, supporting the prediction of weather patterns and extreme weather events.

6. EMISAT
EMISAT is a satellite launched by ISRO on April 1, 2019. It is an electronic intelligence satellite designed to gather signal intelligence and offers a strategic guide to India’s defence forces. It carries superior digital intelligence payloads capable of reading communication signals from different satellites and radars, detecting and intercepting. The satellite plays a vital role in monitoring space and imparting valuable data for defence and surveillance.
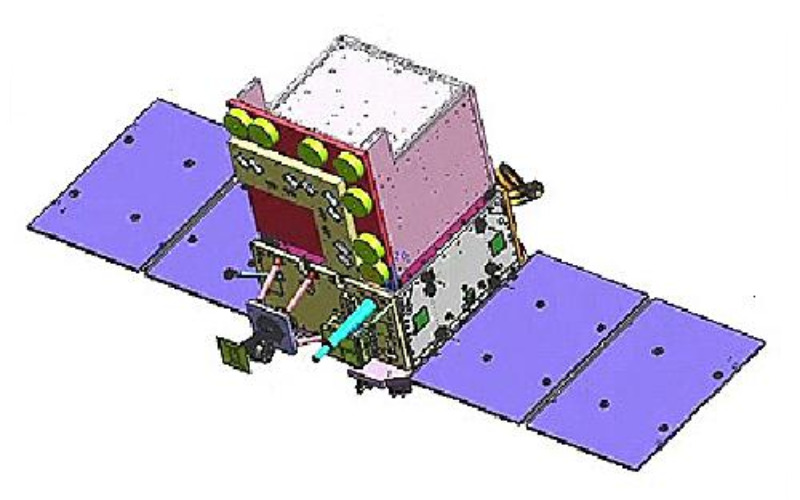
7. GSAT-7 (INSAT-4F)
GSAT-7, called INSAT-4F, is a communication satellite released with the aid of ISRO on August 30, 2013. It is a committed navy communication satellite designed to offer stable and dependable communication for the Indian Navy. It operates in more than one frequency band, facilitating communication among ground stations, naval ships, submarines and aeroplanes. It allows real-time transfer of video, information and voice, enhancing the Navy’s operational abilities and maritime safety.

8. GSAT-29
GSAT-29 is a communication satellite released by ISRO on November 14, 2018. It is a high-throughput satellite designed to offer communication services in far-off and rural areas of India. It includes conversation payloads, together with Ka-band transponders to deliver instructional sources to underserved regions, high-speed net connectivity and telemedicine offerings. This plays a critical position in bridging the virtual divide and permitting virtual empowerment for all.

9. GSAT-30
GSAT-30 is a communication satellite released by ISRO on January 17, 2020. It is designed to offer communication services over the Indian subcontinent and its neighbouring regions. It operates in the Ku-band frequency range and includes transponders for VSAT networks, direct-to-home television broadcasting and telecommunication services. This enhances the availability and quality of communication services, supporting broadcasting, internet connectivity and telephony.

10. Bhaskara-1
Launched on June 7, 1979, Bhaskara-1 became India’s first experimental satellite. It had a primary focus on Earth observation and carried devices to gather information on hydrology, forestry, and geology. This satellite supplied precious insights into India’s environment, natural sources and land use. It played a role in advancing the nation’s remote sensing and laid the foundation for upcoming satellite missions.
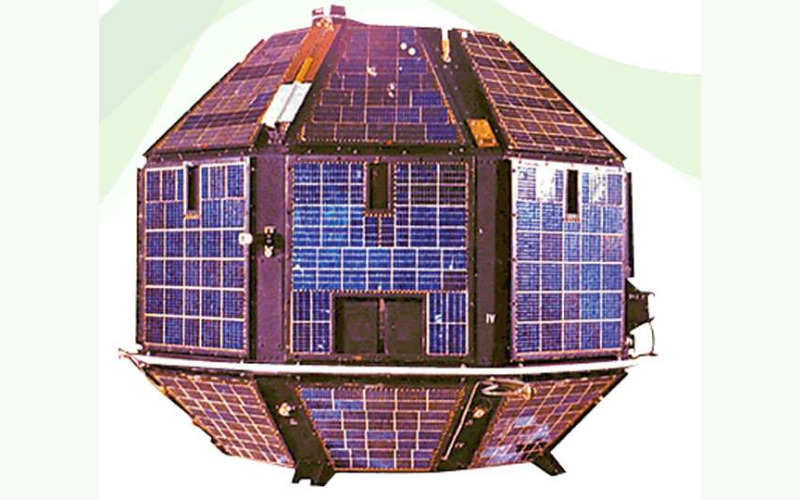

11. Bhaskara-2
Launched on November 20, 1981, Bhaskara-2 turned into the second satellite within the Bhaskara series. It endured the mission of Earth observation and carried advanced instruments to study forestry, oceanography and agriculture. The satellite offers data on coastal vegetation, sea surface temperatures and different environmental variables. It contributed to the understanding of India’s coastal ecosystems and supported numerous scientific studies endeavours.
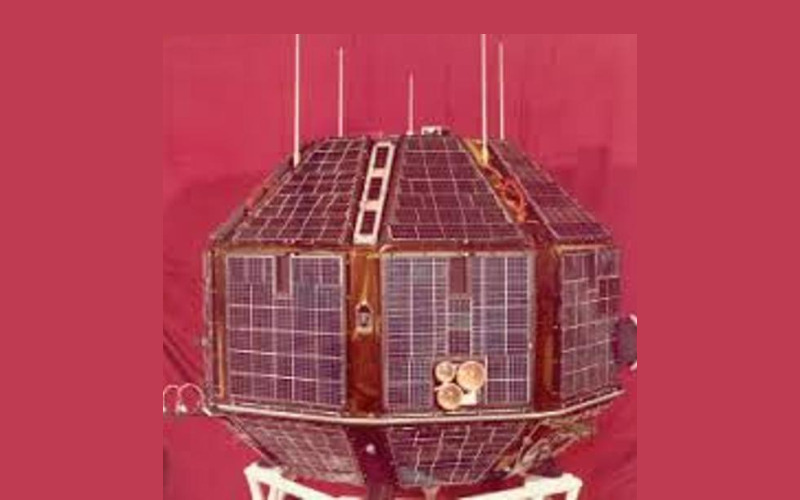

12. Rohini-1
Also known as RS-1, Rohini-1 was India’s first indigenously developed satellite, launched on July 18, 1980. It served as a test bed for building and launching satellites and carried out scientific experiments for research and technology development. The satellite was instrumental in gaining experience in satellite testing, fabrication and launch operations, setting the stage for subsequent missions.
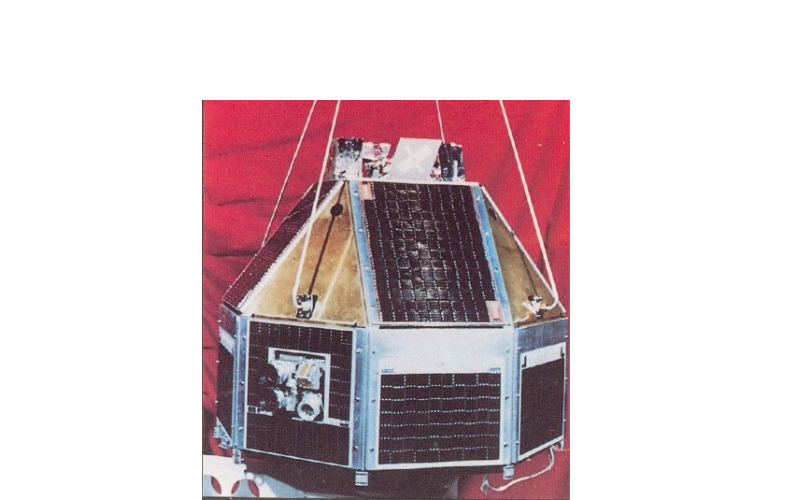
13. Rohini-2
Launched on April 17, 1983, Rohini-2 became the second satellite in the Rohini series. It focused on carrying out scientific experiments in space including microgravity research. The satellite provided possibilities to study the behaviour of fluids, materials and biological systems in microgravity situations. The data obtained helped in expertise in the basic physics and biology in space.
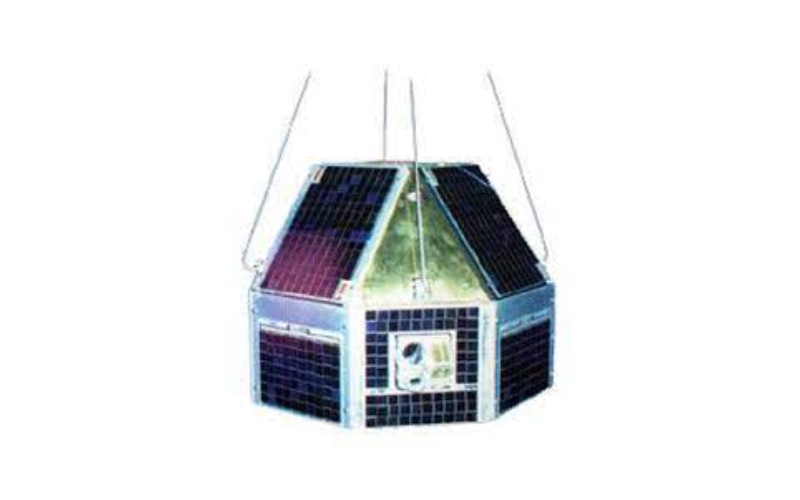

14. Rohini-3
Known as RS-D2, Rohini-3 was launched on May 31, 1981. It carried several scientific payloads, including X-ray astronomy experiments. The satellite played a crucial role in advancing India’s space technology and contributed to the development of scientific instruments and satellite systems.
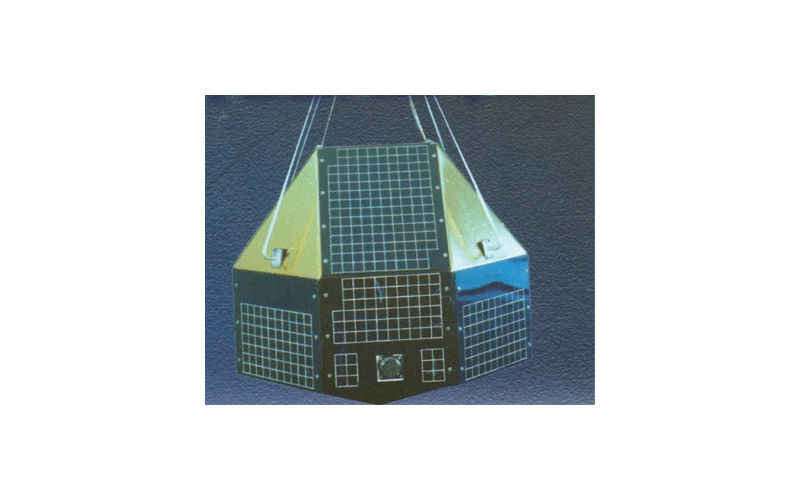

15. IRS-1A
Launched on March 17, 1988, IRS-1A changed into India’s first operational remote sensing satellite. It possesses advanced sensors to capture excellent pictures of the Earth’s surface for diverse applications, which include environmental monitoring, useful resource mapping and land-use planning. IRS-1A supplied precious information for water resources, agriculture, urban development and catastrophe management.

16. IRS-1B
Launched on August 29, 1991, IRS-1B was the second satellite in the Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) series. It carried improved sensors and enhanced capabilities for Earth observation. The satellite provided valuable data for land and water resource management, environmental monitoring and forestry. It contributed significantly to India’s remote sensing capabilities and helped in addressing societal needs.

17. IRS-1C
Launched on December 28, 1995, IRS-1C is the third satellite in the IRS series. It carried advanced sensors capable of capturing multispectral and hyperspectral images of the Earth’s surface. The satellite offered valuable facts for environmental monitoring, natural resource mapping and urban planning. It performed a critical function in helping India’s developmental activities and sustainable management of resources.

18. IRS-1D
Launched on September 29, 1997, IRS-1D was the fourth satellite in the IRS series. It continued the mission of Earth observation and carried enhanced sensors for improved imaging capabilities. The satellite provided valuable data for water resources, forestry, agriculture and disaster management. It contributed to India’s remote sensing capabilities and played a crucial role in supporting various applications for socioeconomic development.
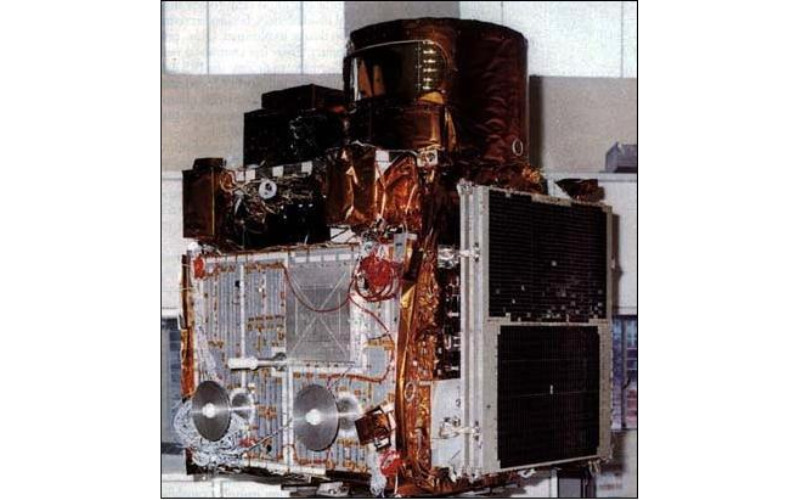
19. INSAT-1A
Launched on April 10, 1982, INSAT-1A was India’s first satellite inside the INSAT series. It was a multipurpose satellite designed to offer broadcasting, telecommunications, and meteorological services. It carried transponders for TV broadcasting, telecommunications, and meteorological information collection. It played an important function in expanding India’s satellite network, improving telecommunication offerings and improving weather monitoring abilities.

20. INSAT-1B
Launched on August 30, 1983, INSAT-1B was the second satellite in the INSAT series. It carried improved and additional transponders to enhance communication and broadcasting services. It featured advanced meteorological instruments for weather forecasting and observation. It played a significant role in strengthening India’s satellite communication infrastructure and providing valuable meteorological data for weather prediction and monitoring.





















