Energy storage is the collection of energy obtained at one time for later use to reduce energy demand-supply imbalances. An accumulator, or a battery, is a device that stores energy. Energy storage is a vital hub for the entire grid, supplementing resources ranging from wind, solar, and hydro to nuclear and fossil fuels, demand-side resources, and system efficiency assets. This can work as a transmission, generation, or distribution asset, sometimes all at once. Energy storage can potentially reduce peak demand while also saving money for customers. In both rural and urban settings, community resilience is essential. Peak energy requirements in densely populated areas can be met with energy storage, lowering the strain on the grid.
1. Biofuel
Biofuel indicates any fuel derived from biomass, such as plant or algae material or livestock manure. Biodiesel is a liquid fuel made from renewable resources, including fresh or utilized vegetable oils and animal fats, that is a cleaner-burning alternative to petroleum-based diesel fuel. Biodiesel is manufactured by combining vegetable oil with alcohol, recycled cooking grease, or animal fat. It is non-toxic and biodegradable. Some other examples include wood, biogas, methanol, ethanol, and butanol.

2. Hydrated Salts
The salts that consist of water molecules are identified as hydrated salts. A hydrated salt seems to be a crystalline salt molecule that has several water molecules loosely attached to it. Salt hydrates are of special interest due to their usually high energy storage density (up to 850 kWh/m3). However, mass and heat transfer limitations must be considered throughout the charging and discharging stages.

3. Hydrogen Storage
Hydrogen can be actually stored as a liquid or as a gas. High-pressure tanks are typically required to store hydrogen as a gas (350–700 bar [5,000–10,000 psi] tank pressure). Because hydrogen’s boiling point at one-atmosphere pressure is 252.8°C, liquid hydrogen storage necessitates cryogenic temperatures. Due to the minimal volumetric energy density, hydrogen is difficult to store. Because it is the lightest and simplest element, lighter than helium, it is easily lost in the atmosphere.

4. Cryogenic Energy
Cryogenic energy storage (CES) refers to the using lower temperature (cryogenic) liquids such as liquid air or liquid nitrogen to store energy. The technology is primarily used for large-scale energy storage. The system is based on proven technology and is used securely in many industrial applications. It does not require the manufacture of any particularly rare or expensive components. It is made of common industrial components, which minimizes the potential losses; and has a lifespan of decades while also being repaired with a spanner.

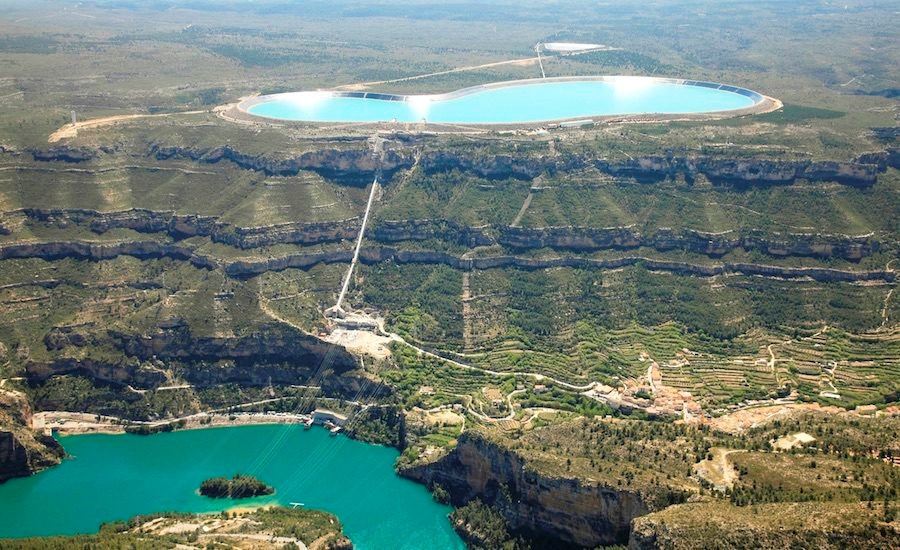
5. Pumped Storage Hydropower
Pumped Storage Hydropower or PSH is a type of hydroelectric energy storage. PHS is a structure of 2 water reservoirs at different altitudes that can generate power as water flows from one reservoir to the other (discharge) and through a turbine. Pumped hydroelectric storage equipment stores energy as water in an upper reservoir pumped from a lower elevation reservoir. When there is a request of high electricity demand, power is generated by releasing stored water via turbines in the same way that a conventional hydropower station does.

6. Liquid Air Energy Storage
Liquid Air Energy Storage, or LAES, uses electricity to cool air until it liquefies, then stores the liquid air in a tank, returns the liquid air to a gaseous state via ambient air or waste heat from an industrial process, and uses that gas to turn a turbine and generate electricity.

7. Eutectic System
A eutectic process is a homogeneous, solid mixture of two or more compounds that form a super-lattice; the mixture melts or solidifies at a temperature lower than the melting point of any individual materials. They are stable, have twice the heat conduction of conventional PCMs, and three times the thermal storage capacity. Commercial eutectic alloys are typically high in purity and thus relatively expensive.
8. The Flywheel Energy Storage System
FESS, or flywheel energy storage systems, uses kinetic energy in a rotating mass with minimal frictional losses. An integrated motor-generator uses electric energy to accelerate the mass to a certain speed. Using the same motor-generator, the energy is discharged by drawing down the kinetic energy. FESS is distinguished by its long lifespan, which is typically 20 years.
9. Gravitational Potential Energy Storage
Gravitational potential energy refers to the energy that an object possesses or acquires due to of a change in its position while in a gravitational field. A gravitational potential is a form of energy associated with gravitational attraction or gravity. A gravity battery is a kind of storage device for energy that stores gravitational energy, also known as potential energy.

10. Solar Pond
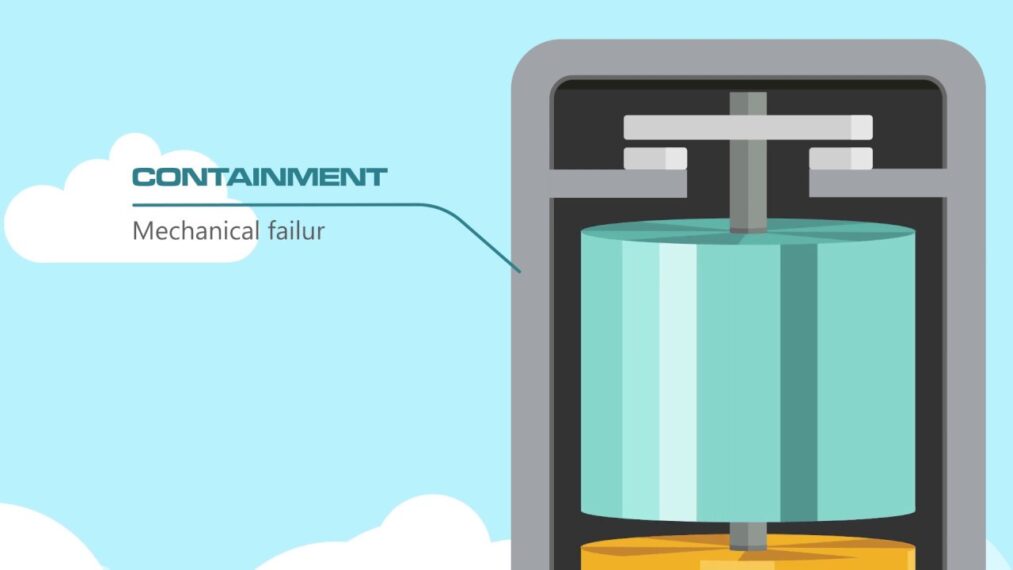
A solar pond is a saltwater pool in which solar thermal energy is collected and stored. Low-salinity water drifts on top of the high-salinity water, forming a vertical salinity gradient. The concentration of salt solutions increases with depth in the layers. Some applications of the solar pond include heat to industrialized processes, house heating and cooling, electricity power generation, swimming pool heating, commercial or cultivational crop drying, desalination, and greenhouse heating.
11. Steam Accumulator
A steam accumulator is essentially an expansion of the boiler’s energy storage capacity. When the plant’s steam demand is minimal, and the boiler is capable of producing more steam than is needed, the excess steam is pumped into a mass of pressure-stored water. The concurrent decrease in energy quality for the steam accumulator and the concrete system may allow for the use of thermal energy cascades.
12. Compressed Air Energy Storage
CAES (compressed-air energy storage) is a method of storing energy for later uses compressed air. The management of thermal energy is a continuing task in large-scale CAES design because the air compression causes an unwanted temperature rise that not only decreases operational efficiency but can also cause damage. Pneumatic energy has existed in various forms for decades. It is compressed and stored in a gas (usually air) before transforming into mechanical energy.

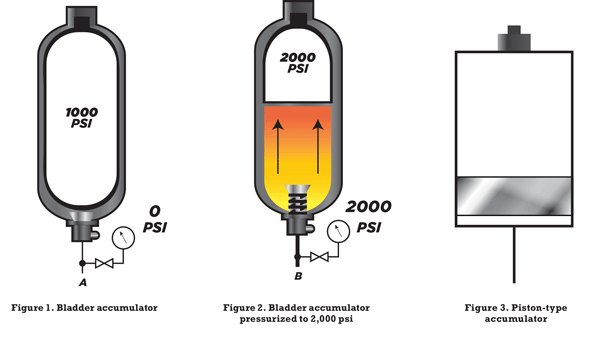
13. Hydraulic Accumulator
A hydraulic accumulator is a pressure vessel in a hydraulic system that performs various functions. They’re used to keep the pressure up and reduce pressure peaks, store and recover energy, power chassis suspensions, and dampen shock, pulsations, and vibration. An accumulator functions similarly to a rechargeable battery. In the case of electricity, electrical energy is stored in a battery.
14. Thermal Energy Storage
Ice is a medium in which energy can be stored for later use, as in ice-based storage systems for thermal energy. Thermal ice storage is an established technique that decreases chiller size and changes compressor energy, condenser fan energy, and pump energy from peak periods when energy costs are high to non-peak periods when energy is more abundant and less expensive.

15. Vanadium Pentoxide
As a catalyst, vanadium pentoxide is used in various industrial processes. Specifically, highly disordered V2O5 nanolayers with interplanar distances of up to 1.1 nm allow for fast transport of K-ions between sections in an aqueous electrolyte and, as a result, high energy storing capacity and power density. Our results are notable for using multiple spectroscopic tools for material characterization and measurements.

16. Storage Heater
A storage heater, also known as a heat bank in Australia, is an electrical heater that stores thermal energy throughout the evening or at night, when electricity is less expensive and releases it during the day as needed. Solar storage heaters, on the other hand, are constructed to store solar energy as heat and release it during the night or other times when it is needed, which is a lower-cost option than selling surplus power to the grid and buying it back at night.

17. Fireless Locomotive
A fireless locomotive is a type of engine that runs on reciprocating engines that are powered by a reservoir of compressed air or steam that is replenished at regular intervals from an external source. The engine operates similarly to a traditional steam engine, with high-pressure steam above the water in the accumulator. As the steam is utilized and pressure loss occurs, the superheated water boils, substituting the used steam.

18. Molten Salt Storage
Molten salt energy storage is a cost-effective, highly flexible solution for long-term energy storage various power generation technologies. It heats liquid salt to 565 degrees Celsius using renewable energy. It is then stored until it is required. Heat generates steam, which drives a turbine and can produce its full rated output for up to 24 hours. When renewable energy is unavailable, fuel heaters can boost the temperature of the salt and offer continuous power.

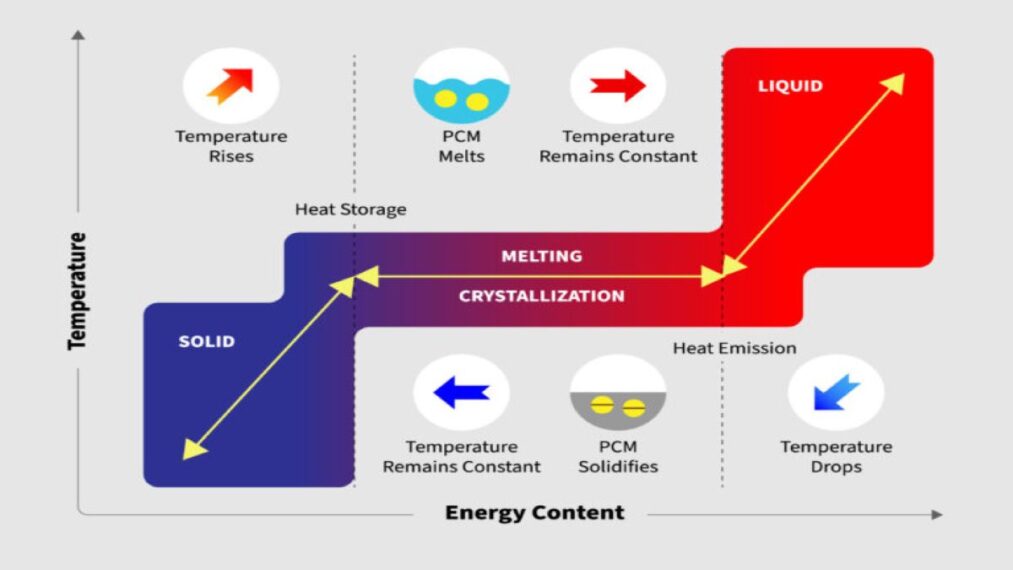
19. Energy Storage Through Phase Change Materials
When substances change phases, they absorb and release heat energy. Whenever a material begins to melt, it transitions from a solid to a liquid state. Many materials can absorb a large amount of heat energy during the phase transition. As they melt, phase change components absorb thermal energy and store it until the material solidifies again. This kind of thermal storage may aid the accelerating energy sector technology development.
20. Hydrogen Peroxide
The electrochemical synthesis of H2O2 from aerated water with a solid superacid cathodic electrode is proposed as a mechanism for storing energy. The subsequent generation of H2 plus O2 via electrolysis on a cathodic superacid electrode to be used in a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cell is described, and thus energy release is included. A full-cycle synthesis with an electrical energy output efficiency of >35% has been estimated for a 50% aqueous H2O2 solution using a tungstated zirconia electrocatalyst with a power density of >0.49 MJ/kg solution and a 50% aqueous H2O2 solution.





















