The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, or IEEE, is a worldwide organisation of professionals committed to furthering innovation and technology. It is made up of specialists from a range of electrical engineering, electronics, computer science, and related sectors, including engineers, scientists, researchers, and other professionals. The advancement and standardisation of technology have benefited greatly from the work of the organisation. Through its technical committees, working groups, and conferences, the organisation significantly influences technological progress. It encourages its members to work together, share expertise, and advance their careers. Additionally, it promotes moral behaviour and backs engineering and technological education. Especially in fields like computer networking, wireless communication, power systems, and software engineering, it is well known for its standard-setting efforts. Some IEEE protocols include:
1. IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet)
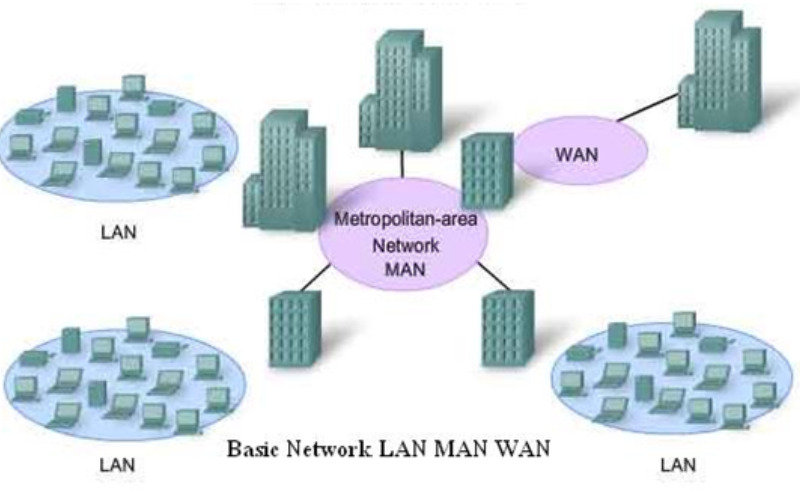
The preferred protocol for wired local area networks (LANs) is Ethernet. It specifies the wiring, signalling, and packet format requirements for Ethernet networks at the physical and data link layers. Ethernet is frequently utilised in both residential and commercial networks for high-speed data transfer.

2. IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi)
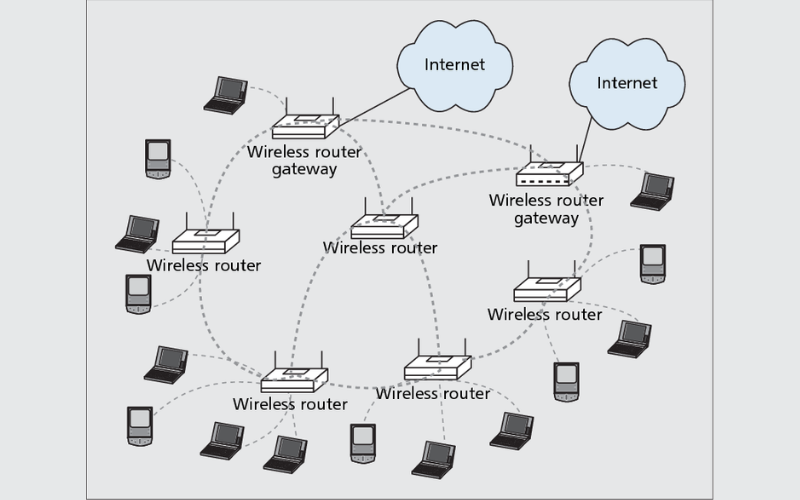
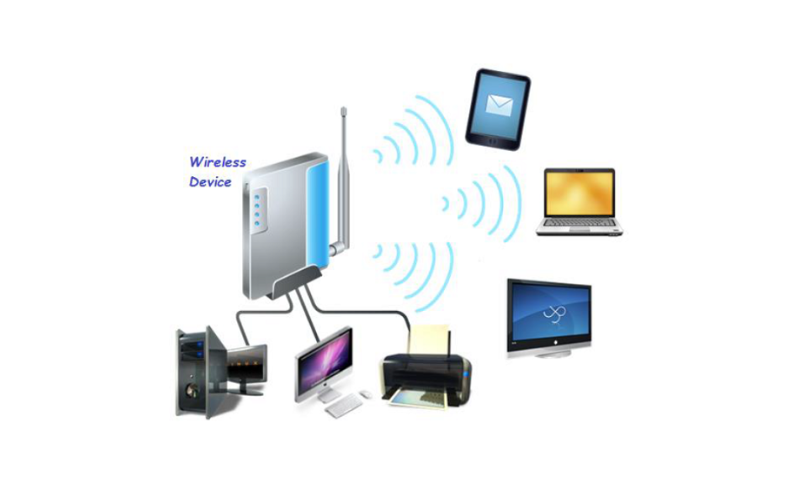
Wireless local place networks (WLANs) appoint Wi-Fi. Between Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets, PCs, and mobile phones, it affords wireless communication and statistics transmission. Wi-Fi networks enable community connections and wireless net get admission to throughout diverse frequency bands and information speeds.

3. IEEE 802.15.4 (Zigbee)
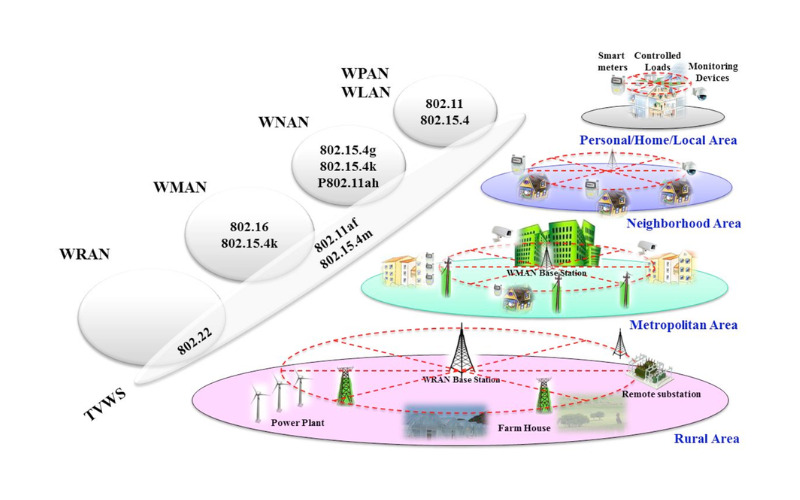
Zigbee is a low-electricity wireless protocol that becomes advanced for low-charge, close-proximity devices. It is used in business automation, home automation, and sensor networks. It makes a network that permits dependable and most economical communication between gadgets.

4. IEEE 802.16 (WiMAX)
High-speed internet connectivity over very long distances is viable with the aid of WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) wireless broadband community preferred. In places wherein stressed connections are not viable, it permits Wi-Fi conversation through operating in licensed or unlicensed frequency tiers. It covers constant as well as mobile programs and presents excessive data speeds.
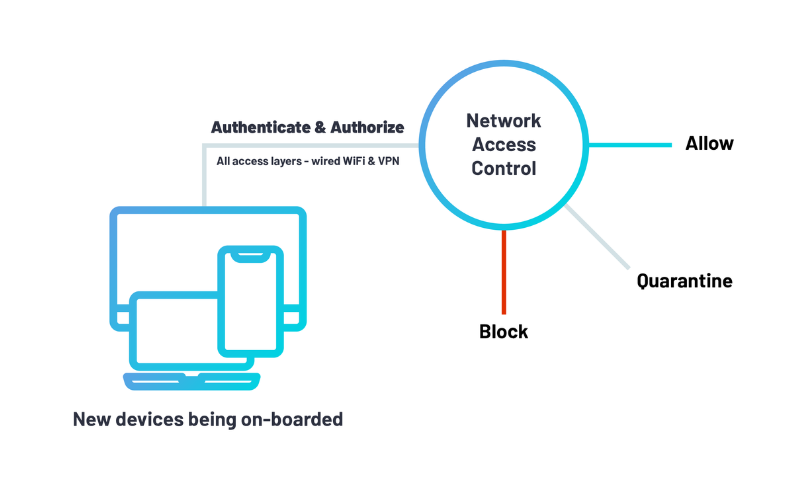
5. IEEE 802.1X (Network Access Control)
Network Access Control (NAC) protocol IEEE 802.1X presents an authentication approach for controlling get right of entry to LANs and WLANs. It demonstrates community protection by way of allowing devices to verify their identification before connecting to a network. A few authentication strategies supported by IEEE 802.1X’s Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) structure encompass e-certificates, smart cards, and passwords.
6. IEEE 802.22 (Wireless Regional Area Network)
IEEE 802.22, additionally known as WRAN (Wireless Regional Area Network), is a wireless verbal exchange in new TV frequency bands. It is intended to supply internet connectivity throughout large distances while efficaciously using the available spectrum resources. It enables wireless networks to function in rural areas, imparting more coverage and stepped forward connectivity.
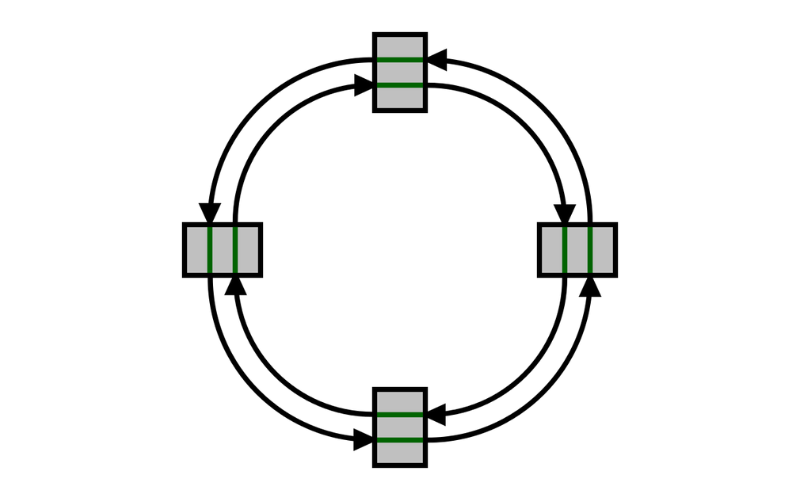
7. IEEE 802.17 (Resilient Packet Ring)
Resilient Packet Ring (RPR) is a generation that IEEE 802.17 affords for constructing packet-primarily based metro Ethernet networks. It gives speedy and reliable connectivity for vital applications by means of employing ring topologies. It enables effective community potential utilisation and gives fault tolerance and quick recuperation within the case of link breakdowns.
8. IEEE 802.20 (Mobile Broadband Wireless Access)
IEEE 802.20 is a broadband Wi-Fi get connection to trendy that offers high-speed Wi-Fi communication. It seeks to provide broadband offerings that enable multimedia applications. It uses cutting-edge radio aid control techniques, which include Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), to optimise spectrum intake and enhance QoS.
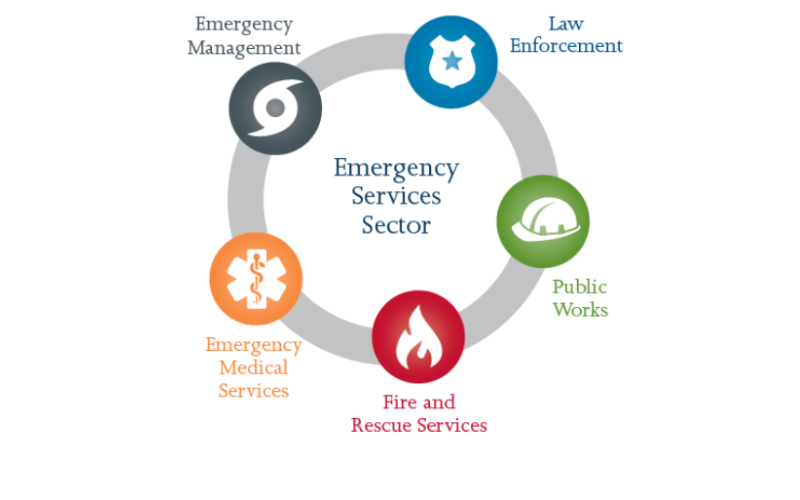
9. IEEE 802.23 (Emergency Services)
A general called IEEE 802.23 focuses on delivering emergency offerings thru IP-based networks. It addresses its particular requirements and challenges that emergency communication systems encounter, ensuring reliable and effective communication in time-sensitive conditions. To offer emergency offerings, it defines mechanisms for QoS, emergency service prioritisation, and network robustness.
10. IEEE 802.24 (Smart Grid Communications)
A widespread called IEEE 802.24 handles the communication needs of clever grid structures. It concentrates on adequate and steady facts switch across many clever grid infrastructure factors, such as smart meters, substations, and control centers. It affords the protocols and policies for smart grid communications, allowing for real-time grid management, monitoring, and control.
11. IEEE 802.25 (Wireless Personal Area Network)
A general known as IEEE 802.25 is directed at Wi-Fi personal region networks (WPANs). A quick-range Wi-Fi community specifies protocols and strategies for effective and stable communication between individual gadgets. Applications of WPAN consist of wireless sensors, domestic automation, and transportable amusement systems. It assures reliable connectivity, minimum power usage, and compatibility among WPAN devices.
12. IEEE 802.26 (Management of Virtual Local Area Networks)
The administration of virtual local area networks (VLANs) is covered by using IEEE 802.26. It outlines strategies and procedures for developing, organising, and coping with VLANs inner community structure. It offers enterprise networks the ability to manage VLANs with flexibility and scalability.
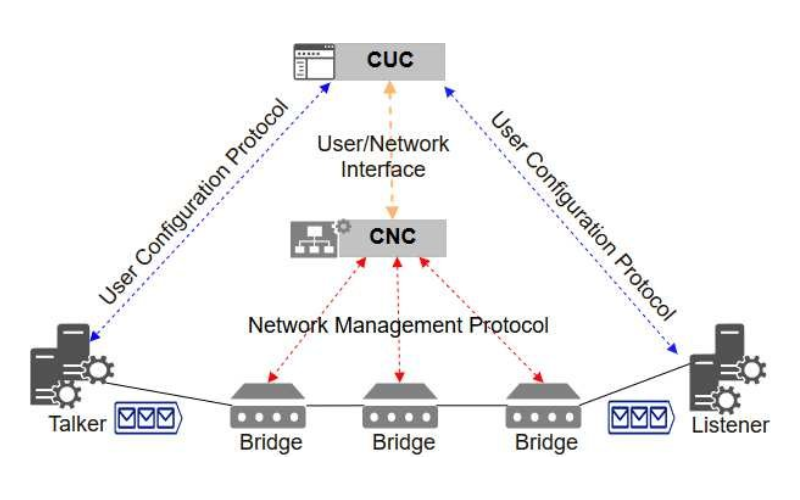
13. IEEE 802.27 (Network Management)
Network management is the principle emphasis of the IEEE 802.27. It outlines requirements, protocols, and processes for controlling and monitoring community assets with the intention to assure the green operation and management of community infrastructures. Security control, network performance tracking, fault management, and configuration control are its features. It offers a foundation for effective network management strategies and community management system interoperability.
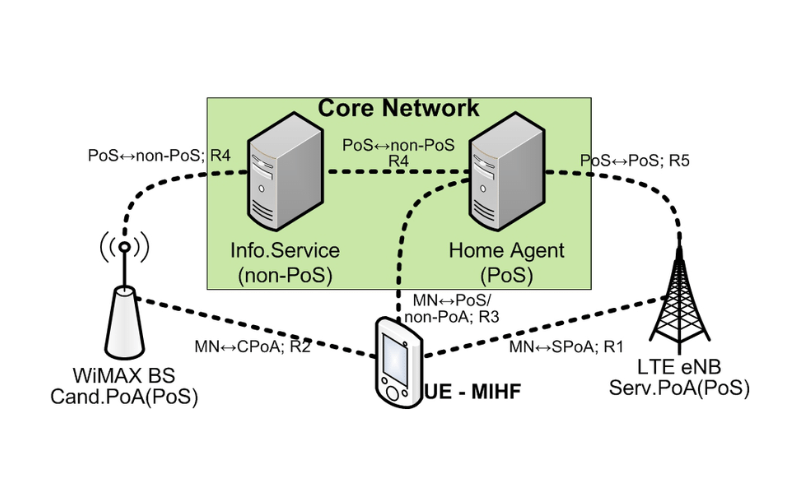
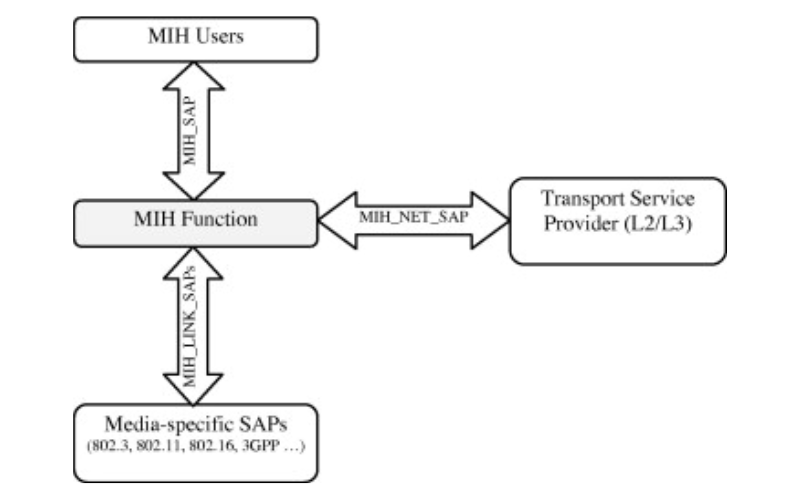
14. IEEE 802.28 (Media Independent Handover Services)
IEEE 802.28 targets to deliver seamless handover offerings to mobile devi across numerous networks and technologies. To prevent service interruptions, it makes positive that mobile devices may stay connected and talk when transferring networks.
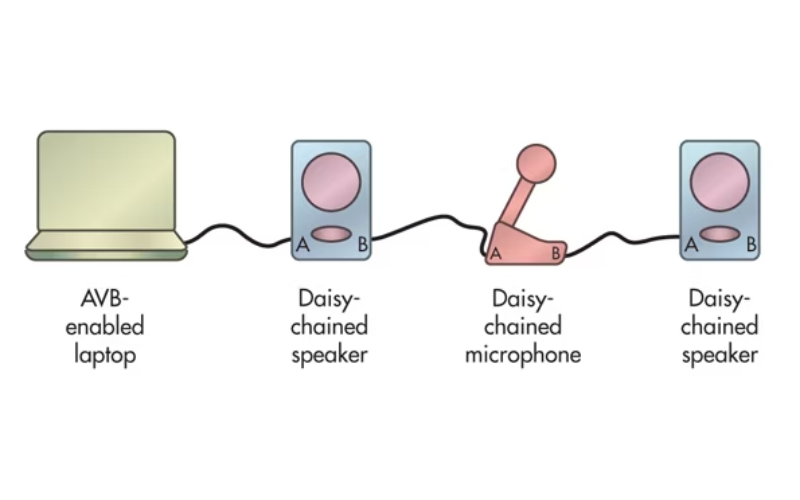
15. IEEE 802.29 (Audio Video Bridging)
IEEE 802.29 popular addresses the necessities for turning in synchronised audio and video streams across Ethernet networks. It focuses on protocols and techniques for real-time applications that call for low latency, wonderful video transmission, and audio, along with professional audio structures and multimedia streaming.
16. IEEE 802.30 (Ethernet Virtual Private Network)
IEEE 802.30 trendy offers personal and secure communication throughout Ethernet networks. Ethernet designs the protocols and techniques for setting up and overseeing Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), an essential transport technology. It facilitates the creation of stable tunnels throughout Ethernet networks to provide encrypted and remote communication among network nodes.
17. IEEE 802.31 (Automatic Neighbour Relationship)
The automated management and discovery of neighbour relationships in a network are carried out via the IEEE 802.31. It specifies protocols and strategies that let gadgets find and connect to their network neighbours mechanically. This widespread makes it possible to effectively discover neighbours, which is specifically useful in dynamic network situations wherein gadgets can be part of and go away the network.
18. IEEE 802.32 (Vehicular Networking)
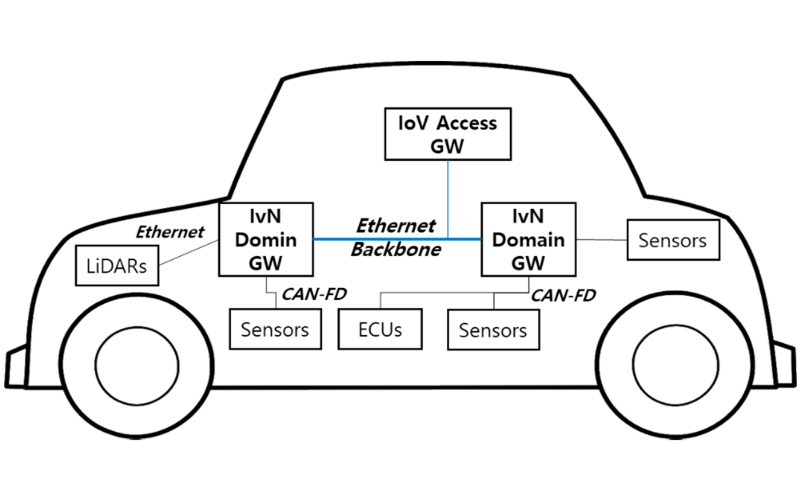
IEEE 802.32 is a networking protocol and mechanism fashionable for vehicles. Along with vehicle-to-vehicle communication, it addresses the problems and desires associated with communication among vehicles and infrastructure. It affords protocols for efficient data exchange, safety applications, and other services in vehicles networks to enhance transportation effectiveness, traffic control, and road protection.
19. IEEE 802.33 (Ethernet Data Rates)
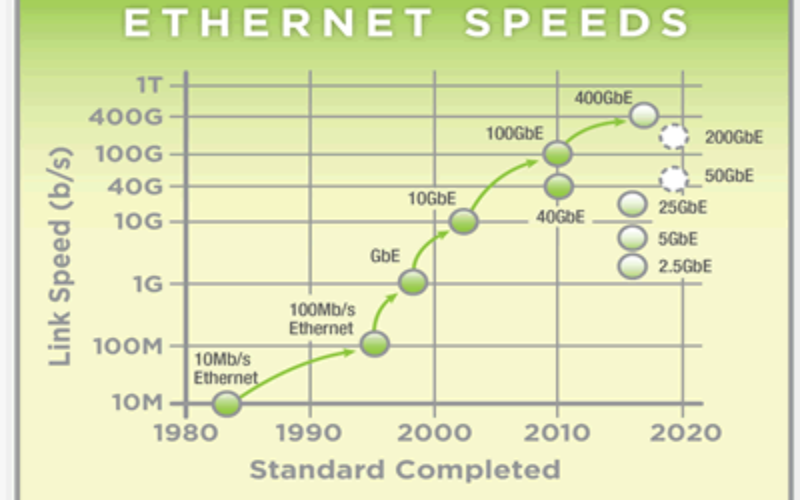
The IEEE 802.33 defines the physical layer specs and diverse data rates for Ethernet networks. In addition to diverse various high-speed versions, it determines the accredited data rates for Ethernet, including Fast Ethernet (one hundred Mbps), Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps), and 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 Gbps). It supports high-speed data transfer in network infrastructures and assures compatibility and interoperability throughout numerous Ethernet devices.
20. IEEE 802.35 (Local and Metropolitan Area Networks – High-Speed Bridging)
IEEE 802.35 is a general and part of the IEEE 802 family of networking protocols. It gives suggestions and recommendations for setting up high-speed bridging devices in local and wide-area networks.