In the rapidly advancing landscape of technology, 3D printing has transcended its initial boundaries to unveil astonishing applications that extend far beyond imagination. While it’s widely recognized for fabricating prototypes, this transformative technology is now shaping bioprinting, surgical planning, prosthetics, art restoration, and even space exploration. From restoring historical artworks with meticulous precision to generating custom-fit prosthetics, 3D printing’s influence is ubiquitous. In this article we’ll delve into the top 20 incredible uses of 3D printing, each reflecting the remarkable fusion of innovation and creativity that defines this technological era.
1. Bioprinting
3D bioprinting uses precise layer-by-layer placement of cells and biomaterials to create 3D tissue structures. Inkjet-based methods deposit “bio-ink” to replicate human tissues and organs. Successful studies have created heart valves, spinal disks, and even tracheal splints. Biotech companies like Organovo aim to revolutionize drug testing using printed tissues, reducing research costs and time. The potential for growing complete human organs for drug screening and transplantation holds promise.
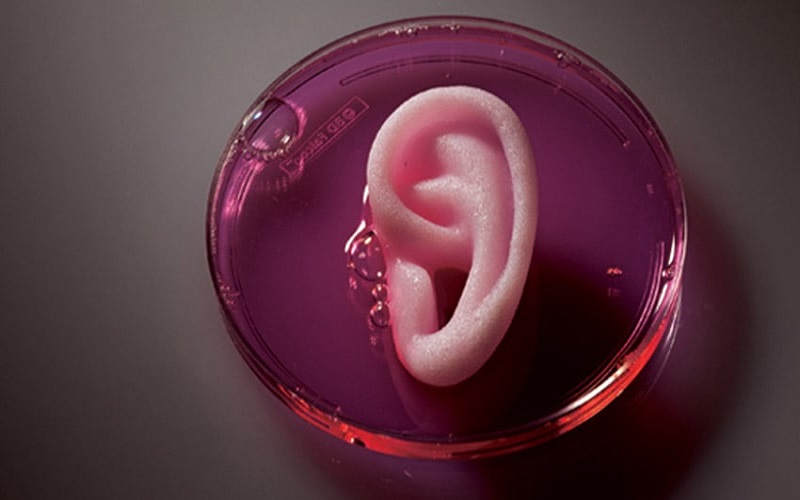
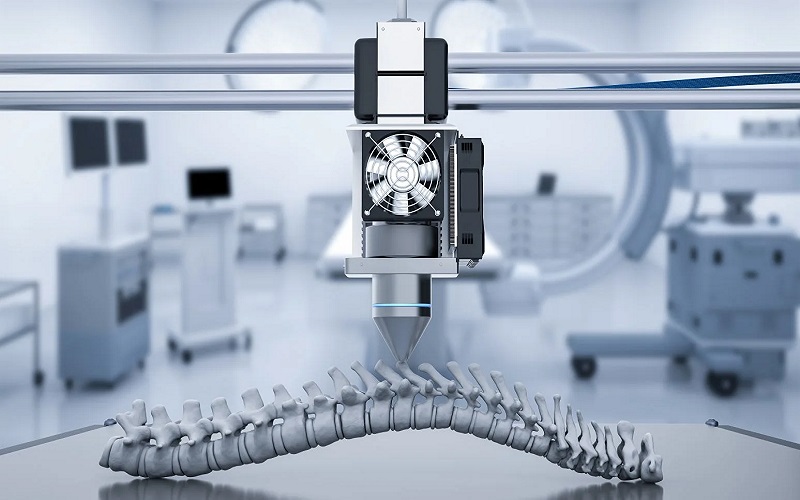
2. Surgical Applications
3D printing enhances surgical planning, offering precise visualization of patients’ anatomy. Surgical templates aid in accurate guidance during procedures, predicting bone angles and sizes. This technology improves surgical outcomes, especially in cardiovascular, neurosurgery, and orthopedic procedures, minimizing errors and increasing patient safety. The technique benefits medical training and is increasingly adopted for its role in preoperative planning and simulation. The ongoing growth in 3D printing’s surgical applications promises to reshape medical practices and training methods.

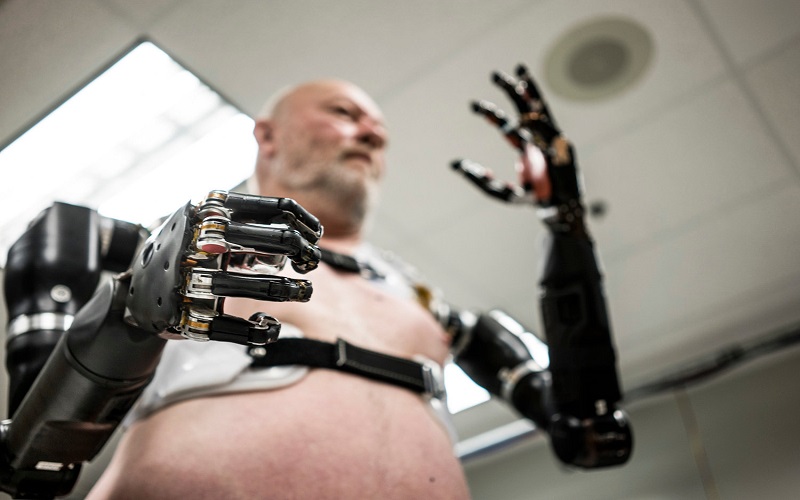
3. Building Prosthetics
Prosthetics have been revolutionized via 3D printing. The use of 3D printing for constructing prosthetics provides customized solutions for improved functionality and affordability. It bridges the gap between traditional methods and personal production, creating prostheses with desired mechanical properties. While challenges like texture and weight persist, 3D printing’s potential to tailor prosthetics to individual needs is transforming lives. It’s not just about restoring function; 3D printing enables advanced prosthetics that exceed conventional limitations, fostering hope for millions in need of artificial limbs and braces.

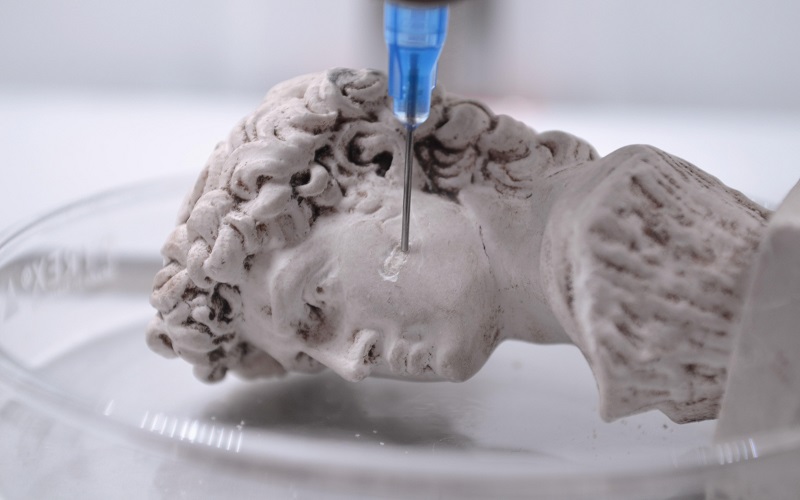
4. Art Restoration
3D printing and scanning have the potential to revive art history’s masterpieces. Mattia Mercante’s work at the Opificio Institute in Florence demonstrates how lost portions of sculptures and artworks can be meticulously recreated using 3D scanning and printing. The process, involving HP 3D Structured Light Scanner and Formlabs 3D printer, preserves intricate details and offers a fast, affordable, and accurate solution for art restoration, allowing audiences to appreciate art in its original form.

5. Housing And Construction
ICON, a company dedicated to changing lives, employs 3D printing to create homes, envisioning affordable communities worldwide. The Chicon house, America’s first permitted 3D-printed home, showcases the potential. ICON collaborates with New Story to address low-income housing, partnering in countries like Mexico, Haiti, and Bolivia. Larger-scale 3D-printed structures also emerged, promising sustainable, cost-effective, and waste-free construction. This technology empowers architects with design flexibility and offers a glimpse of future sustainable living, like the MX3D Bridge in Amsterdam, a stainless steel marvel created through six months of robotic 3D printing.
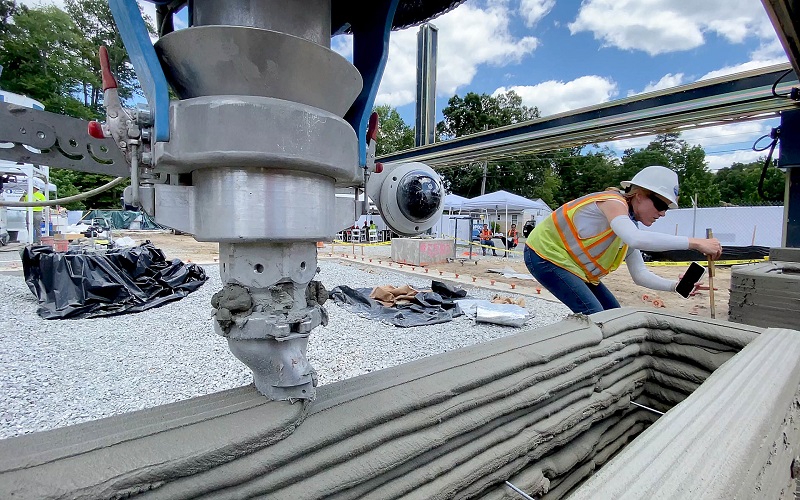

6. Printing Skin
Researchers at WFIRM are pioneering a revolutionary BioMask created through 3D bioprinting. This innovation offers a breakthrough for facial skin grafting, as traditional methods can lead to scarring and graft failure. The BioMask uses custom 3D printing and cell-laden hydrogels to create skin constructs, providing better results and potentially life-changing outcomes for those with facial injuries.
7. Perfect Fit Headphones
3D printing transforms the audio industry by enabling affordable custom-fit ear devices. Manufacturers introduce biocompatible materials for in-house production of ear models and headphone tips. Custom-fit ensures secure, comfortable earphone placement, offering improved noise isolation. Formlabs’ printing technology and mobile scanning, combined with machine learning, expedites customization, reducing lead times from days to next-day or same-day delivery.

8. Space Exploration
Space innovation has now been transformed by the advent of 3D printing. Relativity pioneers aluminum rocket engines, potentially slashing space travel costs. Masten Space Systems, adept in both plastics and metals, employs Formlabs’ 3D printers for plastic rocket engines and custom metals for NASA projects. Their engineering properties align with aerospace needs. This technology empowers efficient and cost-effective space exploration, marking a new era in the industry.
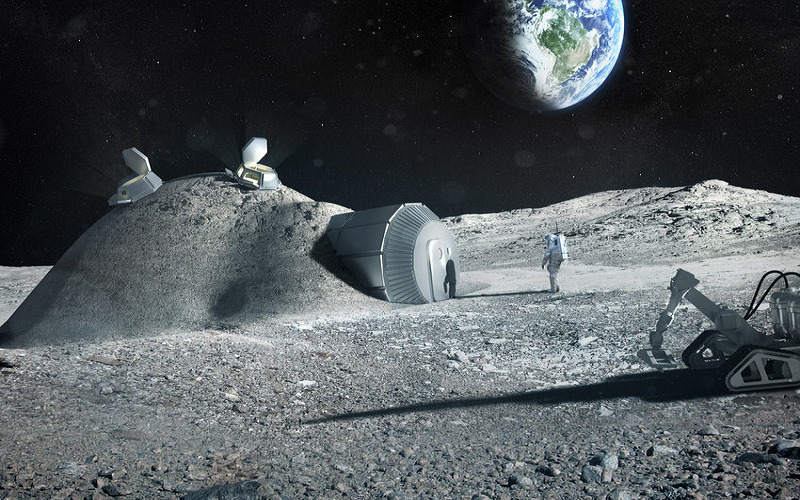

9. Disease Modelling
3D printing can very well aid in disease understanding and surgical planning. Before complex procedures, patient-specific anatomy is replicated, offering clearer insights than imaging methods. High-precision kidney models aid in simulating intricate surgeries, enhancing medical education and diagnostics. This technology extends beyond kidneys, benefiting cardiovascular and liver disease treatments. 3D modeling provides comprehensive anatomical representation, minimizing surgical errors, and ensuring patient safety in various procedures.
10. Generative Design
Generative design, powered by AI, revolutionizes CAD for engineers across industries. Through 3D printing, intricate and organic structures become achievable. AI-driven design iterations lead to rapid, efficient problem-solving, reduced costs, and customized products. This synergy of AI and 3D printing accelerates development and materializes complex shapes for tangible evaluation.
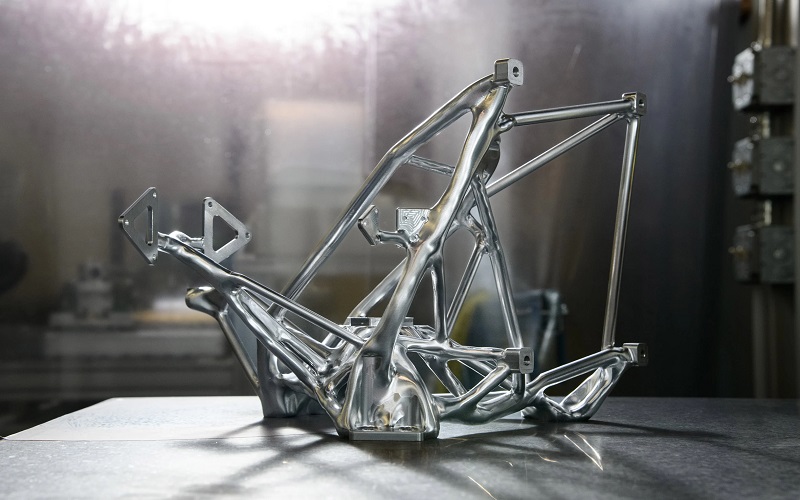

11. Automobile Industry
3D printing transforms the automotive industry, addressing demands for parts, prototypes, and customization. From spare parts to tools, 3D printing offers cost-efficient solutions, short production times, and immediate realization of digital designs. Prominent brands like BMW, Ford, and Volvo integrate the technology for prototypes, supply chain management, and cost reduction. The versatility of 3D printing caters to varied automotive needs, whether large-scale or intricate designs, bridging the gap between innovation and production.

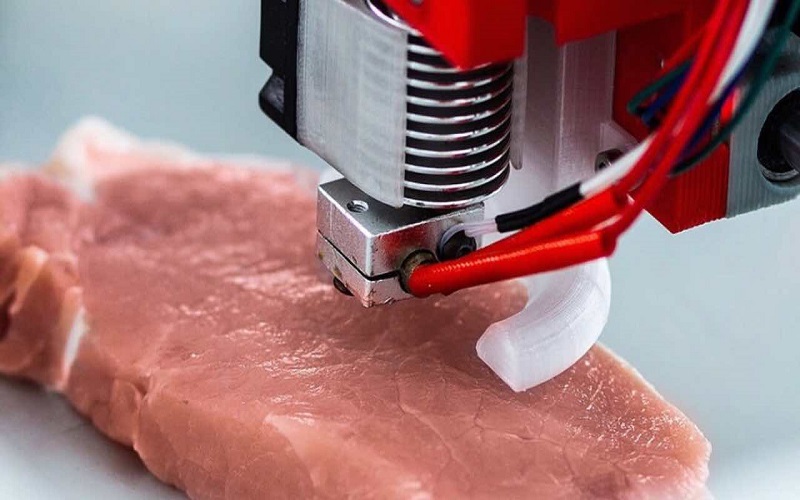
12. Vegan Meat
3D printing takes center stage in crafting vegan meat alternatives. Nova Meat’s CEO, Giuseppe Scionti, introduces a breakthrough method to create plant-based meats with the texture of real beef or poultry. Unlike other substitutes, it doesn’t compromise texture. Scionti’s sustainability-driven approach utilizes eco-friendly ingredients, minimizing environmental impact and imports, offering a promising solution for health-conscious and environmentally aware consumers.

13. Vet Medicine
3D printing aids animals in need from pre-surgery imaging to patient-specific implants. Prostheses for damaged bones, tissues, and muscles can be printed and implanted. Even congenital limb defects find solutions. For instance, a 4-month-old kitten received a 3D-printed prosthesis. Complex patient-specific implants and surgical guides enhance veterinary orthopedics. With growing success stories, 3D printing’s role in animal care is set to expand further.
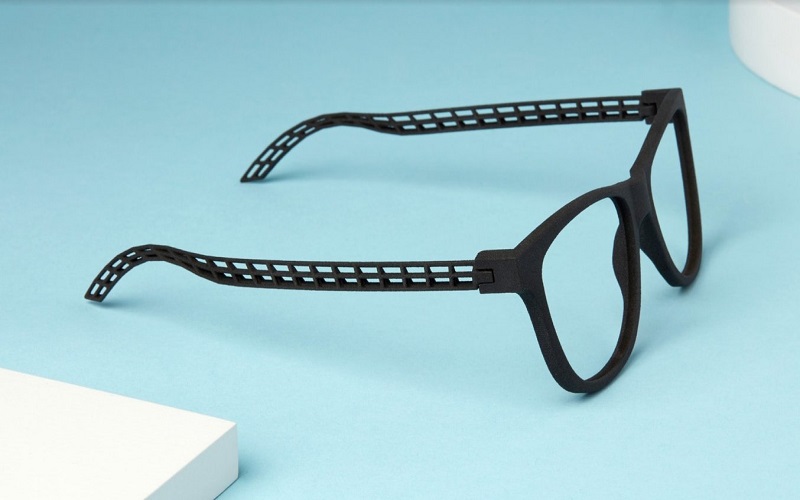
14. Eyeglasses
The eyewear industry has now been revolutionized forever ever since 3D printing came into the picture. Brands like Safilo employ rapid prototyping to accelerate frame development, mimicking finished products’ color and texture. This technique slashes prototype creation time and enhances communication between designers, resulting in improved products. Meanwhile, Marcus Marienfeld AG pioneers unique production methods, integrating selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing for custom eyeglass frames, pushing creative boundaries and innovation in the industry.

15. Drug Delivery Devices
3D printing boasts the capacity for precise drug dosing, personalized medicine, and complex formulations. This transformative technology enables customized medications based on pharmacogenetic profiles and clinical responses. It’s particularly useful for patients with polymorphisms or narrow therapeutic indices. 3D-printed drugs can combine multiple active ingredients in one pill, enhancing patient compliance, especially for those with multiple chronic diseases. This advancement could revolutionize drug manufacturing and personalized patient care.
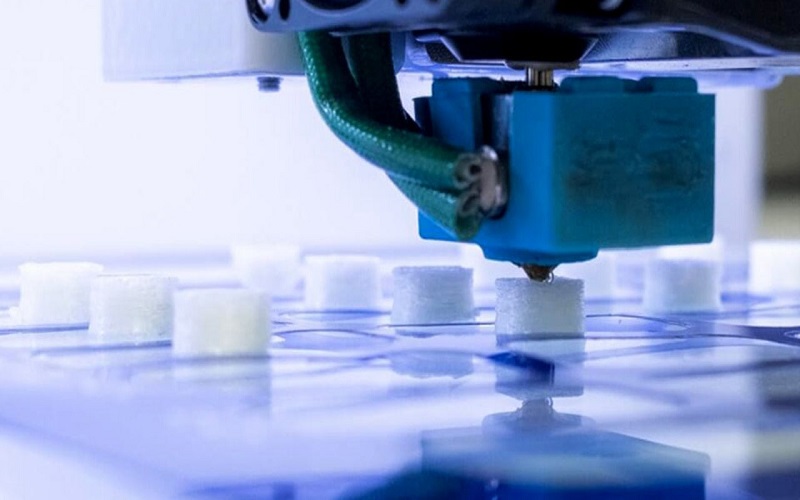

16. Manufacturing
By layering materials to create three-dimensional objects, 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, reduced waste, and customized designs. Manufacturers can quickly iterate and test concepts, accelerating product development. Moreover, 3D printing allows complex geometries and intricate details that traditional methods struggle to achieve. From aerospace to healthcare, its versatility has streamlined production, fostering innovation and efficiency in modern manufacturing.
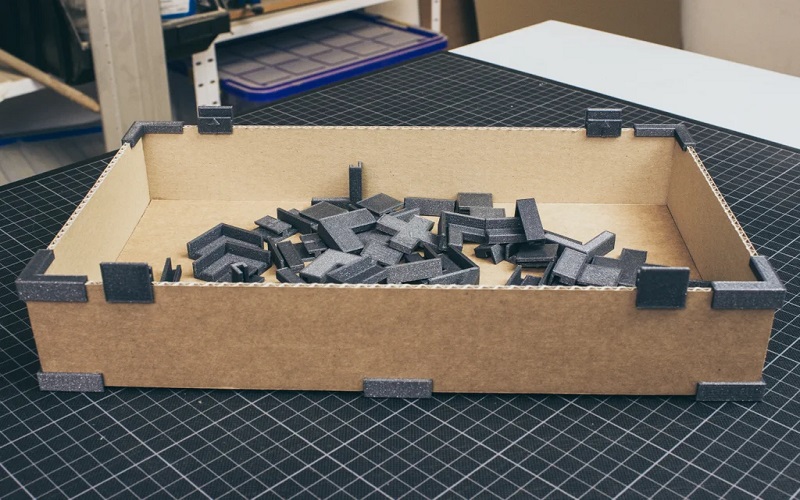

17. Forensics
In forensic investigations, 3D printing aids forensic artists by reconstructing accurate models from incomplete evidence like skulls. By turning CT scans into 3D prints, investigators can replicate and study crime victims’ remains, aiding identification and understanding of crime circumstances. This digital workflow enhances the accuracy of reconstructions and plays a crucial role in legal investigations, showcasing 3D printing’s versatile applications beyond traditional domains.
18. Tissue Engineering Research
In the realm of 3D printing, the development of 3D-printed organs stands out as a groundbreaking endeavor. Researchers like Dr. Sam Pashneh-Tala at the University of Sheffield are making strides by employing high-precision 3D printing to create tissue-engineered blood vessels with intricate geometries. This innovation holds promise for patient-specific vascular grafts, enhanced surgical options, and a platform to test new medical devices, particularly vital for addressing cardiovascular disease, the leading global cause of death.

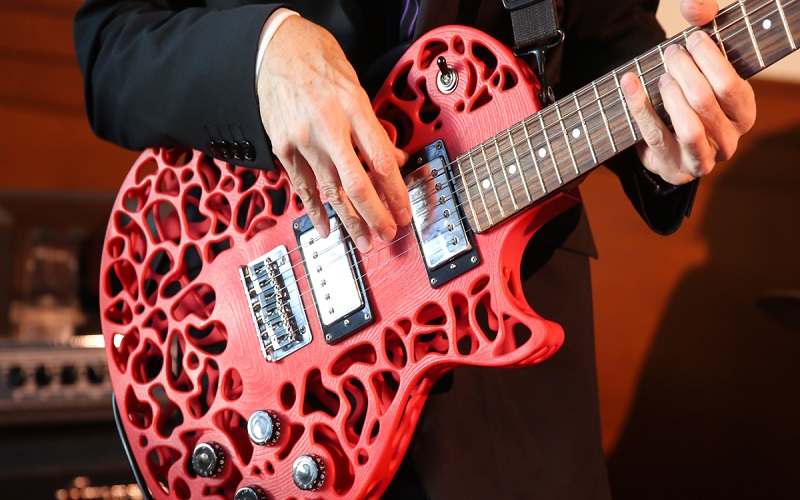
19. Music And Dance
Beyond physical artwork, 3D printing’s creative scope extends to dance and music. It’s reshaping the world of instruments, allowing intricate modifications and novel designs at a fraction of traditional costs. With its design freedom, even the violin, a centuries-old icon, can be reimagined. Formlabs engineer Brian Chan crafted a fully functional acoustic violin using a 3D printer and Formlabs White Resin, revolutionizing the possibilities of musical innovation.

20. Education
Universities are leveraging 3D printing beyond CAD training, integrating it into various disciplines. UMass Lowell transformed sculpting and 3D design courses with Formlabs SLA machines. Yuko Oda, an art and technology enthusiast, teaches 3D modeling, animation, and interactive media. Students learn vital skills for diverse careers, from cinema to sculpture design. The integration of 3D printing and Virtual Reality (VR) enhances accessibility and creativity. VR enables quicker 3D design iterations, making art more achievable and experimental, even for novices.