IT security in business is the practice of protecting the digital assets and information of a company from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction. It includes a range of measures and tools designed to safeguard data, systems, and networks from a various threats, such as malware, hacking, phishing, insider threats, and social engineering. Adequate IT security in business involves a multi-layered approach that combines technical, physical, and administrative controls. Here are some essential IT security measures for businesses.
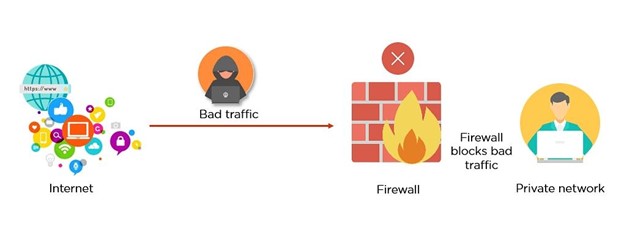
1. Firewall Protection
Firewall protection is one of the most essential IT security measures used to protect computer systems and networks from unauthorized access, malware, and other cyber threats. They work by inspecting each packet of data that passes through the network and applying a set of predefined rules to determine whether the packet should be allowed to pass through or not.
2. Complex And Strong Passwords
Intense and complex passwords are an essential aspect for businesses of all sizes. The use of strong and complex passwords can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and system, and protect against potential security breaches.

3. Regular Security Training
Regular security training is an essential aspect of IT security for businesses. Security training provides employees with the knowledge and skills they need to identify security risks and threats, and to take appropriate action to prevent security breaches.

4. Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA provides an additional layer or security beyond traditional username and password authentication. The idea behind MFA is that using multiple factors makes it harder for unauthorized individuals gain access to a user’s account or device.

5. Anti Virus And Anti-Malware Software
Anti Virus and Anti-Malware software are essential components of IT security for businesses. These software programs are designed to detect and prevent malicious software such as viruses, worms, and Trojan horses from infecting computer systems and networks.

6. Regular Data Backup And Disaster Recovery Plans
Regular Data backup and disaster recovery plans are crucial components of IT security for businesses. Data backup involves creating copies of critical data and storing them safely, while disaster recovery plans include preparing for and responding to potential disasters or system failures.

7. Encryption
Encryption is a critical component of IT security for businesses. Encryption is converting plaintext data into encrypted data, using an algorithm and a key. Encryption is used to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, theft, or manipulation.

8. Software And System Updates
Software and systems updates are important for maintaining the functionality, security, and performance of computers, devices, and networks. These updates involve the installation of patches, bug fixes, and new features that address issues and improve performance

9. Restricting Access To Sensitive Data
Restricting access to sensitive data is a critical component of IT security for businesses. Sensitive data such as customer information, financial records, and proprietary information should only be accessible to authorized personnel with legitimate need to access it.

10. Strict Access Controls
Access control is managing and controlling who has access to specific resources, such as files, folders, applications, and networks. Strict access control ensures that only authorized users have access to resources needed to perform their job duties.

11. Network Activity Monitoring And Logging
Network activity monitoring involves the continuous observation of network traffic to identify suspicious or unauthorized activity, while network logging involves the collection and analysis of data related to network activity.

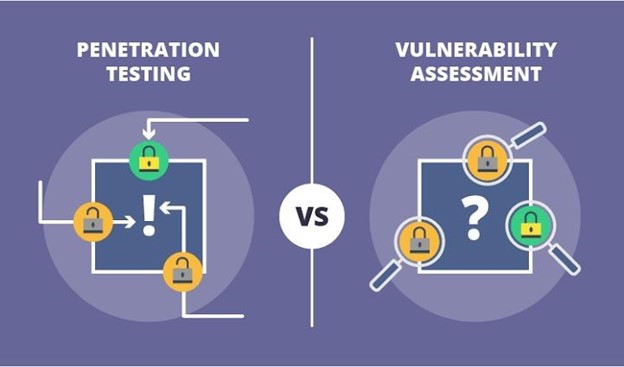
12. Vulnerability Assessments And Penetration Test
Vulnerability assessments involve the identification and evaluation of potential vulnerabilities in a system or network. In contrast, penetration testing consists of the simulation of an attack on a system or network to identify weaknesses and possible entry points for attackers.
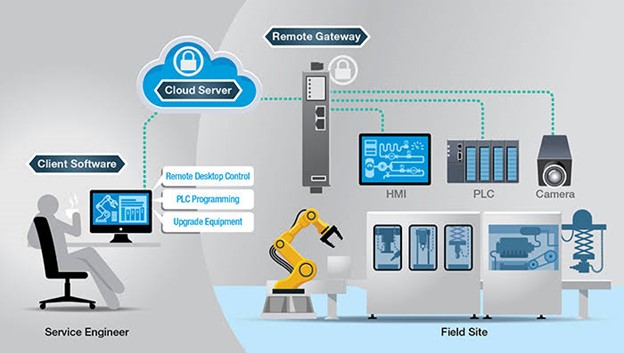
13. Secure Remote Access Solutions
Secure remote access solutions are essential for businesses that have remote employees, partners, or clients who need to access the company network or resources from outside the physical office location. These solutions provide secure access to company resources from remote areas while protecting sensitive data and network resources from unauthorized access.
14. Data Loss Prevention Software
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software is an essential security tool for companies that need to protect sensitive data from being lost, stolen, or accessed by unauthorized users. DLP software helps businesses to monitor and control the flow of data within their networks and endpoints, preventing data breaches and loss.

15. Incident Response Plans
An incident response plan (IRP) is a documented and structured approach to handling and managing security incidents within a business. The IRP outlines the procedure and protocols to be followed by the incident response team when responding to a security incident, such as a data breach or a cyber-attack.
16. Background Checks
Background help businesses make informed decisions about potential employees and reduce the risk of hiring individuals with a history of criminal activity, fraudulent behavior, or other red flags.

17. Reviewing And Updating Security Policies And Procedures
Security policies and procedures outline the guidelines and protocols that employees must follow to ensure that digital assets and information are kept safe. Over time, technology changes, and new threats emerge, which means that policies and procedures must be updated to reflect these changes.

18. Physical Security Methods
Physical security methods are essential in IT business environments to prevent unauthorized access to physical equipment, data, and critical resources. These protecting physical assets from theft, damage, or destruction.

19. Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is dividing a computer network into smaller, isolated sections called subnetworks or segments. Each segment is typically separated by firewalls or other security devices to create a secure boundary around sensitive systems or data.
20. Auditing And Monitoring Security Measures
Regular auditing and monitoring help businesses identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in their security systems and processes before they can be exploited by attackers. By regularly reviewing security logs and other data, businesses can detect and respond to security incidents promptly, on time minimizing the impact on operations and data.