Instead of running on a centralized server or in the cloud, edge computing is a scattered computing approach in which processing happens close to the actual site where data is being gathered and analyzed. As part of this new infrastructure, various devices, such as laptops, and cell phones, are connected to the network, and edge servers securely handle data locally in real time. Edge computing is crucial because it gives industrial and enterprise-level companies new and better ways to maximize operational effectiveness, enhance quality and reliability, automate all essential business procedures, and guarantee “always on” availability. It is a cutting-edge technique for achieving the digitalization of your business practices.
1. Autonomous Vehicles
One of the initial use applications for autonomous vehicles will probably be the platooning of truck convoys. Here, a convoy of trucks follows closely behind one another to conserve fuel and ease traffic. Since the vehicles will be able to interact with one another with extremely low latency thanks to edge computing, it may be feasible to do away with the requirement for drivers in all but the front truck.

2. Industrial Automation
A significant technical development for industrial automation is edge computing. It provides the advantage of real-time data gathering, processing, storing, and analysis for quicker and more informed decision-making in complicated production scenarios.

3. Remote Monitoring
Failures related to oil and gas can be quite bad. Therefore, it is important to keep a close eye on their assets. Remote sites are common for oil and gas plants. Real-time analytics are made possible by edge computing, which brings processing considerably closer to the asset and reduces the need for reliable access to a centrally controlled cloud.

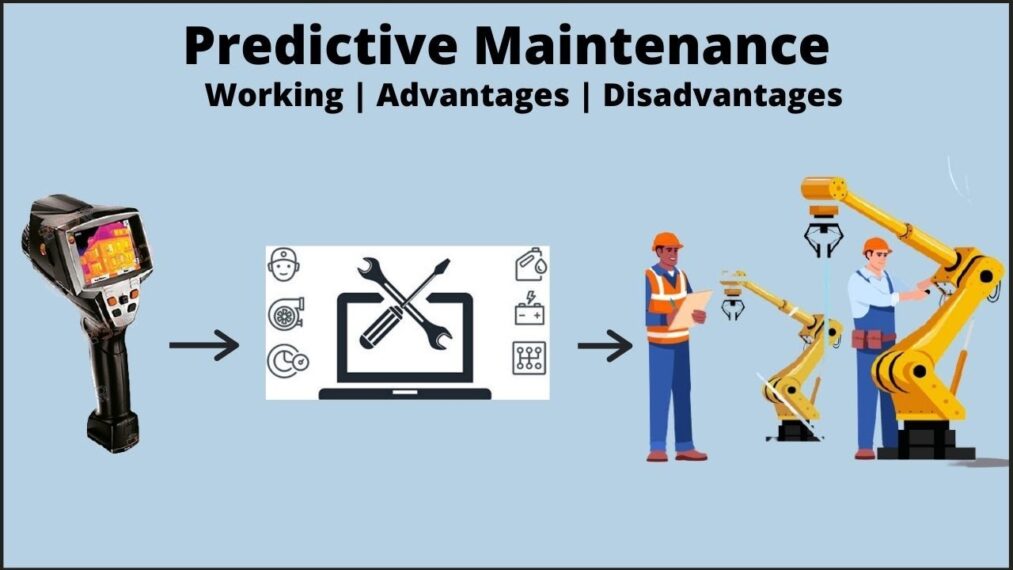
4. Predictive Maintenance
Before a failure happens, companies want to be able to examine and spot changes in their manufacturing lines. By moving data processing and storage closer to the hardware, edge computing is beneficial. IoT sensors can now monitor the health of the machine with minimal latencies and carry out analytics right away.
5. Fleet Management
Vehicle performance, efficiency, and safety are all under the control of fleet management. Advanced telematics alternatives that allow access to fairly close data and analytics can available funds, maintainability, and accessibility in passenger and cargo vehicles. This is made possible by computing technology used in fleet monitoring.

6. In- Hospital Patient Check-Ups
Healthcare offers a several cutting-edge options. Currently, monitoring equipment (such as glucose monitors, health tools, and other devices) are either not linked, or when they are, a third-party cloud would need to be used to store the vast amounts of raw data from the devices. Healthcare providers now have security issues.
7. Health Care Devices
Edge computing complements the cloud by giving IT decision-makers the ability to select the appropriate location for workloads throughout the compute spectrum. This tactic can aid health organizations in streamlining data collection, storage, and analysis—which, for the typical hospital, now amounts to 50 petabytes annually. In the health industry, devices utilizing edge computing technologies reduced the number of database errors.
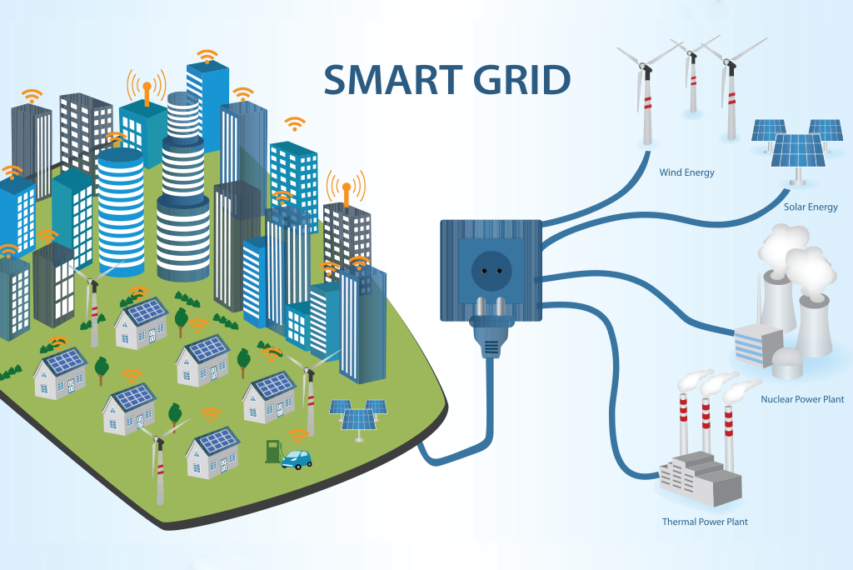
8. Smart Grid
Enterprises will be able to regulate their energy consumption more effectively thanks to edge computing, which will be a key technology in the more widespread deployment of smart grids. In factories, plants, and offices, sensors and IoT-associated devices to an edge network are being used to track power use and analyze it in real-time. With real time visibility, businesses and energy providers can make new agreements, such as those that allow for the operation of powerful equipment during times of lower electrical demand.
9. Smart Homes
IoT devices are essential to smart homes because they gather and process data from all over the house. A unified remote server is frequently used to send and receive this data, processing and storing it there. However, there are issues with backhaul cost, delay, and security with the current architecture. Sensitive data can be analyzed at the edge, reducing backhaul and roundtrip time and putting storage and processing closer to the smart home.

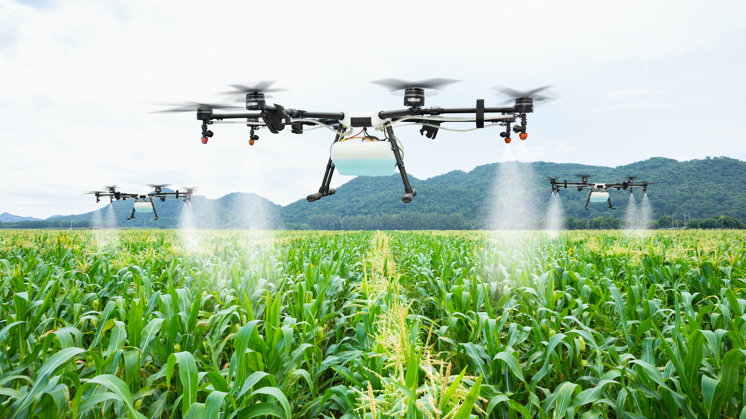
10. Smart Agriculture
By using edge computing, the field or greenhouse can operate independently of its link to the server computer and base its decisions on information from nearby sensors. As a result, agriculture may become more reliable in the process and produce less waste.

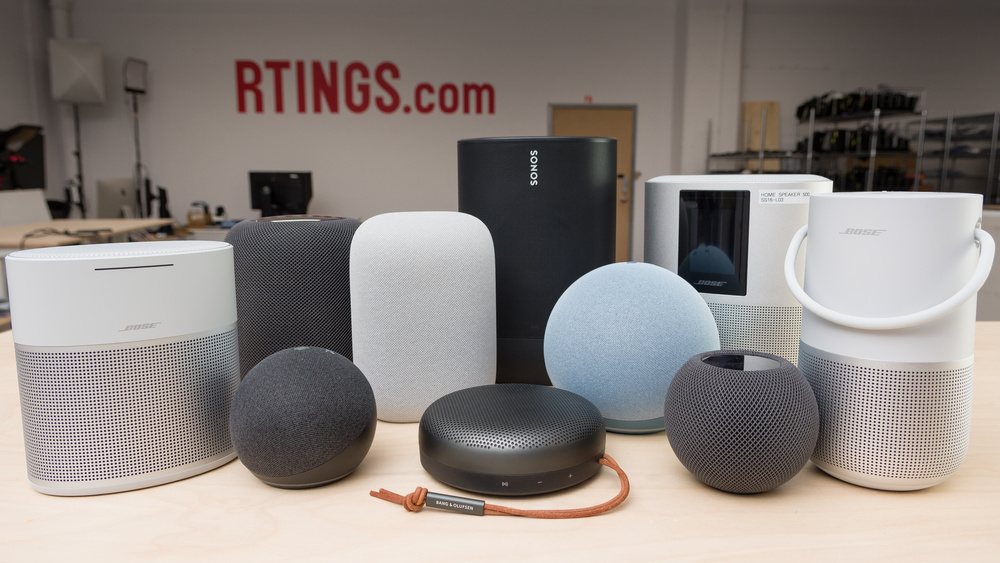
11. Smart Speaker
The majority of the credit for voice assistant services like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Microsoft Cortana goes to cloud platforms. However, this ignores the growing part that edge computing plays in providing speech interfaces. To enable consumers to interact with gadgets by talking to them, a significant amount of visualization and interpretation takes place on the devices themselves.

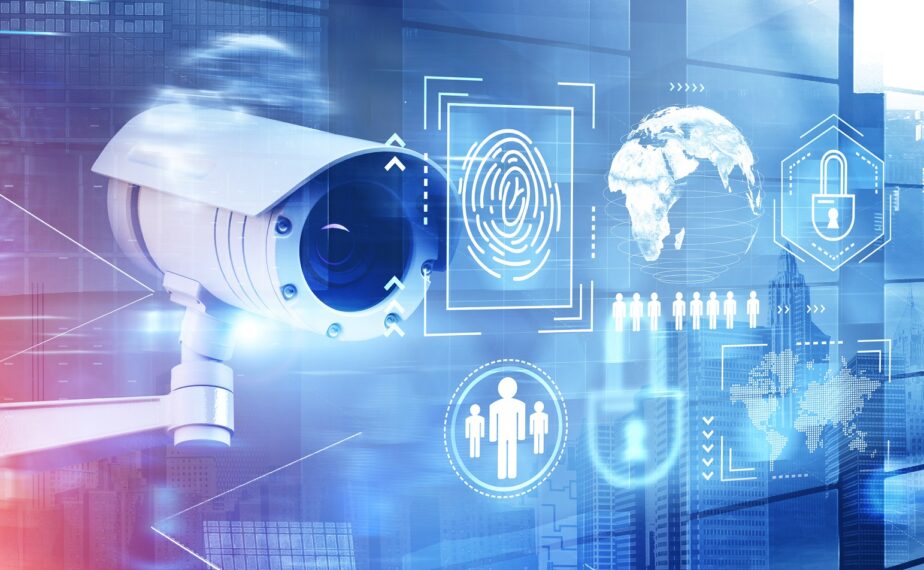
12. Security Solutions
Edge computing poses a distinct security risk than a centralized setting since it is distributed. The firewalls and antivirus software used in private data centers and public clouds do not automatically transfer. A few straightforward actions, such as strengthening each server, actual network surveillance, encrypting data, and implementing physical security measures, are advised by experts.

13. Cloud Gaming
Latency is crucial to cloud gaming, an emerging genre of gaming that sends a real stream of the game to devices. To reduce latency and offer a fully dynamic and immersive gaming experience, cloud gaming businesses are attempting to construct edge servers as close to players as feasible.

14. Traffic
More efficient municipal traffic control may be made possible via edge computing. Applications of this include controlling the closing and opening of extra lanes, managing the frequency of buses given demand changes, and, in the future, managing the flow of autonomous vehicles. By eliminating the need to send massive amounts of traffic data to a centralized cloud, edge computing lowers bandwidth and latency costs.

15. Content Delivery
Delivering material can be considerably enhanced by caching data like music, video streams, and web pages at the edge. There is a significant reduction in latency. To provide network flexibility and customization based on user traffic demands, content providers are aim to spread CDNs even further out to the edge.

16. Virtual Radio Network
Operators are attempting to virtualize more and more of their cellular operators (vRAN). This has advantages in terms of cost and flexibility. The new RAN gear that has been virtualized must do complicated processing with little delay. To facilitate virtualizing the RAN near the cell tower, operators will need edge servers.

17. Video Conferencing
The growth of edge data centers makes videoconferencing technology apps more effective by bringing them closer to the consumer and lowering latency. While micro data centers, like ours, assist Tier II and Tier III cities, traditional data centres are often found in large metropolitan regions. The same connectivity choices are available to individuals in rural areas as they are in metropolitan cities by locating elsewhere.

18. Retail Advertising
Providing a seamless experience between online and brick-and-mortar stores is possible with edge computing. Retailers can install monitors and other equipment at the boundary or in-store and use the real-time data generated by those analyses to make wise business decisions. By locating computing at the edge, businesses may better manage and utilize physical assets and develop fresh, engage human experiences.

19. Machine And Computer Vision
As materials move across a conveyor belt, vision inspection systems employ several high-speed sensors and image software to identify and quantify them. In computer vision, photos or videos are analyzed by computers to extract information from them. Edge computing is the practice of processing data close to the original data source, which usually speeds up and improves processing efficiency.

20. Military And Defense
A sustainable national strategy must include defense. Technologies have a lot to offer a defense system that makes no mistakes. There are numerous uses for edge computing in defense. As an illustration, a network of unmanned aircraft systems (UAS) could gather intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) data about a target by employing their sensors.





















