Analysts are individuals having unique skills, who gather, process, and interpret data for accurate decision-making. They are found in several domains like healthcare, government, business, finance, and marketing. While their job titles vary such as data analyst, financial analyst, business analyst, or policy analyst—their responsibility transforms data into insights. Their significance can hardly be overstated in the virtual world. Analysts are the architects translating information into fast-moving tasks. Here are some of their skills:
1. Analytical Thinking
Analytical thinking aids in breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable components and systematically analysing them to understand the underlying issues. Analysts identify patterns, trends, and relationships within data using analytical thinking. They gather relevant information, dissect problems, and draw logical conclusions.
2. Data Analysis
Data analysis is the core competency of an analyst, which involves the process of transforming, inspecting, cleaning, and modelling data to find useful information, draw conclusions, and aid decision-making. Analysts rely on statistical and computational methods to extract meaningful insights from any data.

3. Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the capacity to evaluate arguments, information, and situations, considering multiple perspectives and potential biases. Analysts identify inconsistencies, question assumptions, and assess the validity of conclusions through critical thinking. It aids in making well-informed decisions based on sound reasoning.

4. Quantitative Skills
Quantitative skills encompass mathematical and statistical abilities that analysts use to manipulate and analyze numerical data. Proficiency in quantitative analysis allows analysts to perform tasks such as forecasting, modelling, and hypothesis testing. These skills are essential for making data-driven decisions with confidence.
5. Attention To Detail
Attention to detail is the diligence in ensuring that no aspect of a task or analysis is overlooked. Analysts must meticulously review reports, data, and findings to catch errors or inconsistencies. This skill maintains data accuracy and produces reliable results.

6. Communication
Communication delivers complex findings, insights, and recommendations clearly and effectively to technical and non-technical audiences. Analysts present their results in a persuasive and comprehensible way via presentations, reports, and visualizations. Strong communication skills ensuring data-driven insights drive tasks and actions.

7. Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is a critical skill for analysts as they are frequently tasked with identifying and resolving complex issues. Analysts approach problems methodically, breaking them down into tiny components, analysing data, and applying logic to find viable solutions. Effective problem-solving includes adaptability, creativity, and critical thinking.
8. Time Management
Time management is vital for analysts working on several projects simultaneously, each with its deadlines. Analysts ought to allocate their time effectively, prioritise tasks, and meet milestones. Effective time management ensures that projects are finished on time, maintains productivity, and lessens stress in fast-paced environments.

9. Forecasting
Forecasting predicts future trends, outcomes, or events based on historical data and statistical modelling. Analysts use forecasting to make informed decisions, plan for the future, and anticipate market changes. Depending on the field, forecasting can involve financial projections, demand forecasting, or trend analysis.

10. Market Research
Market research permits the systematic gathering, analysis, and interpretation of information about a market, including its size, competition, and user preferences. Analysts conduct this research to understand market dynamics, detect opportunities, and manage risks. It aids in launching products, developing marketing strategies, and making informed business decisions.

11. Technical Skills
Technical skills refer to a person’s proficiency in using tools, technologies, and software to perform specific tasks or solve problems. They revolve around data analysis, information technology, or specialised software relevant to their field. These skills vary widely but are crucial for effectively carrying out job responsibilities.
12. Research Skills
Research skills encompass several functionalities related to gathering, evaluating, and interpreting information. For analysts, strong research skills are essential for gathering data, validating assumptions, and supporting their analyses, ultimately contributing to well-informed decision-making processes within organisations.

13. Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical technique used to make inferences about a population based on a sample of data. Analysts formulate a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, then collect data to determine whether there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis. This skill is essential for concluding data, identifying trends, and making informed decisions.

14. Machine Learning
A computer employs a machine learning (ML) algorithm, a set of rules or instructions, to identify patterns in data and then predict or take action based on those patterns. Analysts proficient in ML can classify data, build predictive models, and perform natural language processing and image recognition, aiding in data-driven decision-making.
15. Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition identifies patterns, regularities, and trends within data. Analysts use this skill to recognise anomalies, detect fraud, and make predictions based on historical data. It plays a crucial role in various fields, from finance (identifying market trends) to healthcare (detecting diseases based on symptoms).
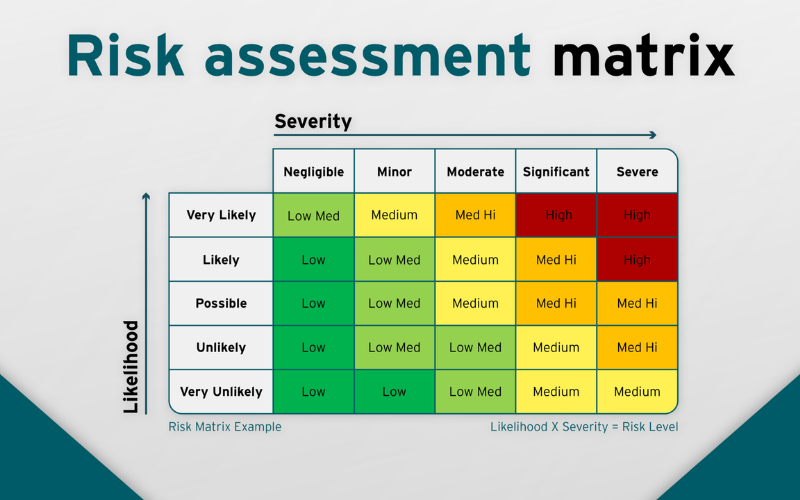
16. Risk Assessment
Risk assessment involves identifying, analysing, and evaluating potential risks associated with a decision or project. Analysts use this skill to estimate the likelihood and impact of risks, helping organizations make informed choices. Effective risk assessment aids in minimizing potential negative consequences and maximizing opportunities.
17. Adaptability
Adaptability is the capacity to adjust to new conditions and environments effectively. In the fast-paced world of data analysis, adaptability is vital. Analysts should embrace new technologies, tools, and methodologies as they evolve. It also involves being open to changing project requirements and adjusting analytical approaches accordingly.
18. Ethical Judgment
Ethical judgment involves making morally sound decisions in a professional context. Analysts often deal with sensitive data and must adhere to ethical principles. It includes ensuring data privacy, avoiding biases, and making decisions that consider the impact on stakeholders and society.
19. Crisis Management
Crisis management involves the ability to handle unexpected and challenging situations effectively. Analysts may need to make rapid decisions during crises or disruptions, such as market crashes or cybersecurity breaches. Effective crisis management minimises damage and helps organisations recover quickly.

20. Continuous Learning
Continuous learning is a mindset of lifelong learning and skill development. In the rapidly evolving field of data analysis, staying up-to-date with the latest tools, technologies, and best practices is crucial. Analysts who prioritise continuous learning remain adaptable and can offer more value to their organisations.





















