Technology is ever-changing and evolving. With newer technologies come newer ways of performing tasks. This article sheds light on the newest technology trends of 2022 which would make your interaction with technology more awestruck.
Here is the list of the top 20 new Technology Trends:
1. Augmented Reality (AR)& Virtual Reality (VR)
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that enhances your physical surroundings by adding digital parts and features to provide a live perspective, which is often provided by a smartphone camera. Virtual Reality teleports you mentally into a simulated real-life environment. AR coexists with the real world whereas VR provides a complete simulation and replaces the real world.

2. Artificial Intelligence(AI)
Artificial Intelligence(AI) is the simulation of human intelligence in machines that have been trained to think and act like humans. AI is already a very huge part of our daily lives such as AI in the camera, AI and machine learning in speech recognition such as Siri and Google assistant along with object recognition and AI in hardware.

3. Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed database that maintains information in a digital format. They are well known for their role in cryptocurrencies as they help in maintaining records of transactions in a stable and decentralized form. Blockchain holds the data in blocks and has specific storage, in which data is filled and stored and interlinked with the previous block. Hence it forms a series of blocks forming a blockchain.

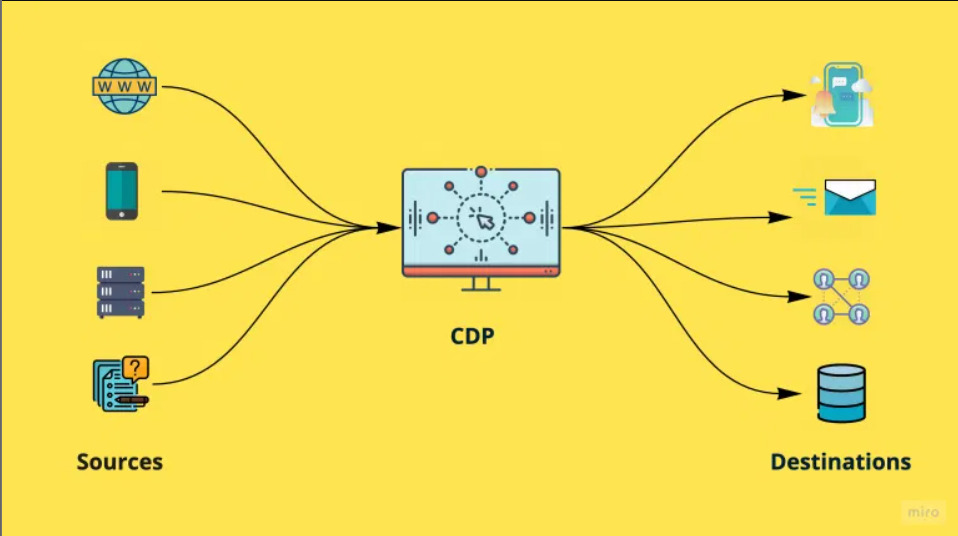
4. Customer Data Platform (CDPs)
A customer Data Platform (CDP) is a piece of software that collects and combines data from multiple tools and creates a centralized database for a customer. It collects data from certain touchpoints of a customer such as Facebook, email, and any other place that the customer interacts with the company, and combines them into a single customer database profile. This allows the organization to segment its target groups and produce more personalized marketing efforts.
5. Metaverse
A Metaverse is a network of the 3D virtual worlds or a simulated digital environment that focuses on social connection with the help of augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and blockchain. It represents a highly connected three-dimensional world. In the metaverse, anyone can perform trading of any assets and explore spaces.

6. NFTs
NFTs are crypto-assets/tokens on a blockchain that cannot be replicated. They represent real-life items such as real estate, artwork, music, video games, memes, virtual fashion, etc. These assets are tokenized reducing the possibility of fraud involved in their buying and selling. MFTs represent an individual’s identity, property rights, and more.

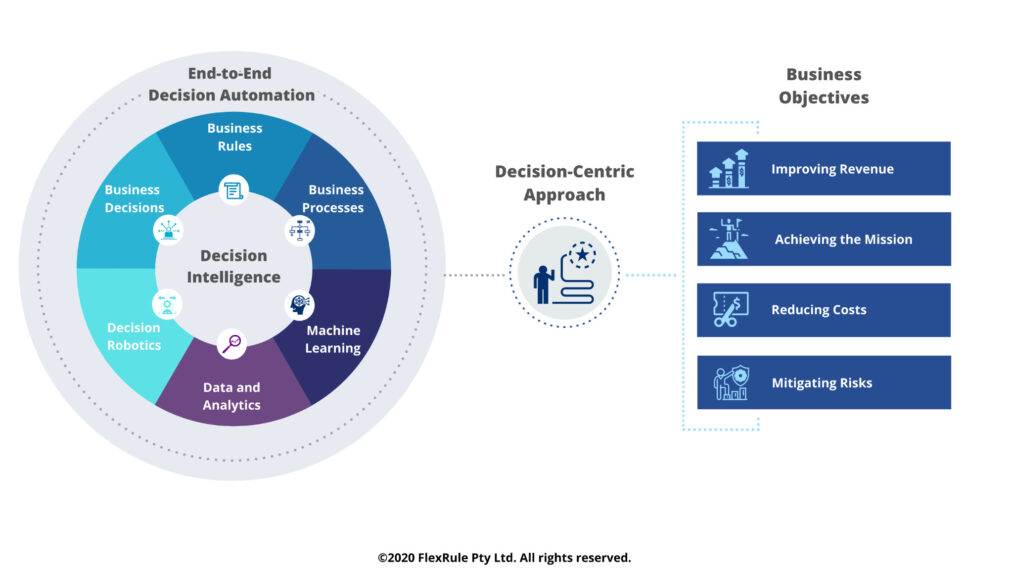
7. Decision Intelligence
Decision Intelligence applies data science to the world of business problems. It takes into account the behavior of the stakeholders and affects decision-making. It’s a technology that helps companies and businesses to understand the possible outcomes of a decision before making the move. Helps in making descriptive and consistent decisions in the long run.
8. Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity safeguards internet-connected systems including hardware, software, and data from cyberthreats. Cybersecurity professionals identify these threats and give high-tech solutions to safeguard against all types of cybercrimes.

9. RPA
RPA is the use of software that uses AI and ML to perform the repeated works that were previously done by humans. These include automating jobs, dealing with data, doing transactions, and replying to emails.

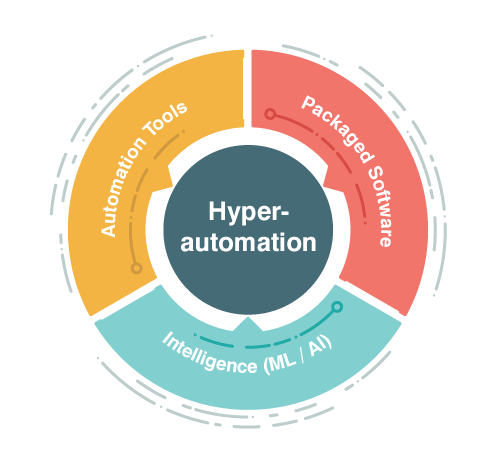
10. Automation And Hyper Automation
Automation uses automation technologies such as Robotic Process Automation(RPA), Machine Learning(ML), Artificial intelligence (AI), and business process management which helps in decision making and scaling tasks across businesses. Hyperautomation refers to the automation of everything that can be automated in a company. It provides high-quality automation data collected from various sources.
11. Edge Computing
Edge Computing deploys the storage and computing resources at the location closer to the sources of data. It saves response time and bandwidth.
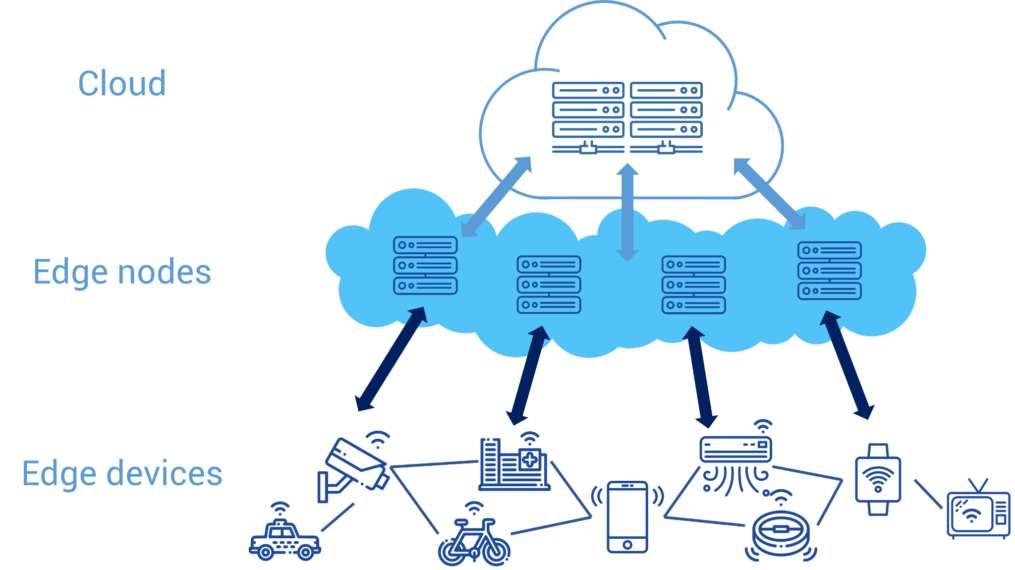
12. Internet Of Things
Internet Of Things means interacting with the internet without a keyboard or screen but by sharing the IP address. These include sensors, personal devices such as fitness trackers, etc. The IoT devices gather data and send it through the internet for processing, then the data is analyzed and then the results based on the analyzed data are sent to the devices.
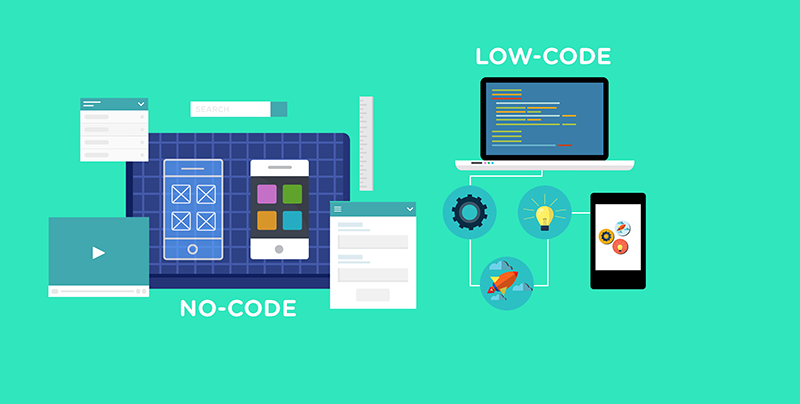
13. Low Code/ No Code
Low Code/ No Code allows creating businesses and mobile apps with little to no coding. Low code requires basic coding skills for users whereas no code doesn’t need any coding knowledge. This is mainly used by supply chain managers, manufacturers, accounting and finance, HR, and IT departments.
14. 5G
5G follows the IoT trend. With 3G and 4G, people had better access to the internet with increased speed but 5G would enable services that would rely on AR and VR. 5G services would be used in the advancement of societies, the transformation of industries along with elevating the experience of AR and VR.

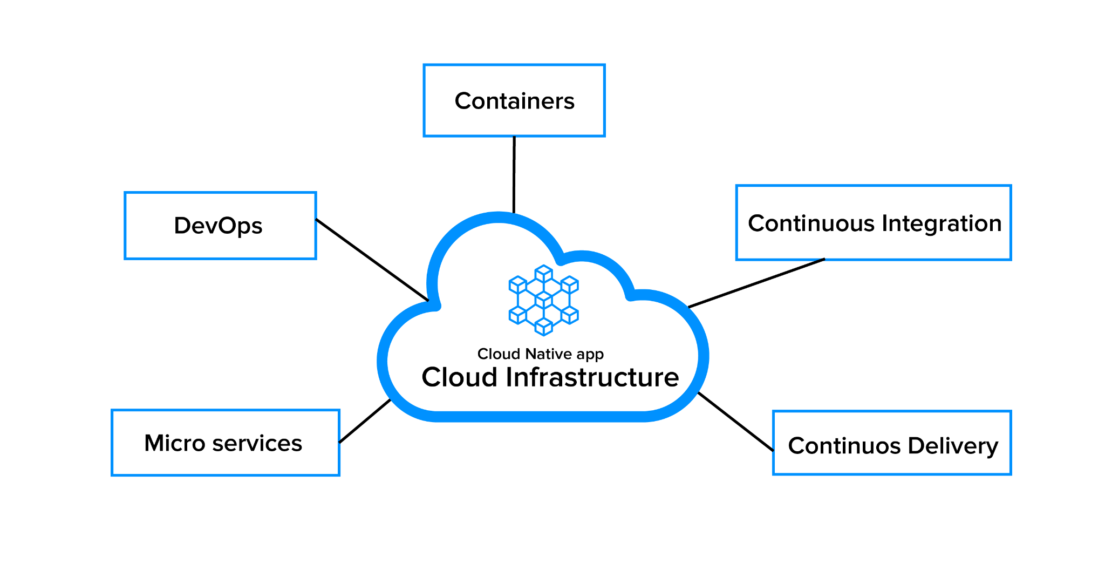
15. Cloud-Native Platforms
Cloud-Native is the concept of building and running applications to take advantage of the distributed computing offered by the cloud delivery model. This allows companies to build and run applications in public, private, or hybrid clouds.
16. AI Engineering
AI Engineering focuses on the development of tools, systems, and processes that enable the application of artificial intelligence in the real world scenario.

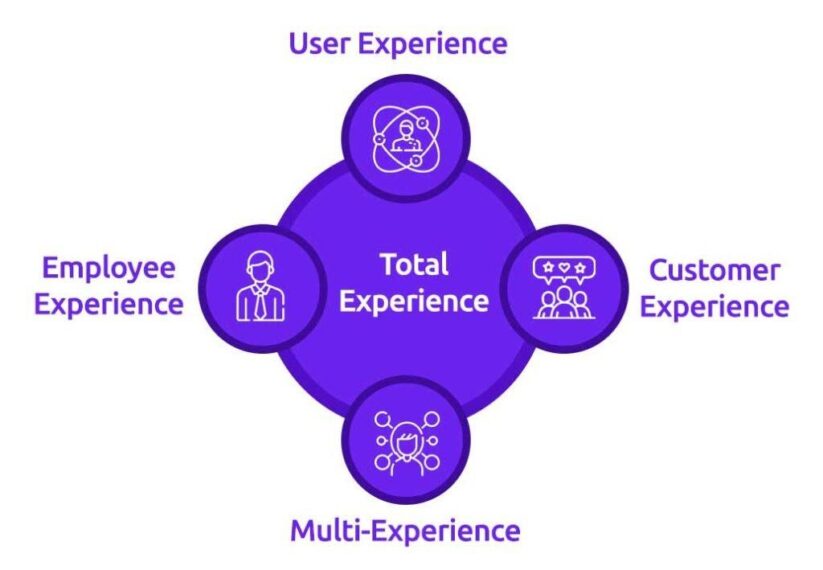
17. Total Experience
Total Experience is a business strategy that combines employee, customer, and user experience across many touchpoints. This links the network and bridges the gap between customers and employees providing customer satisfaction and improved end product and services.
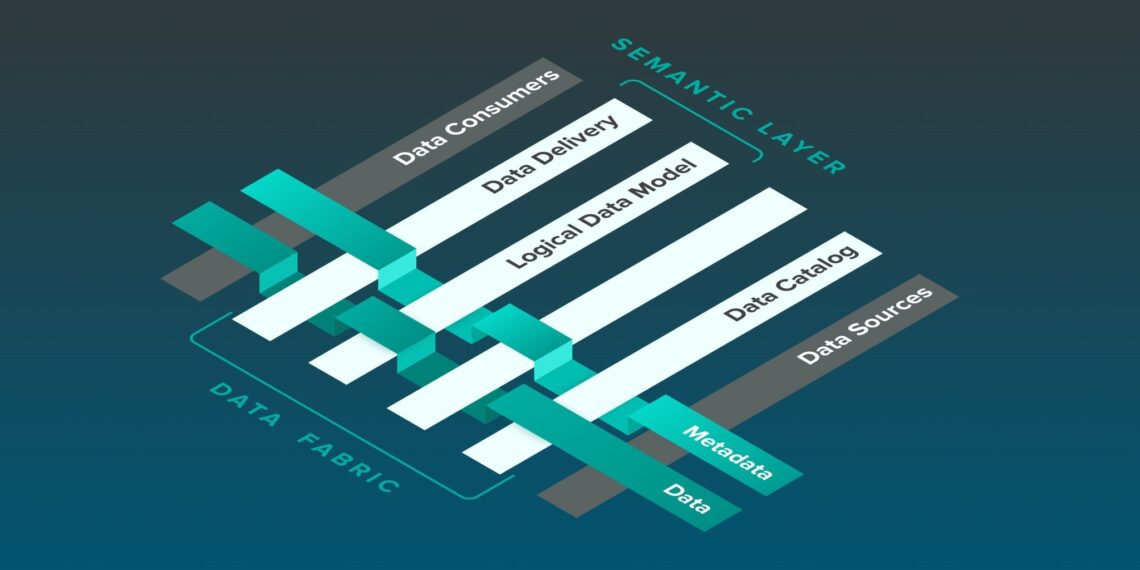
18. Data Fabric
Data Fabric allows the flexible and reliable combination of data sources across platforms and users inside an organization. It allows data to be available and adapt everywhere.
19. Privacy Enhancing Computation
Privacy Enhancing Computation helps protect data in use while maintaining privacy and secrecy at the highest level. They use zero-knowledge proofs, multi-party computations, homomorphic encryption, and differential privacy techniques to safeguard the data.

20. Anywhere Operations
During the recent pandemic, many businesses instead of focusing on a return to work policy focused on developing a sustainable “Anywhere Operations” model. This model was people-centric and independent, which allowed virtual collaboration and digital readiness. Hence this would improve the access to more talent and opportunities.