Benjamin Franklin is the father of Electricity. All home appliances run on it. It is a true gift, as today’s life isn’t possible without electricity. There are many ways electricity is being used in our society. Its versatility and significance make it an integral part of our lives and the functioning of several industries. But usage is easy than creating it. Producing energy involves complex systems and technologies that require specialised knowledge and infrastructure. Here are a few methods to generate power:
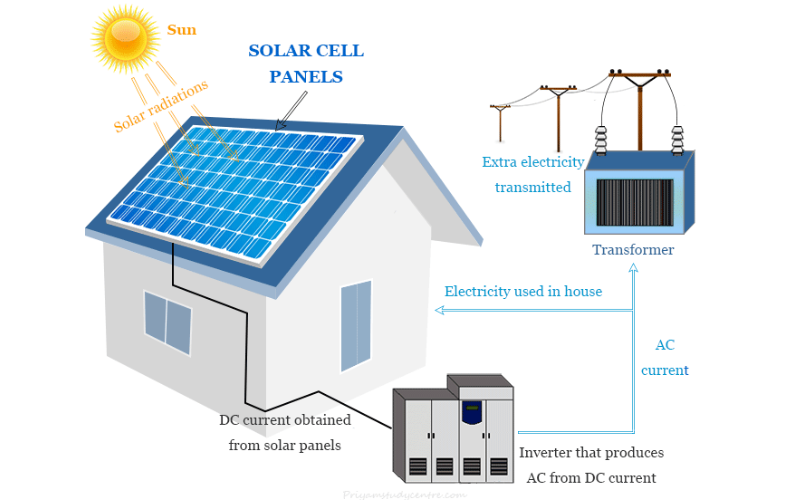
1. Solar Power
Solar Power includes using photovoltaic (PV) panels to transform sunlight into energy. These panels include semiconductors that generate a flow of electrons when open to sunlight. Solar energy is a renewable and easy electricity source, harnessed for several applications, from powering houses and industries to providing power for locations.
2. Wind Power
Wind energy harnesses the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity. Windmills consist of large blades that rotate when exposed to wind, converting the rotational movement into energy via a generator. Wind electricity is a sustainable and considerable power supply, and wind farms are constructed on land or offshore to take advantage of strong and consistent winds.
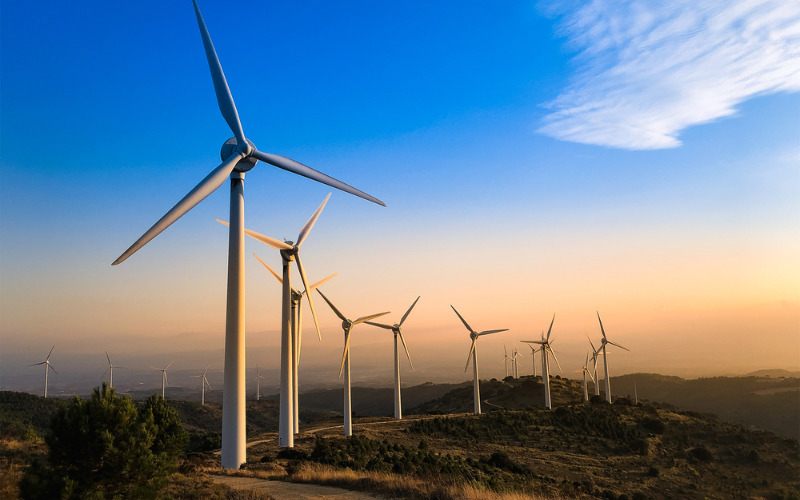

3. Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power uses the pressure of flowing or falling water to generate energy. Dams are stone or concrete structures constructed to store water in a reservoir, and the water is then released, flowing via generators to generate electricity. Hydroelectric electricity is a reliable and established renewable electricity supply that provides a consistent electric supply.
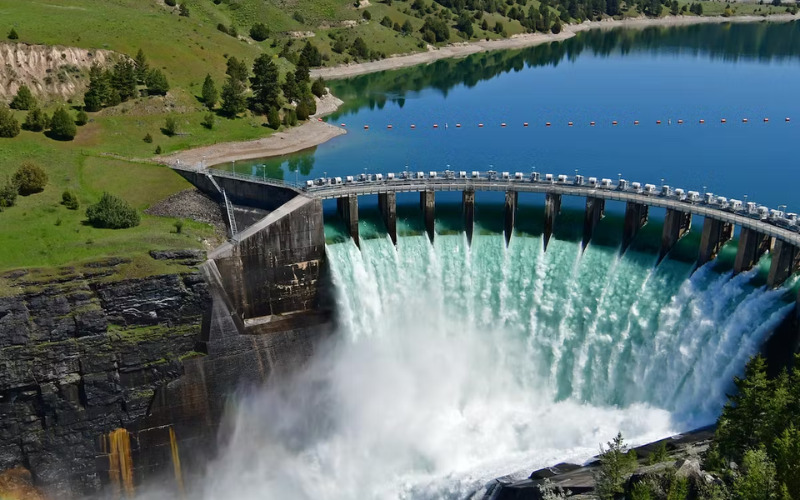

4. Geothermal Power
Geothermal power taps into the heat stored below the Earth’s surface to generate power. Geothermal electricity plants use wells to access hot water or steam from geothermal reservoirs. This steam is used to power turbines, which produce electricity. Geothermal energy is a reliable and sustainable power source that can operate constantly, imparting a constant baseload power supply.
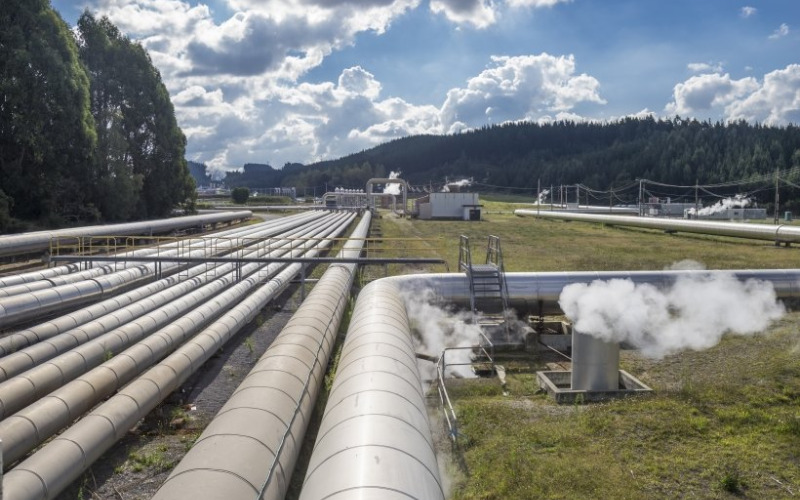

5. Biomass Energy
Timber, agricultural waste, or biogases are a few examples of the natural resources that can be used in biomass power to produce electricity or heat. Heat may be generated from burning biomass directly, or it can be turned into biogas via processes like anaerobic digestion. Biomass energy is considered as a renewable energy resource as organic matter can be replenished.

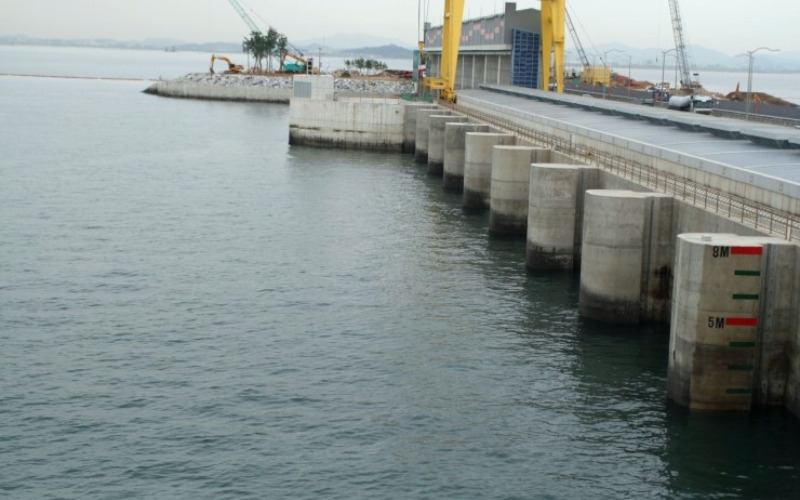
6. Tidal Power
Tidal power harnesses the power from the gravitational pull of the moon and the solar, which creates tidal movements inside the oceans. Tidal energy plant life uses tidal barrages or tidal turbines to capture the energy from the tides and convert it into electric power. Tidal energy is a predictable and renewable power source, as tides comply with a predictable pattern.

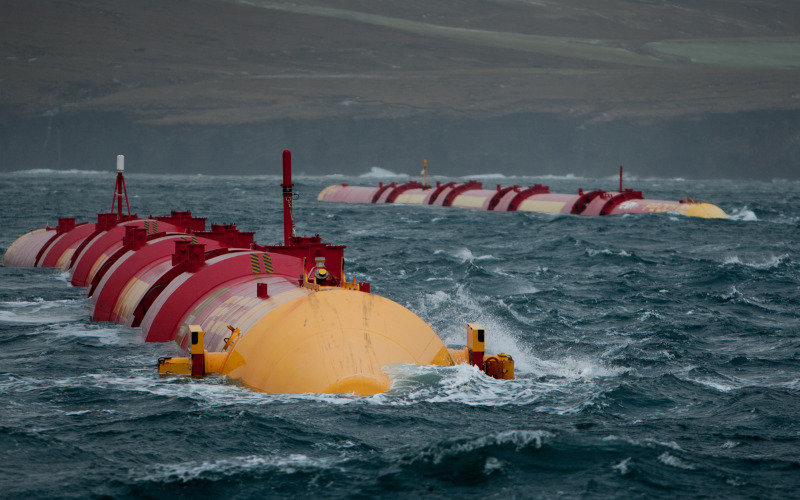
7. Wave Power
Wave power harnesses the energy from ocean waves to generate electricity. Wave energy converters capture the motion of waves and convert it into electric or mechanical energy through several technologies consisting of floating devices, oscillating water columns, or submerged pressure differential structures. Wave electricity is a renewable energy resource with great potential, particularly in coastal regions with strong wave activity.

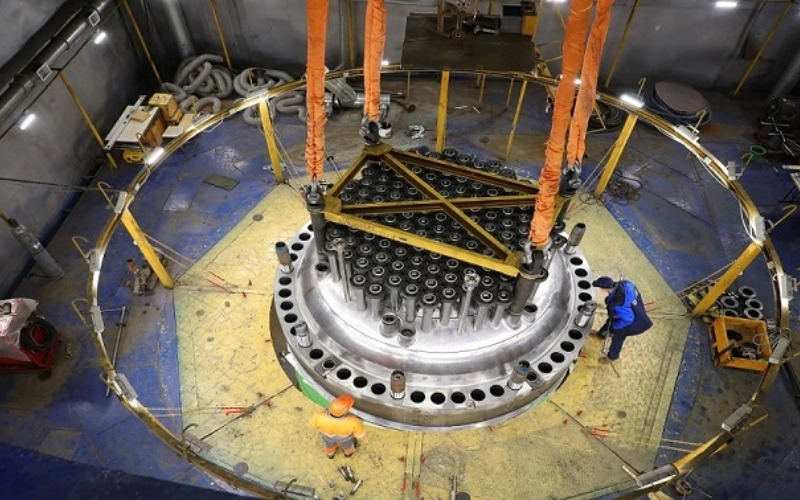
8. Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is generated energy through nuclear reactions, using uranium or plutonium as fuel. Nuclear reactors produce heat via controlled nuclear fission, which heats water and generates steam to drive turbines and produce energy. It is a dependable and powerful energy source that provides a significant portion of the electricity in many countries. However, it additionally poses demanding challenges associated with waste disposal and safety concerns.

9. Natural Gas
Methane dominates the composition of natural gas, a fossil fuel that is utilised for a several purposes, including the production of electricity. Natural gas power plants burn natural gasoline to provide high-pressure steam, which drives turbines connected to generators. Natural gas is a cleaner fossil fuel compared to coal and oil, emitting low levels of carbon dioxide and pollutants when burned.
10. Coal
Coal is a fossil fuel used for electricity production. Coal-fired power plants burn crushed coal to produce steam, which drives generators and generates power. However, coal combustion releases large quantities of carbon dioxide and other pollutants, contributing to air pollution and climate change issues. Efforts are made to transition to cleaner and more sustainable electricity sources.
11. Oil
Oil, also known as petroleum, is commonly used as a transportation fuel; however also can be used in energy production. Oil-fired power plants burn oil to produce steam and generate electricity. However, oil is much less generally used for power generation than other resources due to its high cost and environmental effects. It is used in regions where different power resources are limited.
12. Biogas
Anaerobic digestion of organic materials, such as food waste, agricultural waste, or sewage, produces biogas, a sustainable energy source. Microorganisms break down the organic material during digestion to create biogas, which is mostly made of methane and carbon dioxide. Biogas can be used for heat generation, power production through combustion, or as fuel for vehicles.
13. Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are electrochemical devices that convert the fuel’s chemical energy into electricity. The fuel cell includes an electrolyte and two electrodes, and the fuel reacts with an oxidant to produce electric power, heat, and water. Fuel cells offer high performance, low emissions, and versatility, making them appropriate for various applications, which include transportation, electricity generation, and portable devices.

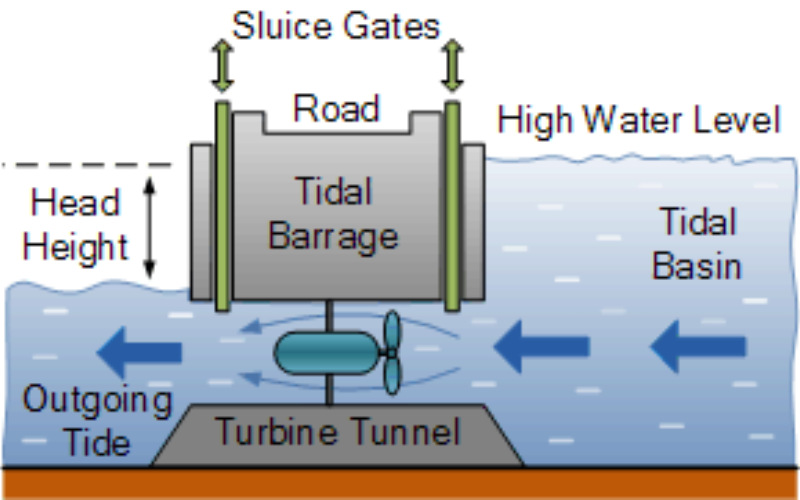
14. Tidal Barrages
Tidal barrages are structures constructed across estuaries or tidal rivers that capture and release the potential energy of tidal movements. As the tides rise and fall, the water flows through turbines, using turbines to produce electricity. Tidal barrages are a form of tidal power generation that could provide a predictable and reliable source of renewable power. Still, their generation and environmental impact should be carefully considered.
15. Kinetic Energy Harvesting
Kinetic energy harvesting involves capturing and changing the kinetic energy from various sources, including human motion, vibrations, or moving vehicles, into usable electric power. It utilizes small generators or transducers which convert mechanical power into electrical energy. It is used in wearables, wireless sensor networks, or self-powered structures in locations wherein conventional energy sources are impractical.
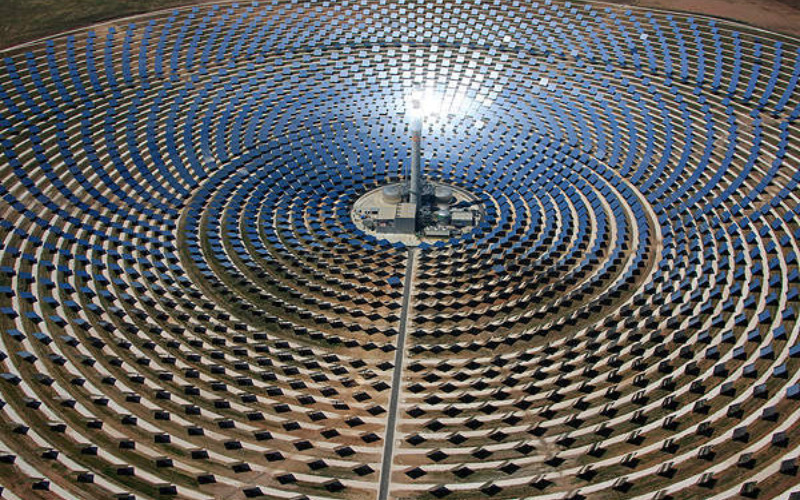
16. Concentrated Solar Power
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, such as a solar thermal collector or a solar tower. The focused sunlight heats a fluid or medium, which produce steam to drive turbines and generate electric power. CSP systems can store excess thermal power for later use, offering a non-stop power supply even when the solar isn’t shining.

17. Waste-to-energy
Waste-to-energy is a method that converts waste materials, consisting of municipal stable waste or biomass, into usable power. Various technologies, including incineration, gasification, or anaerobic digestion, are used to extract energy from the trash. The energy can be in the form of heat, electricity, or biofuels. It helps reduce the quantity of waste and exists as a source of renewable electricity.
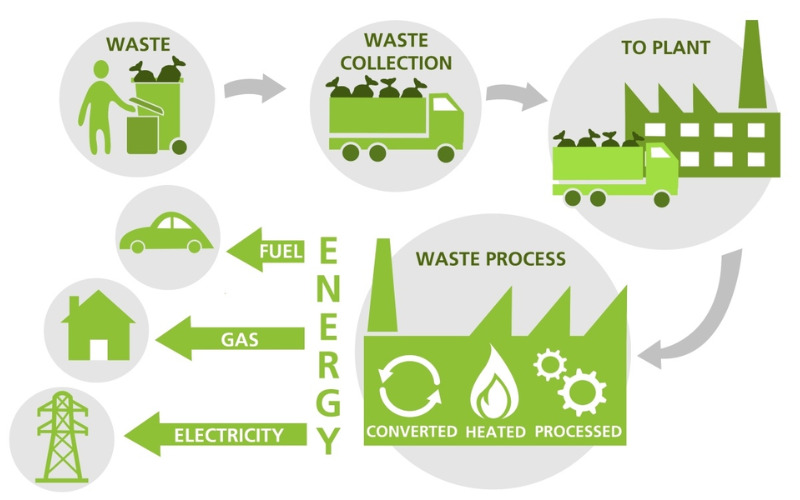
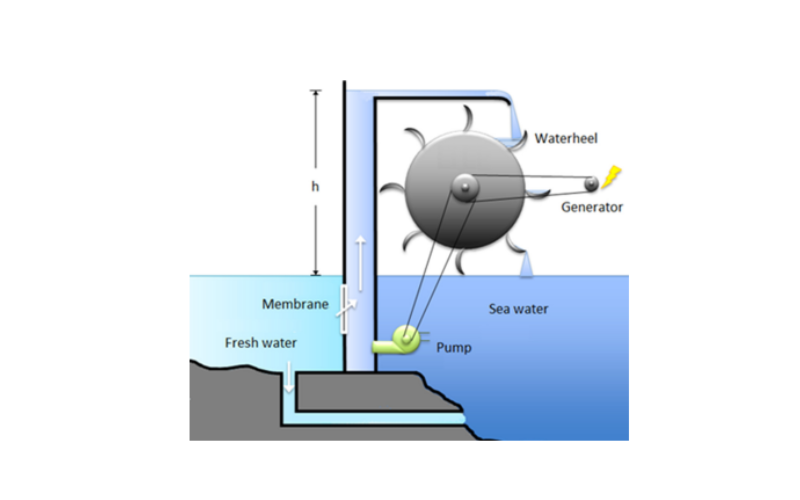
18. Osmotic Power
Osmotic power, known as salinity gradient power, uses the difference in salt concentration between freshwater and saltwater to generate power. The system involves the passage of saltwater and freshwater via a selectively permeable membrane, creating osmotic pressure. This pressure can drive turbines and generate power. Osmotic strength is a promising renewable energy resource, particularly in areas wherein rivers meet the sea or in desalination plants.
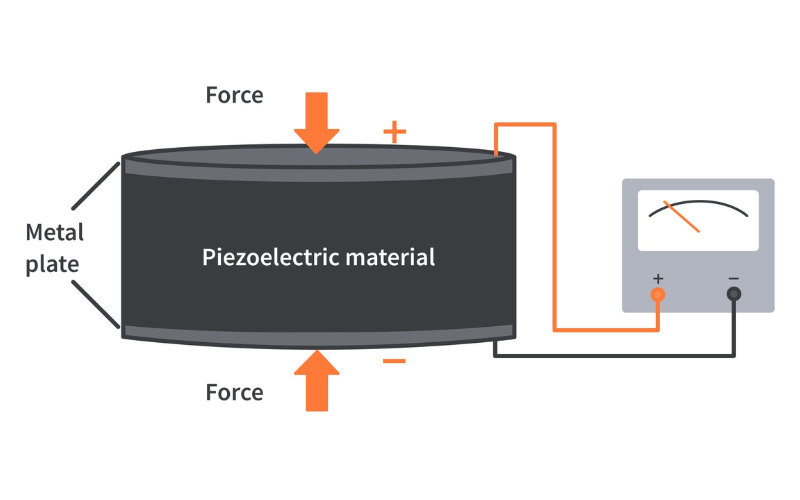
19. Piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity is a phenomenon in which specific materials generate an electric charge when subjected to mechanical strain or pressure. This principle is employed in several applications, which include piezoelectric generators, which convert mechanical vibrations or stress into electric power. Piezoelectric substances can be incorporated into devices or structures to capture and convert mechanical energy, supplying a potential for renewable power.
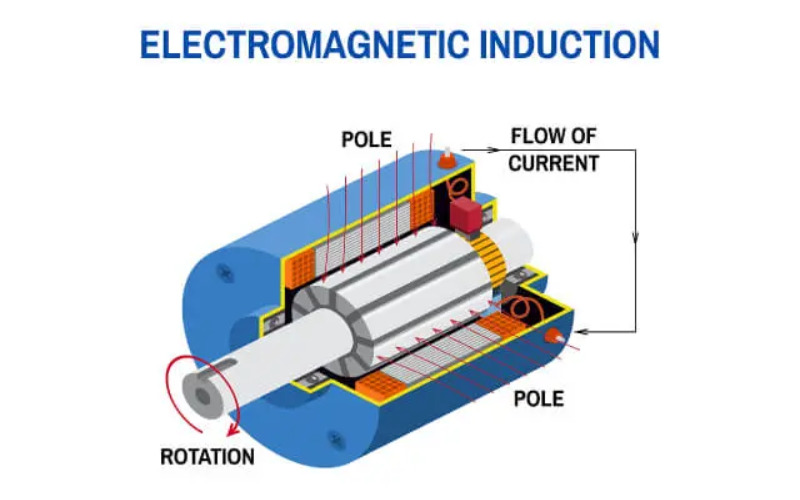
20. Magnetic Induction
Magnetic induction or electromagnetic induction, involves generating energy through the relative motion of a magnetic field and a conductor. When a conductor is exposed to a varying magnetic field, an electric current is induced in the conductor. It is utilized in various devices, including turbines and transformers, to transform mechanical or electrical energy into electricity and vice versa.