Microsoft has equipped us with built-in recovery options that can assist in troubleshooting and resolving these issues. In this article, we will delve into the details of the 20 essential Windows system recovery options, explaining their functionalities and when it is appropriate to utilize them.
1. Safe Mode
Safe Mode is a mode in Windows that starts up with the necessary drivers and services. Safe Mode booting assists you in locating and resolving any issues that may arise from conflicts between drivers or applications. It’s a starting point for troubleshooting and diagnosing issues with your system.
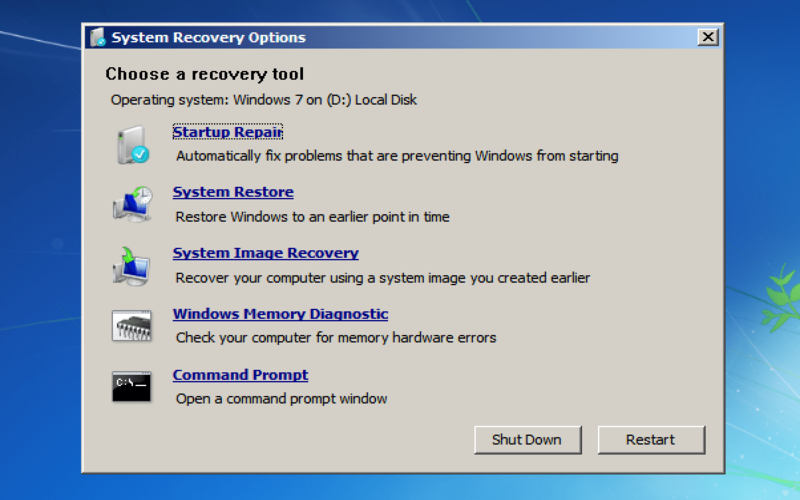
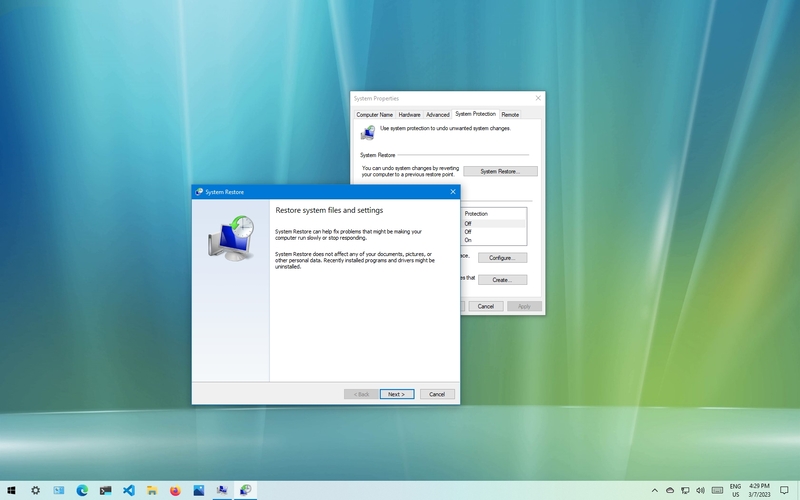
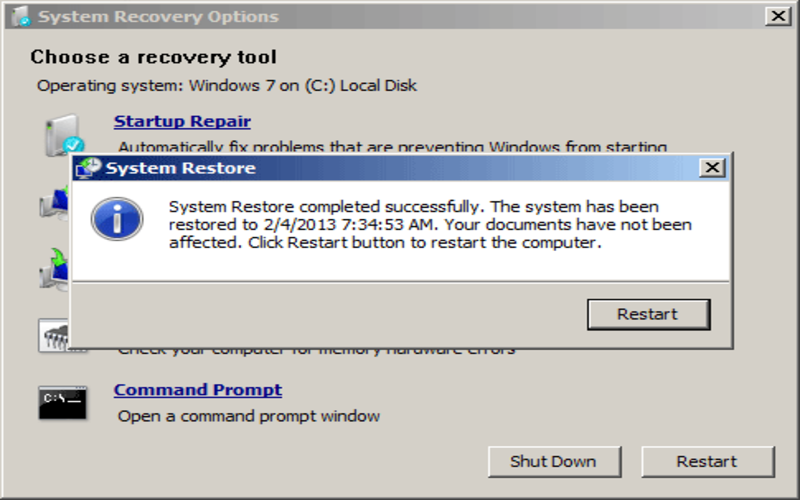
2. System Restore
System Restore enables you to restore your system to a state where it is functioning. It generates points at intervals or before significant changes to the system, like installing software. You can reverse any system changes that might have caused problems or conflicts by using System Restore.
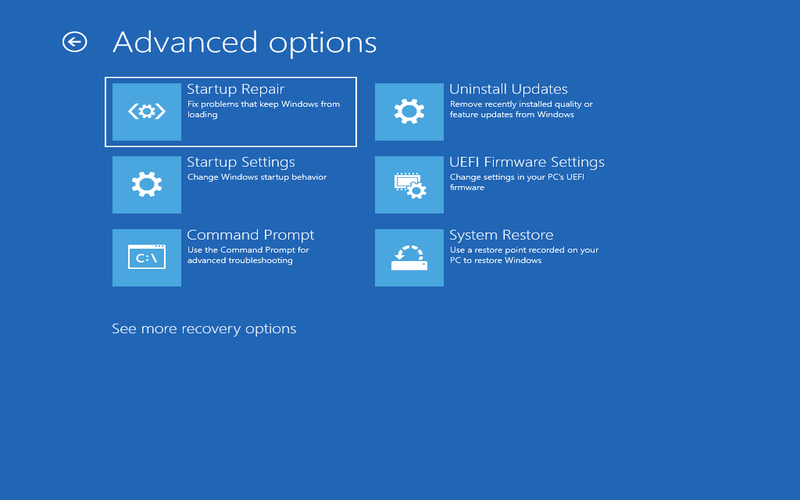
3. Startup Repair
Startup Repair is a tool that automatically assists in resolving problems that may hinder your computer from starting. It carefully scans your system to identify and address issues like corrupted system files, missing boot files, or incorrect startup settings. It aims to restore your computer’s functionality and ensure smooth startup operations.
4. System Image Recovery
You can use an image backup created to restore your system with the help of the System Image Recovery function. This option is for the previously installed programs, settings, and files that are still present on your machine.
5. Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE)
WinRE is an operating system that offers a range of recovery tools. To access it, restart your computer. Press a combination of keys during the boot process. Once in WinRE, you’ll have access to options such as System Restore, Startup Repair, Command Prompt, and additional tools for troubleshooting purposes.
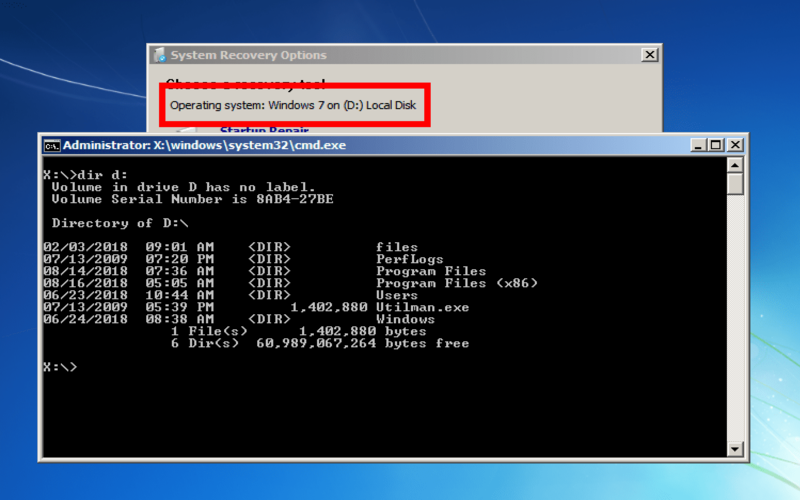
6. Command Prompt
The Command Prompt is a text-driven interface that enables you to execute commands and scripts. It serves as a tool for addressing and resolving file system errors, system configurations, and driver issues. Skilled users can leverage the Command Prompt to repair or diagnose commands.
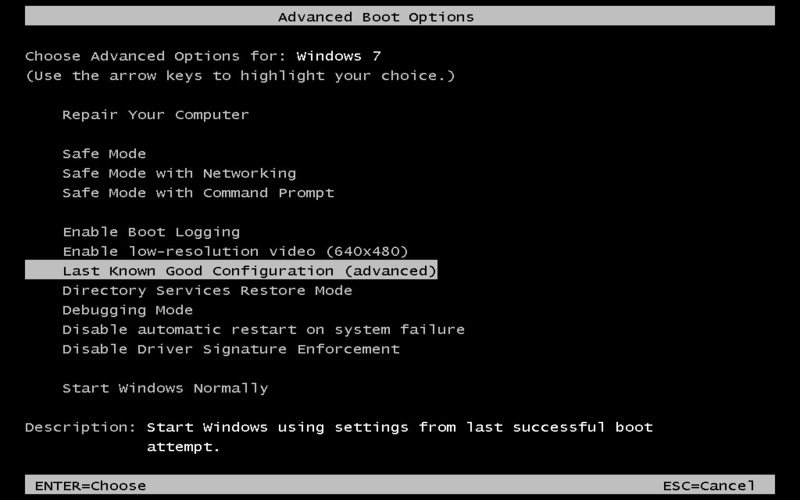
7. Last Known Good Configuration
The Last Known Good Configuration is a recovery choice that utilizes a stored setup that successfully initiated Windows. When recent changes—like installing drivers or updating software—have caused instability in the system, it may be helpful.
8. Automatic Repair
Automatic repair is a feature that comes pre-installed in Windows. Its purpose is to help troubleshoot and resolve problems that may prevent your computer from starting up. If you encounter any issues during startup, Automatic Repair will step in. Perform a series of checks and fixes to get your system back on track.
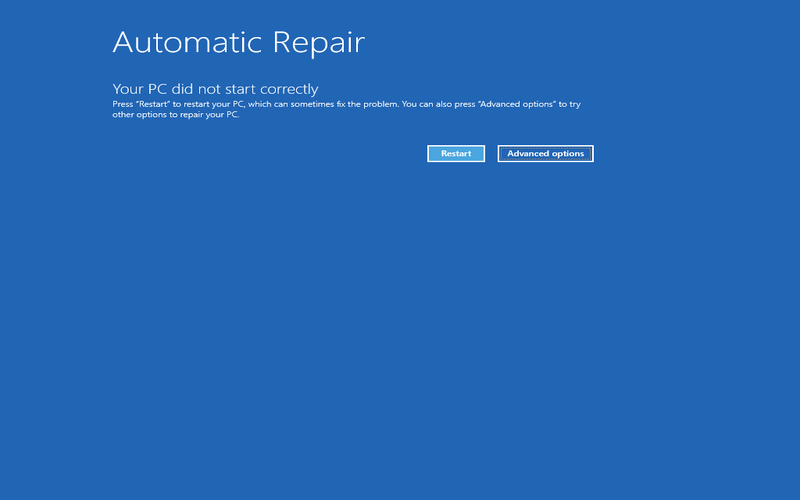
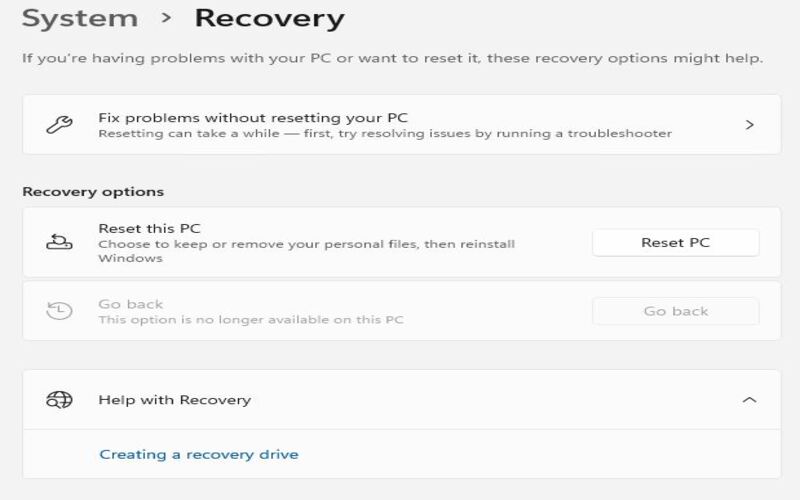
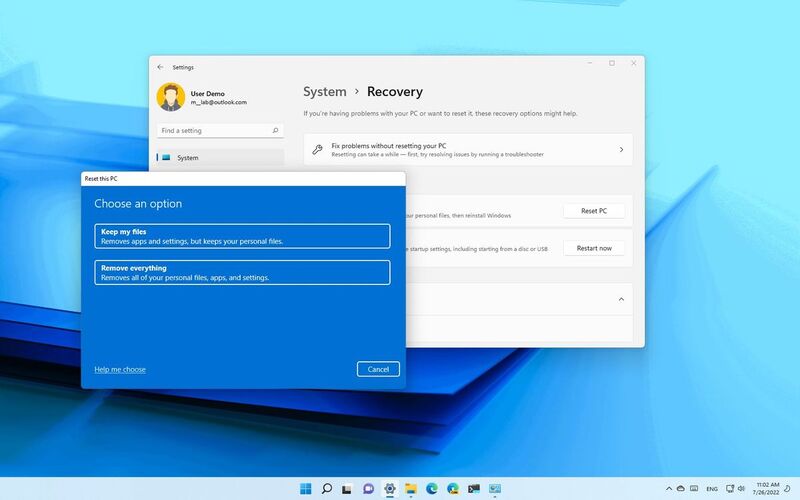
9. Reset This PC
Resetting your PC is a feature that lets your files and installed applications while keeping your Windows operating system intact. It comes in handy when your system becomes unresponsive or experiences issues. Resetting Windows gives you a fresh start by returning it to its original configuration.
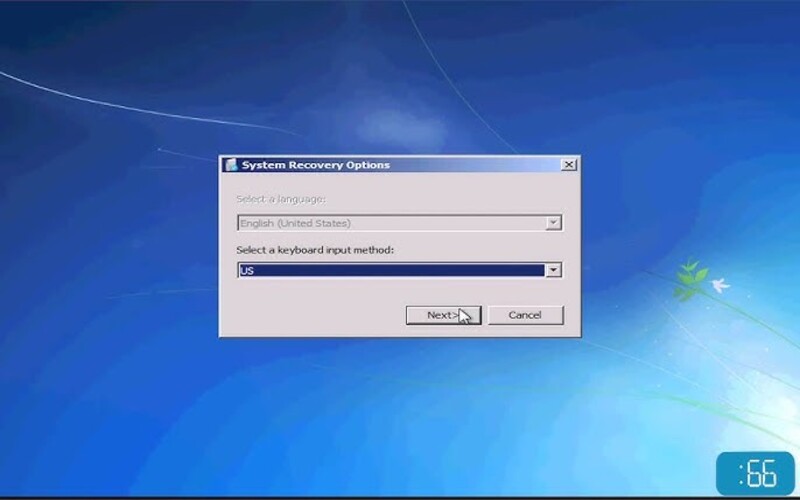
10. Refreshing Your PC Reinstalls
Windows while keeping your files and settings intact. This feature aims to tackle any problems related to the performance or stability of the system that may arise due to software or system configurations. It provides a clean slate for your operating system while preserving your data.
11. Disable Driver Signature Enforcement
You can choose to override the requirement for drivers to be digitally signed. Signed drivers are to guarantee their authenticity and compatibility with Windows. However, if you have a driver that isn’t digitally signed, this option allows you to install or use it.
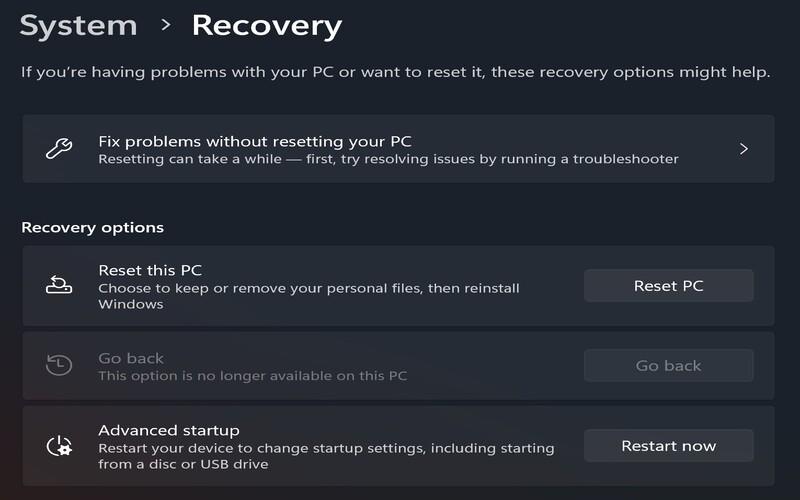
12. Booting From A Windows Installation Disk Or USB Drive
When you start up your computer using a Windows installation disk or USB drive, you gain access to recovery options. This method fixes system issues, restores backups, or reinstalls the operating system. It comes in handy when your computer is unable to boot into Windows.
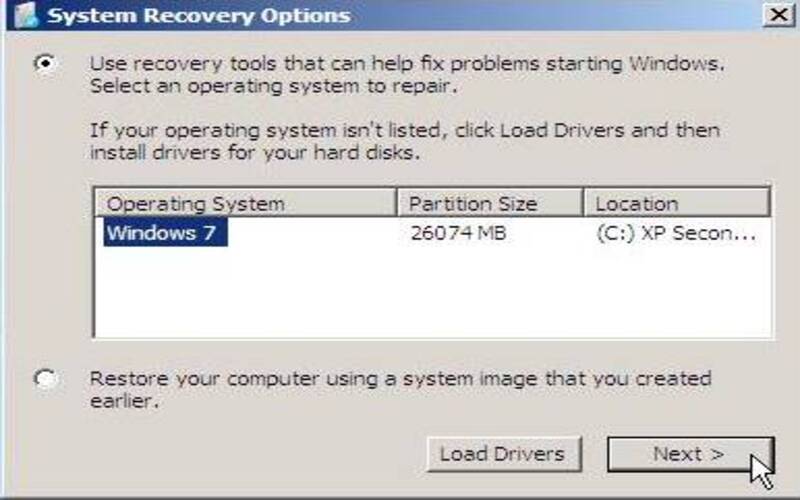
13. Check Disk (CHKDSK)
CHKDSK is a tool used via the command line to scan for and fix problems with your file system and hard drive. It causes sluggish performance, crashes, or corrupted data. Running CHKDSK allows you to rectify any inconsistencies in the file system and retrieve data from sectors.
14. SFC (System File Checker)
SFC is a tool that comes pre-installed on Windows operating systems. Its purpose is to check the integrity of system files and replace any damaged files with copies stored in a folder. This utility can be handy in resolving problems caused by missing system files, which can often lead to system instability or unexpected crashes.
15. DISM (Deployment Image Servicing And Management)
DISM is a tool that operates through the command line to fix issues with the Windows system image. Its capabilities include servicing, managing drivers, and performing recovery operations. DISM proves valuable when the Windows Update service encounters problems or essential system files are lost or corrupted.
16. Registry Editor
You can alter the values and settings kept in the Windows registry by using the Registry Editor. This registry holds information about your system configurations and installed software. It’s careful when using this tool, as making changes can lead to system instability. However, if used correctly, it can help resolve problems caused by damaged registry entries.
17. Device Manager
Device Manager helps you update, revert, or remove drivers, which can help resolve any compatibility or performance issues you may experience with devices connected to your computer.
18. Event Viewer
Event Viewer keeps a record of events and errors that happen on your system. It offers a log of events and can assist in identifying the underlying causes of issues by analyzing the corresponding event logs. By using Event Viewer, you can effectively diagnose problems. Troubleshoot them with precision.
19. Windows Memory Diagnostic
Windows Memory Diagnostic is a tool that scans your computer’s memory (RAM) to check for any errors or problems. When your RAM is faulty, it can lead to system crashes, blue screens, and overall instability. By using Windows Memory Diagnostic, you can easily detect any modules. Then steps, like replacing the faulty RAM.
20. System Configuration Utility
System Configuration Utility includes startup programs, services, and boot options. It serves as a tool for troubleshooting startup problems, managing system resources, and identifying applications or services that may be causing issues.
Conclusion
Windows offers a range of recovery options that can assist you in troubleshooting and resolving problems. Safe Mode, System Restore, Command Prompt, and booting from an installation disk.




















