Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles or driverless cars are a groundbreaking technological advancement in the automotive industry. These vehicles can operate without human intervention, relying on a combination of sensors, cameras, RADAR, LiDAR, and sophisticated software to perceive their environment, make driving decisions, and navigate safely from one point to another. They have the potential to revolutionize transportation by offering safer, more efficient, and more accessible mobility solutions. However, achieving full autonomy while addressing the associated challenges remains a complex and ongoing endeavour. Here are a few advantages and disadvantages of Self-driving cars:
1. Enhanced Safety
Enhanced safety is the most significant advantage of self-driving cars. They are equipped with several sensors, offering a 360⁰ view of the surroundings. These sensors detect pedestrians and other vehicles with high precision. AI algorithms in self-driving cars can react quickly than humans reducing the risk of accidents caused by human error.
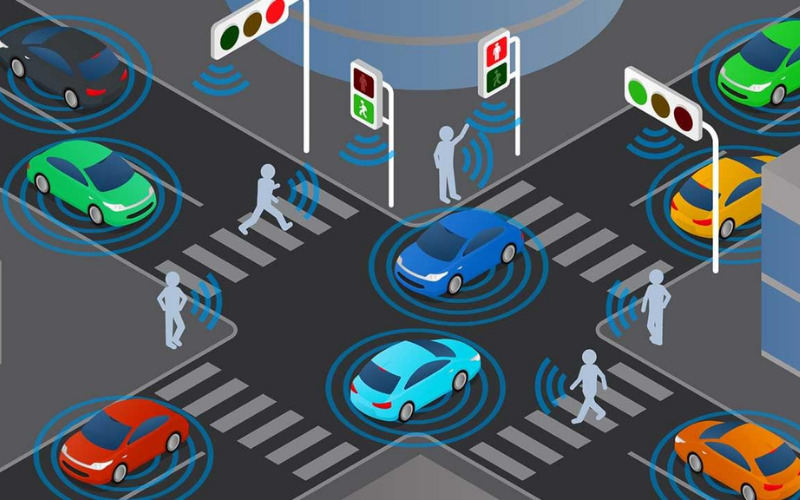
2. Reduced Traffic Congestion
Self-driving cars communicate and cooperate to optimise traffic flow. They share real-time traffic information and adjust their speed and routes through Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) communication. They avoid congested roads, select the most efficient routes, and manage their speed, maintaining a consistent traffic flow.

3. Improved Fuel Efficiency
Autonomous vehicles operate with optimal fuel efficiency. They can accelerate and decelerate smoothly, maintain consistent speeds, and select routes, minimising fuel consumption. These behaviours result in fuel savings compared to conventional vehicles. They are equipped with predictive analytics to assess traffic conditions, weather, and road gradients.

4. Increased Mobility
Self-driving cars offer increased mobility to those who have limited access to transportation. It includes individuals with disabilities, the elderly, and those living in areas with inadequate public transportation. They aid in maintaining an active lifestyle, accessing healthcare services, and participating in the workforce.

5. Lower Emissions
The enhanced fuel efficiency and optimized driving patterns of self-driving cars can lead to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Autonomous vehicles minimise unnecessary acceleration and braking, reduce idling time, and choose routes that produce fewer emissions. The shift towards electric and hybrid autonomous vehicles can further reduce the carbon footprint of transportation.

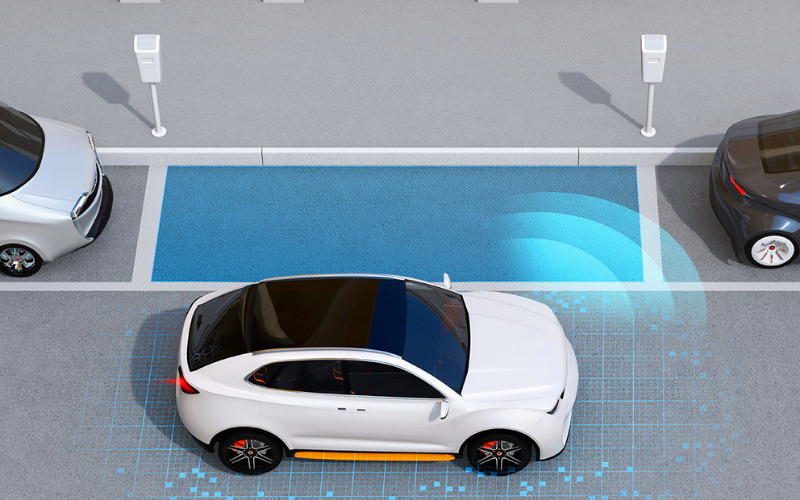
6. Reduced Parking Needs
Self-driving cars can drop passengers off at their destinations and then find parking spaces more efficiently. This reduces the need for expansive parking lots and garages in urban areas, freeing up valuable land for other purposes. It decreases the time spent searching for parking spaces contributing to reduced traffic congestion.
7. Time Savings
Self-driving cars allow passengers to use travel time more productively. Commuters can work, read, relax, or engage in entertainment during their journeys, effectively converting travel time into valuable personal or professional time. This time-saving aspect can enhance the overall quality of life, reduce stress, and increase productivity.

8. Improved Traffic Management
Self-driving cars contribute to improved traffic management by adhering to traffic laws and regulations consistently. This leads to smoother traffic flows as they maintain safe distances, obey speed limits, and follow traffic signals with precision. They can communicate traffic conditions to other vehicles and traffic management systems, enabling more effective management of congestion and accidents.
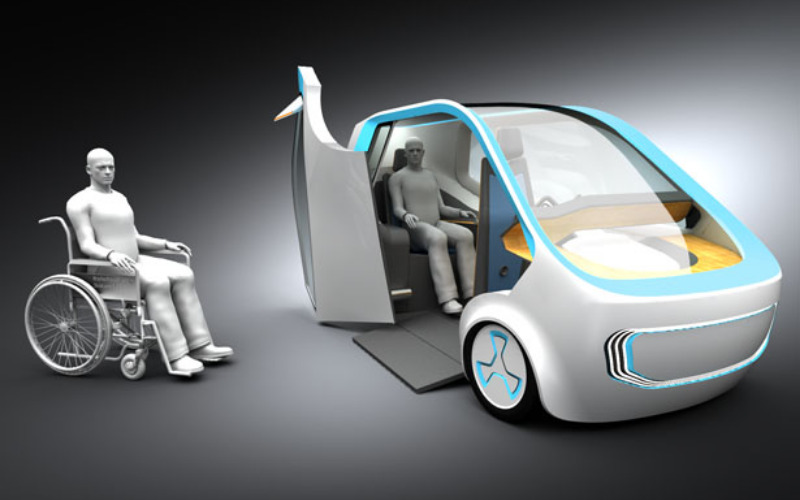
9. Accessibility
Autonomous vehicles can be designed with accessibility features to accommodate passengers with disabilities, making transportation more inclusive. These features might include wheelchair ramps, automated boarding systems, and specialised controls for passengers with limited mobility.

10. Reduction In DUI Cases
Every year, countless accidents and fatalities occur due to impaired driving caused by alcohol or drugs. Self-driving cars can significantly reduce cases of driving under the influence (DUI). They are programmed to make safe and responsible driving choices every time.

11. High Initial Cost
Self-driving cars have a plethora of advanced technologies like sensors, cameras, LiDAR, RADAR, and complex computer systems. The expense is not only for the hardware but also for the integration and development of software. Consequently, they tend to be more expensive than conventional vehicles.

12. Limited Availability
Despite the growing interest in self-driving cars, their availability to the general public remains limited. Autonomous vehicles are still in the testing and development phase, and only some companies have deployed them commercially in selected regions. Limited availability restricts users’ choices, making it difficult for most people to experience self-driving technology.

13. Data Privacy Concerns
Self-driving cars generate large amounts of data, including real-time location, sensor readings, and passenger behaviour. This information can enhance traffic management, vehicle performance, and user experience. However, it raises significant data privacy concerns. Striking a balance between utilising data for improving autonomous systems and protecting individual privacy is a complex challenge.

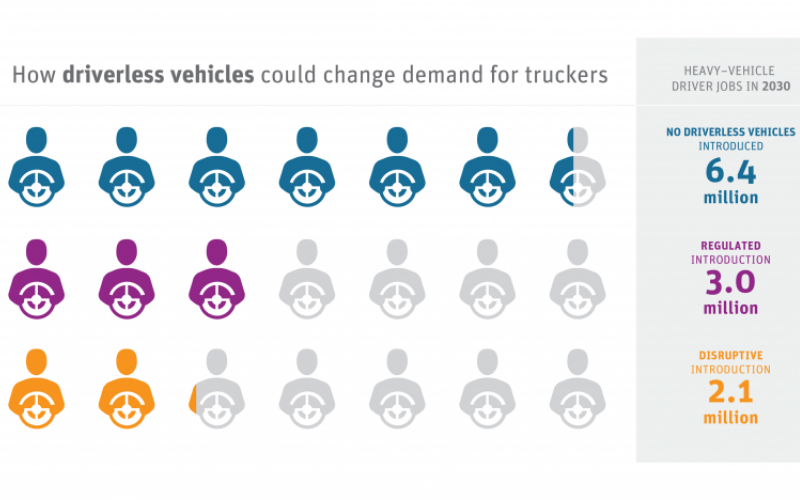
14. Loss Of Jobs
The widespread adoption of self-driving cars could disrupt various industries and lead to job losses. Professions like truck drivers, taxi drivers, and delivery drivers could see reduced demand as these jobs become automated. The shift could result in unemployment for a significant portion of the workforce. This potential job displacement is crucial as retraining and reskilling affected workers for new roles in the evolving job market.
15. Technical Challenges
Self-driving cars must navigate complex and ever-changing environments, which poses significant technical challenges. Adverse weather conditions, unpredictable road situations, and uncooperative human drivers are a few of the obstacles autonomous vehicles encounter.

16. Regulatory Hurdles
The deployment of self-driving cars is subject to a complex web of laws and regulations. Governments and regulatory bodies are still establishing comprehensive policies for autonomous vehicles, leading to uncertainty and inconsistency. Standardised regulations are vital for ensuring the safety and legality of self-driving cars on the road.

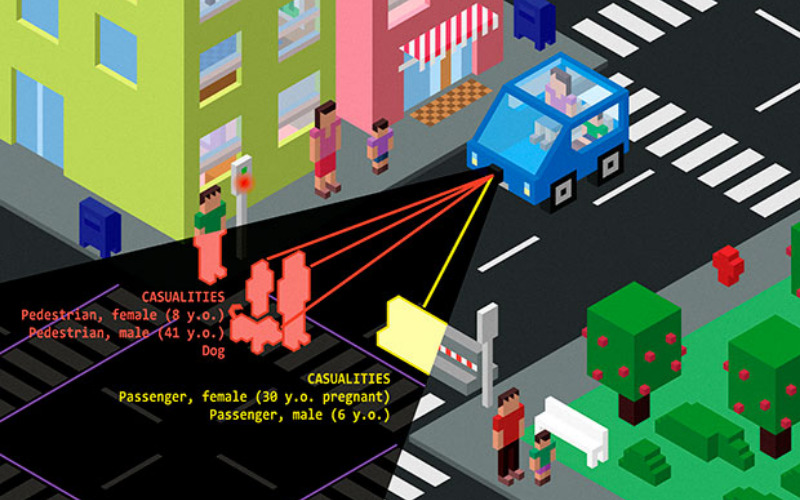
17. Ethical Dilemmas
Self-driving cars encounter situations where ethical decisions must be made, such as during emergencies or accidents. They can lead to public debate and even legal disputes. Determining a universal ethical framework to guide these decisions is challenging. The lack of a clear, standardised approach to ethical choices in autonomous vehicles can undermine public trust and acceptance.
18. Cybersecurity Risk
Self-driving cars rely on communication networks and software, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks. The cybersecurity risk is a major concern for manufacturers, as ensuring the security of self-driving cars is a challenge. Hackers can control an autonomous vehicle’s systems causing dangerous consequences. A breach in security can put lives at risk and erode public confidence. Continuous efforts to develop robust security measures and protect against evolving cyber threats are required.

19. Infrastructure Upgrades
Infrastructure upgrades aid in realizing the full potential of self-driving cars, as they rely on accurate, real-time data and communication with other vehicles and infrastructure elements. The slow pace of infrastructure development can hinder the adoption and efficiency of self-driving technology in certain areas.

20. Maintenance Complexities
Self-driving cars have complex sensor arrays, cameras, LiDAR, and other advanced components. However, maintaining and servicing these vehicles can be more challenging and expensive than traditional cars. Autonomous vehicles require specialised technicians trained to work with advanced systems. It increases maintenance costs and creates new service centers and technicians with specialised skills.





















