Embedded systems are the new heroes of modern technology, powering devices and complex industrial systems. Embedded systems are specialized computer systems which perform dedicated functions or tasks within larger systems or products. They are vital for automating tasks, and enhancing convenience and efficiency in various domains. The field of embedded systems continues to evolve as technology advances, enabling smarter, more capable devices in our digital world. Designing embedded systems presents unique challenges. Developers must balance functionality, cost, power consumption, and space constraints. Here are a few applications of Embedded Systems:
1. Consumer Electronics
Embedded systems operate devices like electric stoves, washing machines, smartphones, smart TVs, and ovens. They process data, manage user interfaces, and enable connectivity, delivering improved user experiences.

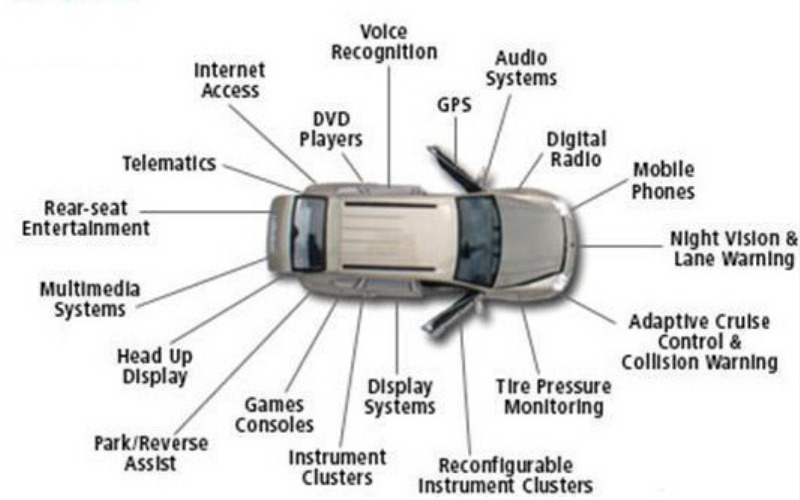
2. Automotive
In the automotive sector, embedded systems are instrumental in managing critical functions. They control engine management, airbags, anti-lock braking systems (ABS), and GPS navigation. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) leverage embedded technology for features like adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assistance. Embedded controllers manage infotainment, navigation, and communication interfaces. They optimize sound reproduction in vehicle cabins, adjusting for factors like noise, speed, and occupant positions.
3. Industrial Automation
Embedded systems are the vitals of modern manufacturing. They control conveyors, robots, and assembly lines, enabling efficient and precise operations. They offer process control, real-time monitoring, and data acquisition for quality control and optimization.

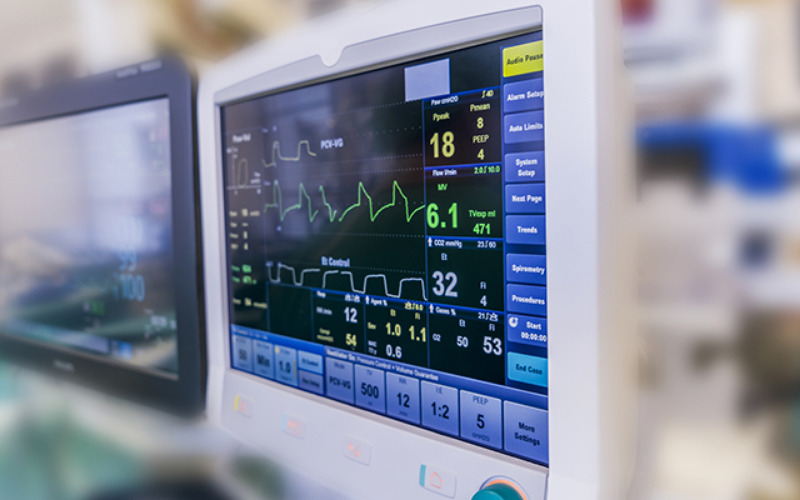
4. Medical Devices
Infusion pumps, dialysis machines, pacemakers, MRI machines, X-ray machines, and CT scan machines use embedded systems. They provide functions for data processing, precise access, and safety functionalities, assuring the efficacy and dependability of medical equipment.
5. Telecommunications
Embedded systems play a crucial role in network infrastructure. They operate network routers, switches, and base stations, managing data traffic, and routing, and ensuring seamless connectivity in telecommunications networks.

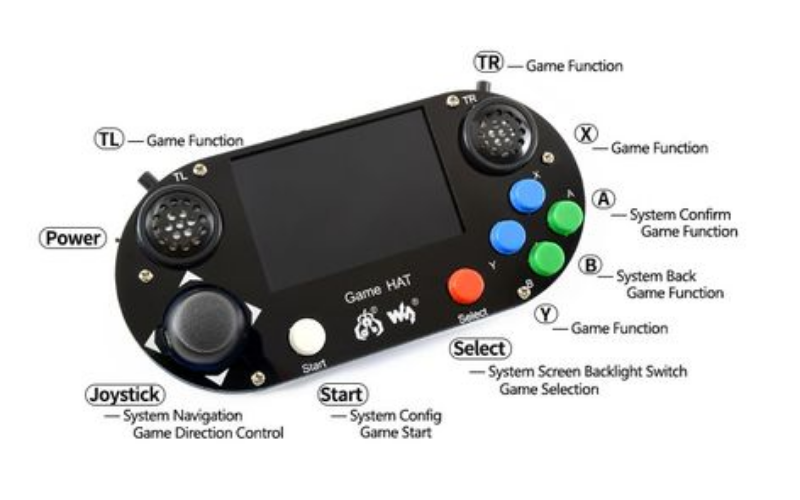
6. Gaming
Embedded systems power gaming consoles and handheld devices. They handle graphics processing, user interfaces, and real-time game logic, providing immersive gaming experiences.
7. Energy Management
Embedded systems are used to control and optimize energy consumption in smart grids, buildings, and industrial facilities. They offer real-time monitoring and automation of energy distribution and consumption enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability.

8. Security Systems
Embedded systems are the core of security systems like surveillance cameras, access control systems, and alarm systems. They process video feeds, manage access permissions, and trigger alerts, enhancing security and safety.

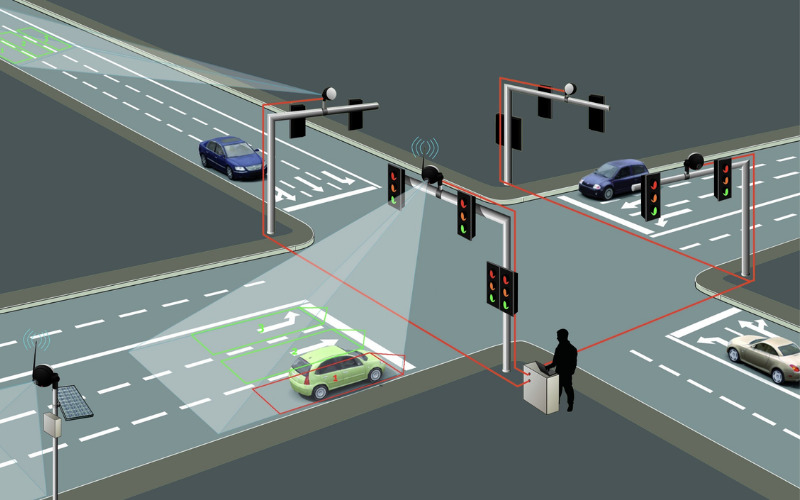
9. Traffic Control
Embedded systems control traffic lights, digital signage, and intelligent transportation systems across the city. They aid in traffic flow management, optimise signal timing, and collect traffic data for analysis. They reduce congestion and improve safety and urban mobility.
10. Elevators And Escalators
Embedded systems are integral to the operation of elevators and escalators in buildings. These systems control the movement, stopping, and levelling of the elevators, ensuring safe and efficient transportation in multi-storey structures. Elevator controllers utilise sensors and algorithms to respond to user commands and maintain precise floor alignments. Escalator control systems manage speed, direction, and safety features, enhancing the convenience and safety of vertical transportation.

11. Agriculture
Embedded systems play a pivotal role in modern agriculture facilitating precision farming and automation. These systems optimise resource utilisation and enhance crop yields. They monitor temperature, soil moisture, and nutrients, offering valuable data for decision-making. They are utilised in several applications like GPS-guided tractors, automated irrigation systems, and remote monitoring of crop conditions.

12. Scientific Instruments
Scientific instruments use embedded systems to access and collect data from several sensors and detectors. Laboratory equipment and embedded systems assess temperature, pressure, and sample handling, and ensure precise and repeatable experiments. In analytical instruments such as spectrometers or microscopes, embedded controllers offer scanning, data acquisition, and signal processing to perform complex analyses efficiently.
13. Networking Devices
Embedded systems are fundamental in networking devices such as routers, switches, and access points. These systems handle data packet routing, network protocol management, and security features. They ensure the seamless flow of data within computer networks and the internet, enabling communication between devices and users worldwide.

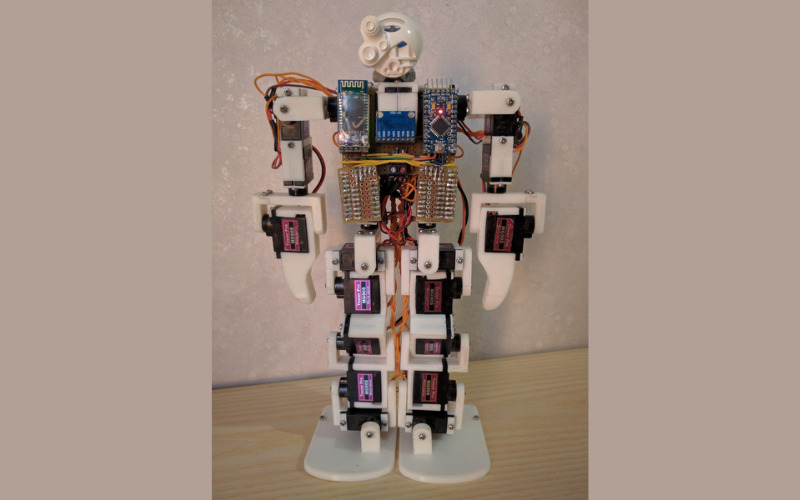
14. Robotics
Embedded systems control robot movements, sensors, and decision-making processes. From industrial robots used in manufacturing to autonomous drones and household robotic vacuum cleaners, these systems enable robots to perceive their environment, make decisions, and perform tasks autonomously.
15. Marine Electronics
Embedded systems are critical in marine applications like navigation, communication, and safety systems on ships and boats. They manage RADAR, GPS navigation, SONAR, and weather monitoring. They communicate with other vessels and coastal stations to enhance maritime safety and efficiency.

16. Gym Equipment
Modern gym equipment often includes embedded systems to provide users with interactive and personalised workouts. These systems control exercise machines, monitor users’ performance, and offer features like preset workout programs, tracking, and entertainment options. Embedded displays provide real-time feedback, creating engaging and effective fitness experiences.

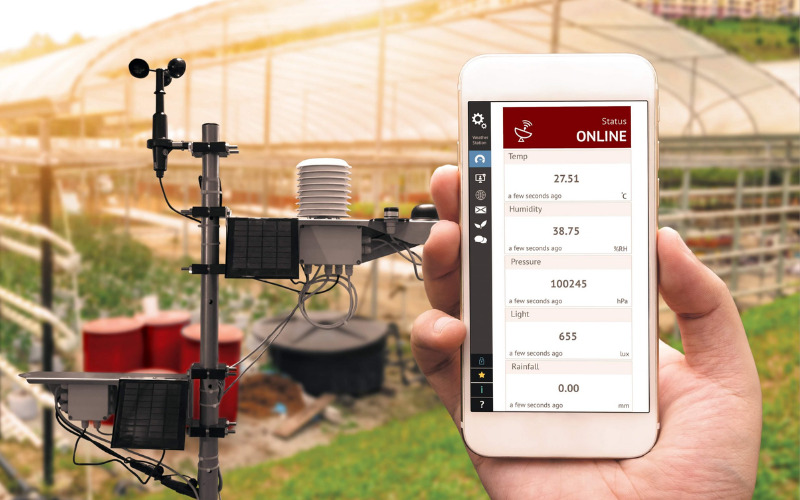
17. Environmental Monitoring
Embedded systems are deployed in environmental monitoring stations to collect air quality data, water quality, and weather conditions. They transmit this data to central hubs or online platforms, enabling real-time monitoring of environmental parameters and early detection of issues like pollution or extreme weather events.

18. Cameras
Embedded systems are a core component of digital cameras and surveillance cameras. They manage image capture, processing, storage, and transmission. These systems ensure high-quality image and video capture, support features like autofocus and image stabilization, and enable remote monitoring and recording in security cameras.

19. Aerospace
Embedded systems transformed the aerospace industry, enabling the safe and efficient operation of aircraft and spacecraft. They manage critical functions like navigation, flight control, engine monitoring, and communication. They use sensors, GPS, accelerometers, and gyroscopes to ensure precise flight paths, stability, and safety. They track and adjust aircraft parameters continuously, aiding pilots to maintain control and respond to changing conditions.

20. Audio Systems
Embedded systems are pervasive in modern audio systems, enhancing sound quality, functionality, and user experience. In-home audio equipment like soundbars, AV receivers, and smart speakers, embedded systems control audio processing, equalization, and the integration of streaming services. They also enable multi-room audio synchronization and voice recognition for hands-free control. Portable audio devices, such as smartphones and headphones, integrate embedded systems to decode audio formats, manage wireless connections (e.g., Bluetooth), and extend battery life through power-efficient processing. Noise-cancelling headphones use embedded systems to analyse and counteract external sounds, providing a quieter listening experience.





















