In this digital era, cybersecurity plays a vital role in safeguarding sensitive data and stopping cyber threats, which have become increasingly more advanced and prevalent. Cybersecurity is the process of protecting networks, computer systems, and information from unauthorized access, harm, or theft. It uses several technologies, procedures, and practices for safeguarding data and ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. It demands steady updating, monitoring, and adapting to threats and technology. It is an integral part of today’s digital world, where digital technologies and the web have increased exponentially. It is a crucial part of the latest commercial operations for shielding sensitive records and keeping trust with clients and stakeholders. Here are some features of its tools:
1. Firewall Protection
Firewalls are a barrier between a trusted internal network & untrusted external networks (typically the Internet). They examine incoming and outgoing network traffic, permitting or blocking data packets based on predefined security rules. Firewalls help prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. They can be hardware or software-based.
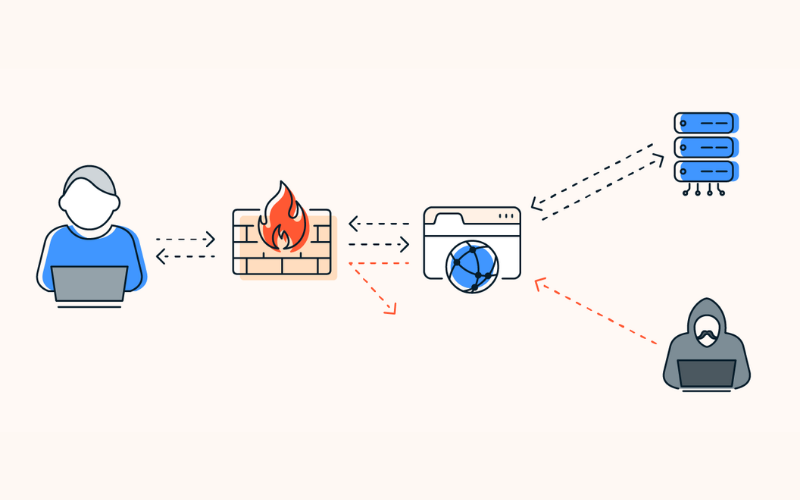
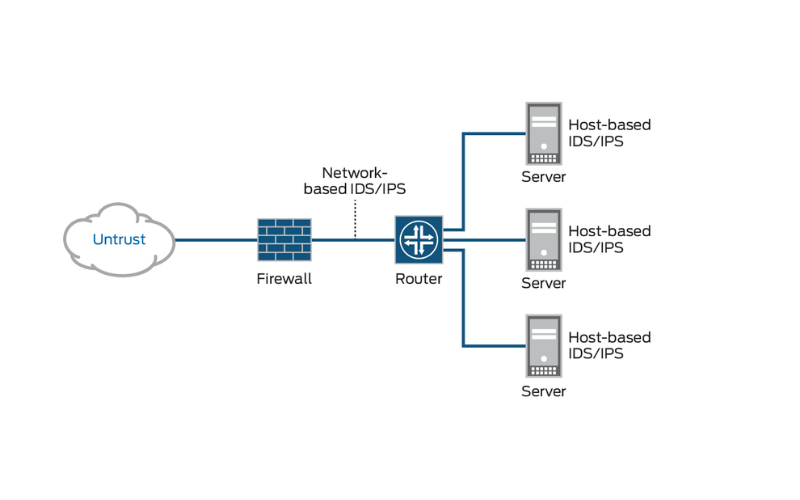
2. Intrusion Detection/Prevention System (IDS/IPS)
IDS and IPS are security systems designed to detect and respond to suspicious activities and potential threats within a network. IDS monitors network traffic and system activity, looking for patterns that match known attack signatures. When it identifies a possible intrusion, it generates alerts for further investigation. IPS actively blocks or mitigates threats in real-time based on predefined security policies. It can respond to detected threats automatically.
3. Antivirus And Antimalware
Antivirus and antimalware applications prevent, detect, and remove malicious software (malware) from personal computers, mobile devices, and networks. It includes viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, and other threats. They use signature-based and behaviour-based analysis to identify and quarantine or remove malware.

4. Data Encryption
Data encryption converts plain-text data into a secure, unreadable format (cipher text) to protect it from unauthorized access. It secures data during transmission (e.g., SSL/TLS for web traffic) and storage (e.g., encrypted hard drives).

5. Two-factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds a layer of security beyond a username and password. It asks users to give two different authentication factors, typically something they know (password) and something they have (e.g., a mobile app-generated code or a physical token).

6. Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanning tools identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities in a network or system. These tools perform automated scans to discover security flaws, misconfigurations, and outdated software. Administrators patch or mitigate the identified vulnerabilities, reducing the attack surface.

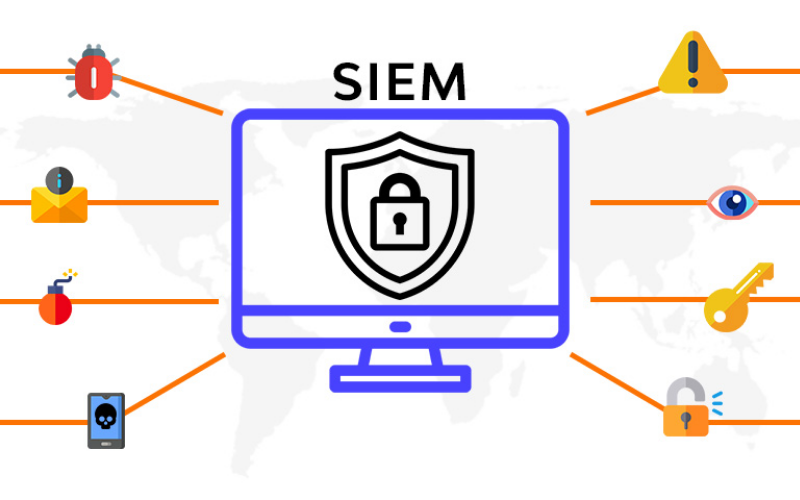
7. Security Information And Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM is a comprehensive solution combining security event management (SEM) and security information management (SIM). It centralizes the security-related data from several sources like logs and network traffic. It offers threat detection, real-time monitoring, and incident response capabilities. They identify and respond to security incidents and for meeting compliance requirements.
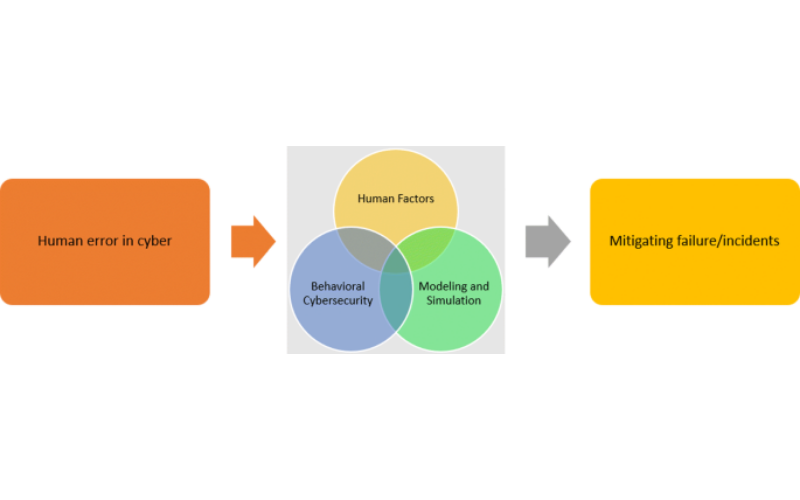
8. Behavioural Analysis
Behavioural analysis focuses on monitoring the behaviour of users and systems within a network. It establishes a baseline of normal behaviour and alerts when deviations from this baseline occur. It detects zero-day attacks and insider threats that may not have known signatures.
9. Network Monitoring
Network monitoring tools track network traffic and device status continuously. They offer insights into traffic patterns, network performance, and potential issues. It identifies anomalies that could indicate security threats or operational problems. Network monitoring is essential for maintaining network availability, integrity, and confidentiality.

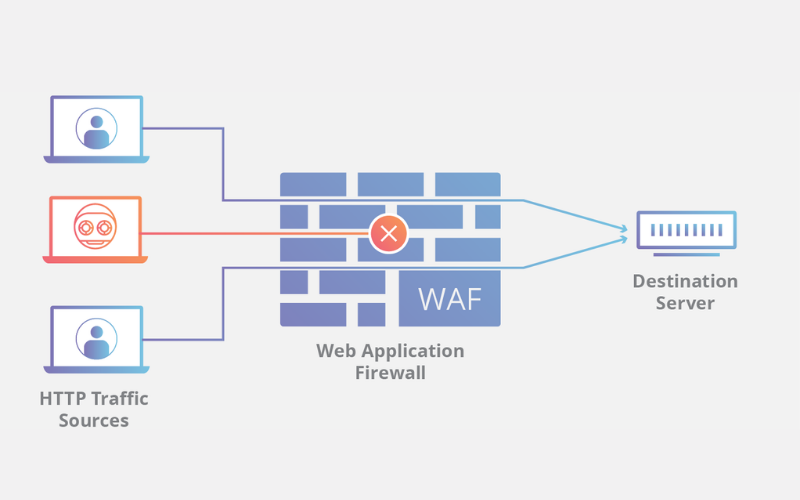
10. Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Web Application Firewall is a security solution that protects web applications from various online threats, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other web-based attacks. WAFs filter and inspect web traffic, allowing legitimate traffic while blocking malicious requests. They help safeguard web applications and protect sensitive data.
11. Endpoint Protection
Endpoint protection secures individual devices (endpoints), such as computers, smartphones, and tablets, from cybersecurity threats. It includes antivirus software, host-based intrusion detection, and firewalls. It is vital as endpoints are common entry points for cyberattacks.
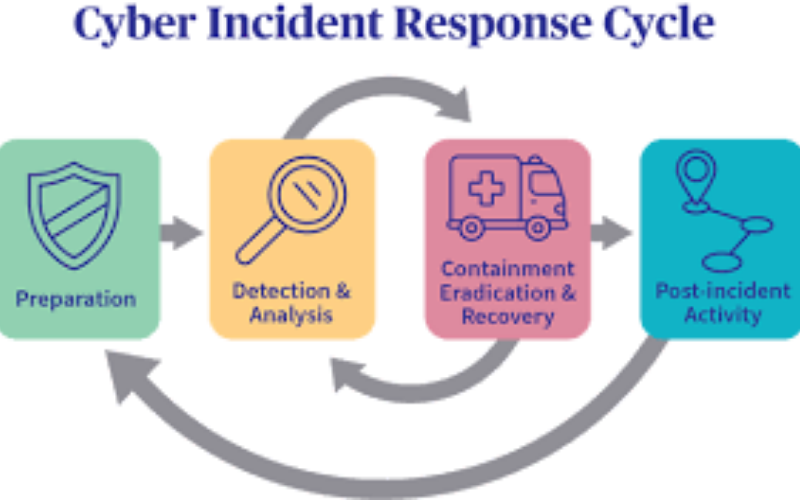
12. Incident Response
A structured method of mitigating and controlling cybersecurity issues is called incident response. Strong incident response mitigates the effects of a breach and averts similar incidents in the future. It summarises processes for identifying incidents, containing threats, and restoring normal operations.
13. Security Auditing And Compliance
Security auditing involves assessing an organization’s adherence to security policies and industry regulations. It ensures that security controls are adequate and in place. Compliance refers to meeting specific security standards and legal requirements. Security auditing and compliance activities help firms identify and rectify security gaps.
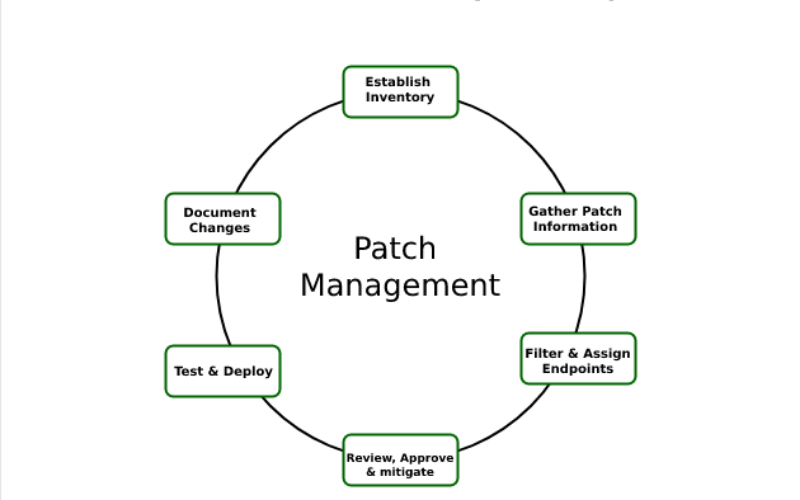
14. Patch Management
The process of updating operating systems, software, and applications with the most recent security patches and upgrades is known as patch management. Attackers may take advantage of software vulnerabilities; therefore, timely patching helps protect against security breaches. It automates the patch deployment and ensures systems are protected from known vulnerabilities.
15. Secure File Transfer
One essential component of data safety is secure file transfer. Safe file transfers can be achieved via secure protocols and encryption, necessary for complying with data protection regulations. It ensures that files are exchanged securely between people or systems, protecting private data from being accessed or intercepted in transit.

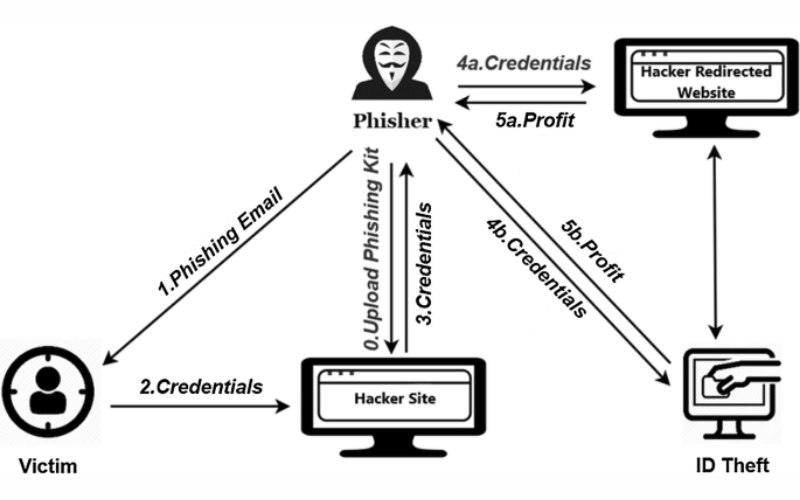
16. Phishing Detection And Prevention
Phishing detection and prevention solutions use several methodologies, like URL analysis, email filtering, and behavioural analysis, to identify and block phishing attempts. It is vital for protecting against phishing attacks aimed at firms and individuals.
17. URL Filtering
URL filtering involves controlling access to websites based on their URLs. It allows firms to restrict access to malicious or inappropriate websites, reducing the risk of malware infections and maintaining productivity. URL filtering solutions maintain categorized website databases and apply policies to allow or block access based on predefined criteria.
18. Application Whitelisting/Blacklisting
Application whitelisting and blacklisting are strategies to control which software applications are executed on a system. Whitelisting allows only approved applications to run while blacklisting blocks known or unauthorized applications. This approach aids in preventing malicious or unauthorized software from running on devices, enhancing security and compliance.

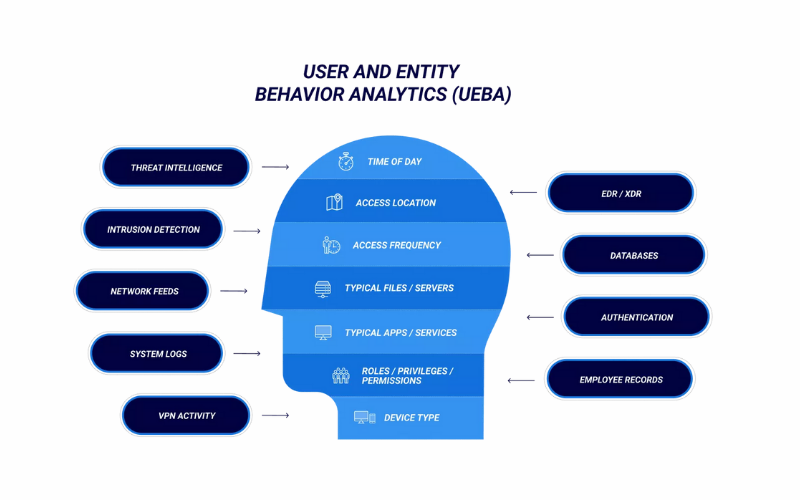
19. User And Entity Behaviour Analytics (UEBA)
UEBA solutions employ machine learning and behavioural analysis to identify abnormal activities or deviations from expected user and entity behaviours. It improves security by providing risk assessment and real-time threat detection. By tracking user actions, insider threats, compromised accounts, and other suspicious activities that may go unnoticed using traditional security measures can be identified.
20. Automated Threat Response
Automated threat response tools enable organizations to automate the process of identifying, mitigating, and responding to security incidents. These solutions can automatically apply predefined actions when specific threats are detected, reducing response time and minimizing the impact of security breaches. Automated threat response is for addressing threats promptly in the era of rapidly evolving cyberattacks.