Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that processes data closer to its source, instead of sending it to a centralized cloud or data centre for evaluation. It is revolutionising industries by allowing innovative applications and use cases that rely on real-time data evaluation and rapid decision-making. It is especially applicable in IoT, manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, retail, and smart cities, wherein timely insights are important. It enables faster data processing, decreased latency, and better real-time decision-making. As the proliferation of connected devices continues, its significance is expected to grow further, contributing to a more efficient and responsive digital ecosystem. Here are some of functionalities of Edge Computing:
1. Low Latency
Low latency is a main feature of edge computing for instantaneous data processing and response times. In traditional cloud computing, information travels to distant data centres for analysis, leading to delays due to network latency whereas Edge computing places computational resources closer to the data source, minimizing the time for data transmission and response.
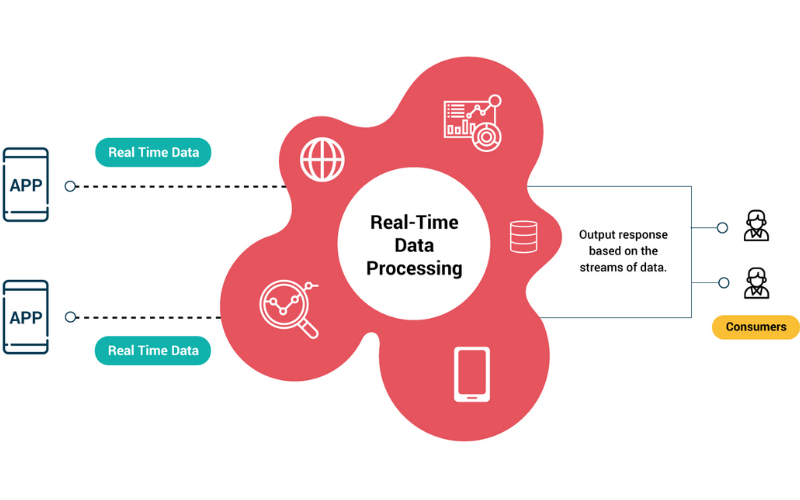
2. Real-time Processing
Real-time processing is an important feature of edge computing enabling immediate data analysis and decision-making. This feature is for applications requiring rapid responses and instant insights like industrial IoT, healthcare monitoring, and financial trading, data needs to be processed as soon as it is generated to trigger timely actions.
3. Decentralization
Decentralization is a core tenet of edge computing, as it requires distributing computing resources across multiple edge nodes or devices. Unlike traditional centralised cloud models, where data is processed in remote data centres, edge computing pushes processing closer to the data source. It is valuable for applications requiring rapid processing, autonomous decision-making, and scalability.

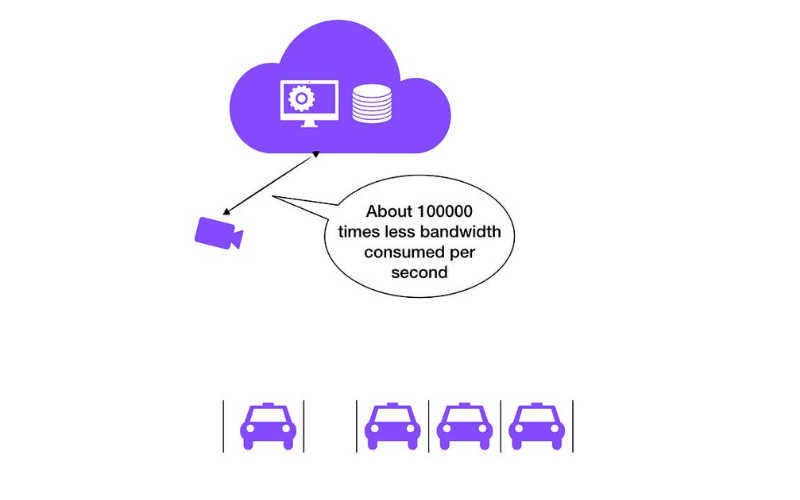
4. Reduced Bandwidth Usage
Edge computing minimises the need for transmitting huge volumes of data over networks to principal cloud servers for evaluation. Instead, information is processed and filtered at the edge, sending the most effective applicable data to the cloud. It reduces bandwidth consumption and optimises network sources. It contributes to faster data transmission times and lower latency, ultimately enhancing the application’s overall performance and responsiveness.
5. Improved Reliability
Edge computing enhances reliability by distributing computing and processing tasks across multiple edge nodes. This approach mitigates the risk of a single factor of failure disrupting the entire network, making the overall system resilient. In cases of network connectivity issues or cloud outages, devices can function independently, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
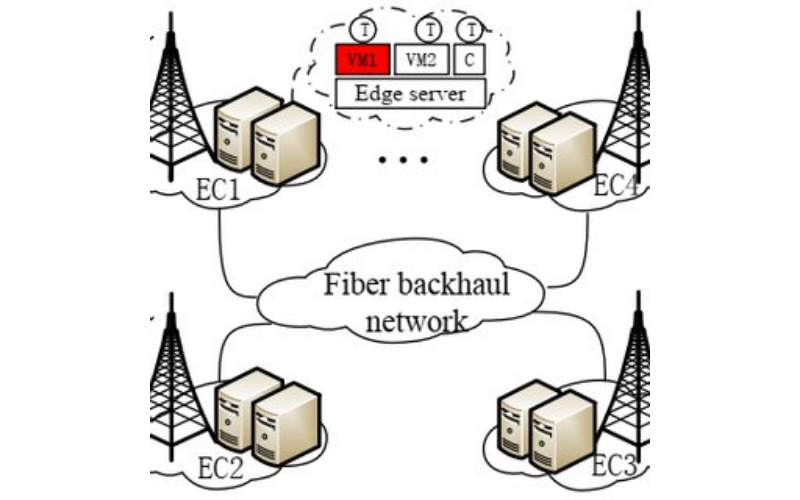
6. Enhanced Security
Edge computing improves security by permitting data to be processed and analysed regionally, minimising the need to transmit sensitive information over networks. It reduces the attack surface and points of vulnerability. Edge Devices use security measures like encryption, authentication, and access controls directly on the source.
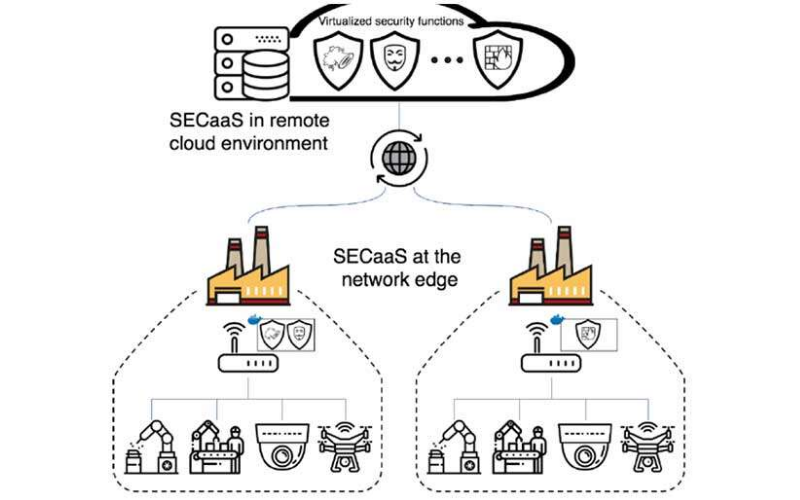
7. Autonomous Operation
Autonomous operation is a pivotal characteristic of edge computing that enables devices and systems to feature independently with minimum human intervention. In an edge computing environment, devices have the intelligence to make decisions and perform actions locally, without relying on constant communication with a centralized cloud server. It is useful in scenarios where real-time responses are crucial and network connectivity is probably unreliable.

8. Edge Analytics
Edge analytics refers to the capability of performing data analysis at devices or nodes without the need to transmit data to a centralised cloud for processing. This feature permits firms to extract valuable insights and generate intelligence from data. Edge analytics is relevant in applications in which real-time insights are required for decision-making.
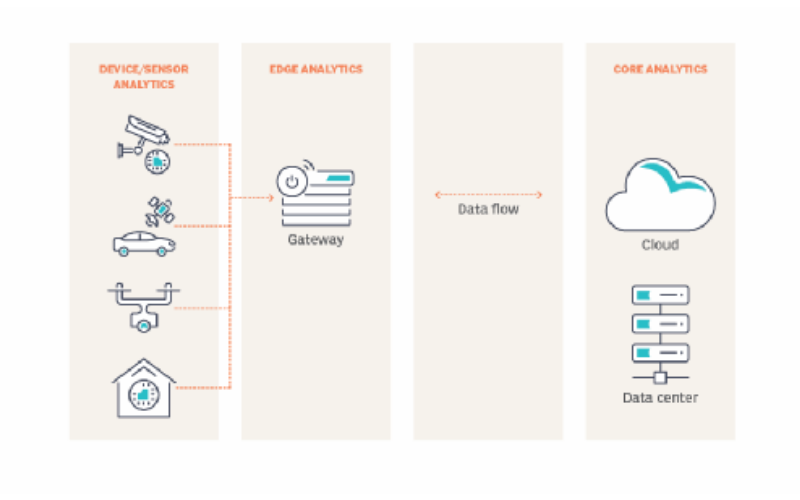
9. IoT Integration
Internet of Things (IoT) integration is a foundational aspect of edge computing, as these principles are deeply intertwined. Edge computing offers the infrastructure to help IoT devices by permitting data processing and evaluation near the data centre. This integration enhances the capabilities of IoT devices, allowing them to perform tasks beyond simple data collection.
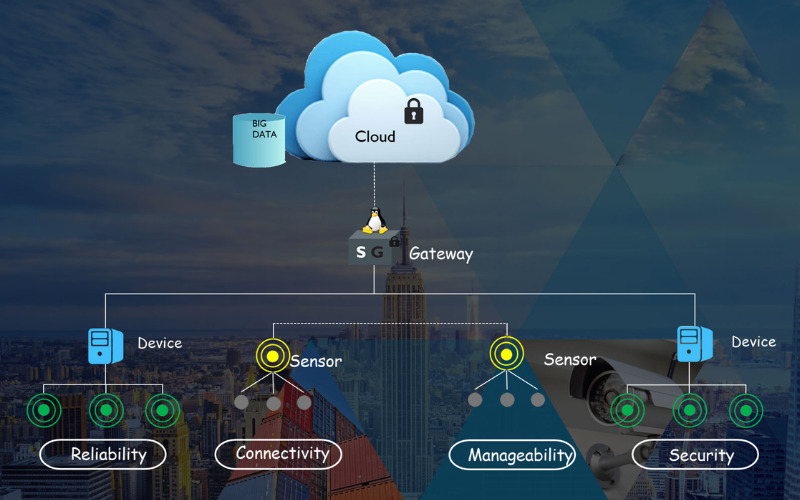
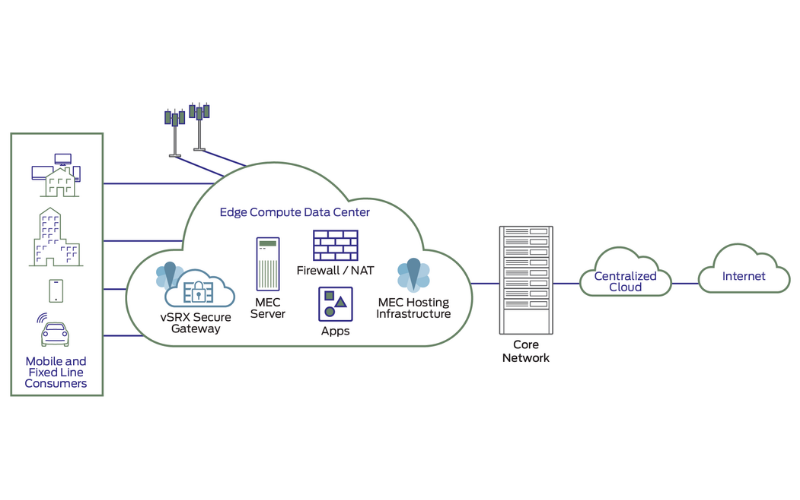
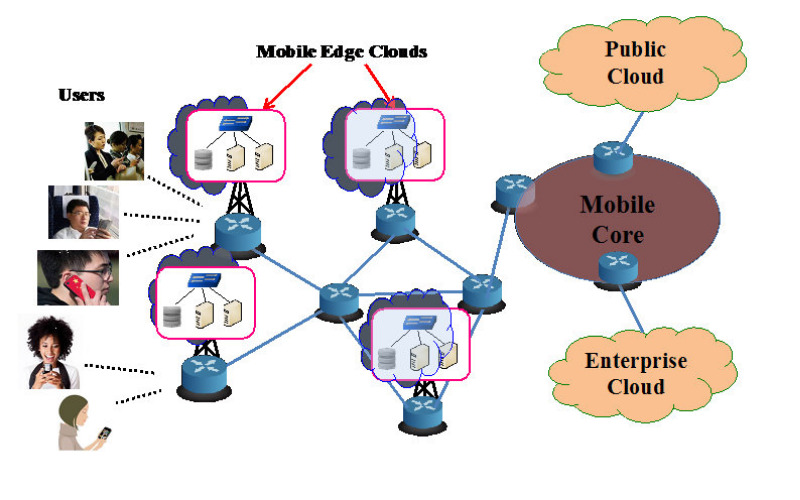
10. Mobile Edge Computing (MEC)
Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) is an extension of edge computing specifically tailor-made for mobile networks and gadgets. It brings computational abilities for cellular base stations, lowering latency and enhancing the quality of mobile applications. It is important for applications that require low-latency communication, such as Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality.
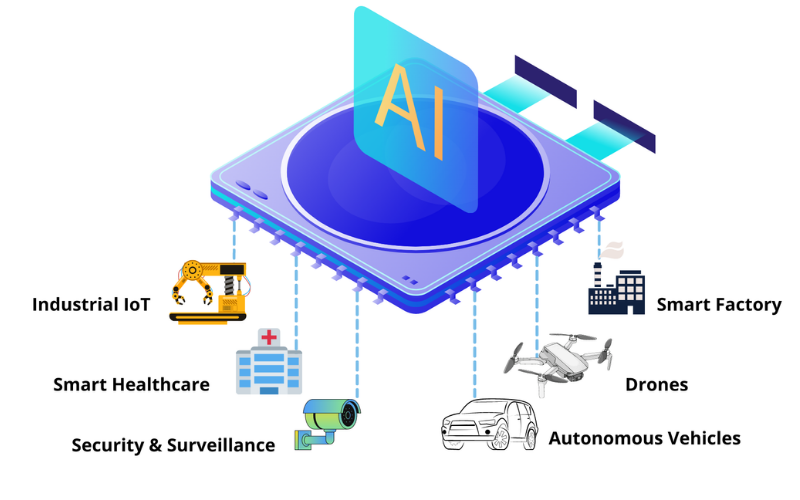
11. AI At The Edge
AI at the Edge refers to the combination of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities directly into edge devices. It performs state-of-the-art data evaluation and decision-making locally, without depending on cloud resources. It permits applications consisting of real-time image recognition, predictive maintenance, and autonomous decision-making.
12. Local Data Storage
Local information storage is an essential function of edge computing permitting data to be stored on edge devices or nodes. It is for applications that need quick access to data and offline access features. It reduces latency and enables data-driven actions even in environments with restricted or intermittent connectivity. It ensures that relevant data is available without relying on constant network connectivity.

13. Edge Orchestration
Edge orchestration is the intelligent management and coordination of edge sources and services to ensure overall performance and efficiency. This feature involves allocating computational tasks dynamically, data processing, and communication across edge devices to achieve outcomes. It optimizes resource usage, minimises latency, and ensures proper load balancing.
14. Customized Data Processing
Customized data processing includes tailoring information evaluation and processing methodologies to applications and use cases. Edge computing allows businesses to define and enforce data processing pipelines that cater to their precise requirements. This flexibility enables fined-tuned data analytics, real-time decision-making, and immediate response to events.

15. Fog Computing
Fog computing, related to edge computing, extends the concept by developing a hierarchical structure consisting of intermediate nodes between edge devices and centralized cloud servers. These intermediate nodes, known as fog nodes, offer computational and storage abilities closer to edge devices whilst enabling more advanced processing than typical edge devices. Fog computing is suitable for applications requiring stability between local processing and cloud resources.
16. Edge Security
Edge security addresses the protection of information, applications, and devices at the edge of the network. It encompasses authentication, encryption, access control, intrusion detection, and malware prevention. It is apt for applications such as commercial automation to healthcare, in which data privacy and operational integrity are paramount.

17. Scalability
Scalability in edge computing refers to the ability of the system to accommodate many devices and applications without sacrificing performance or efficiency. It is carried out by techniques like load balancing, resource pooling, and dynamic allocation of computing resources. By ensuring scalability, firms can future-proof their edge computing deployments and support several use cases while maintaining amazing service delivery.
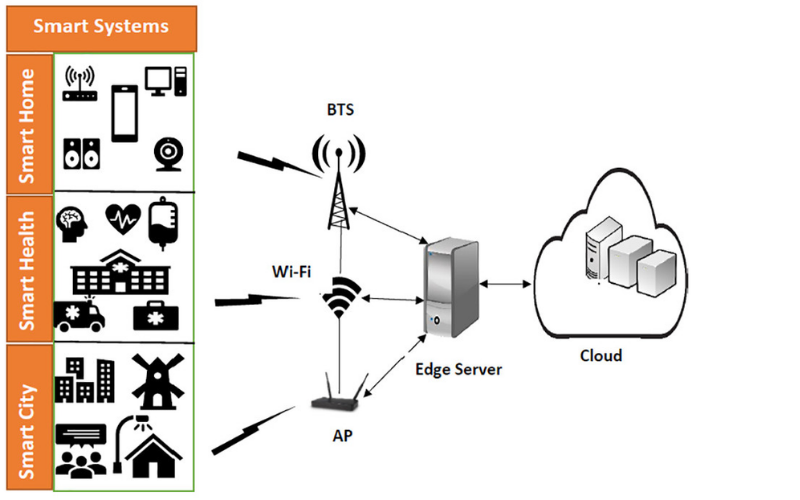
18. Energy Efficiency
Energy Efficiency focuses on minimizing energy consumption while maintaining performance. Edge devices perform with limited power resources, making energy-efficient operations vital. By processing information locally and avoiding the necessity to transmit it to remote data centres, edge computing reduces power consumption related to data transmission.
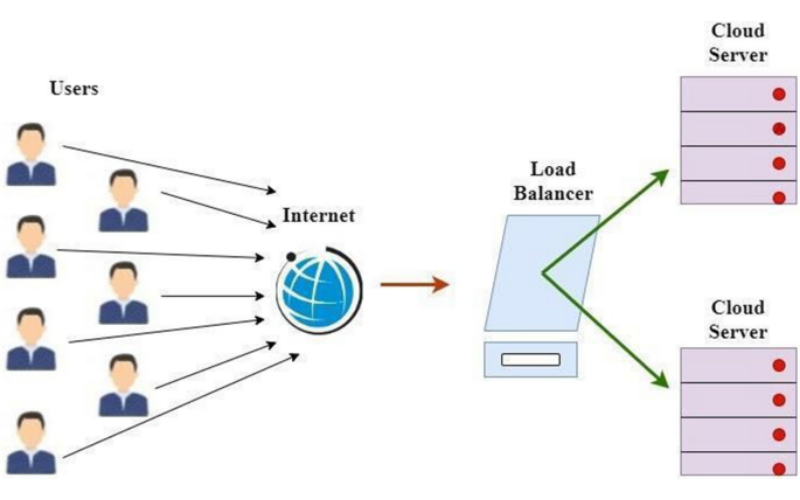
19. Edge-to-Cloud Synergy
Edge-to-cloud synergy involves the seamless collaboration and data transfer between edge devices and centralised cloud resources. It ensures that information gathered at the edge is transmitted to the cloud for processing, historical analysis, or global insights. It addresses low-latency processing and real-time decision-making.
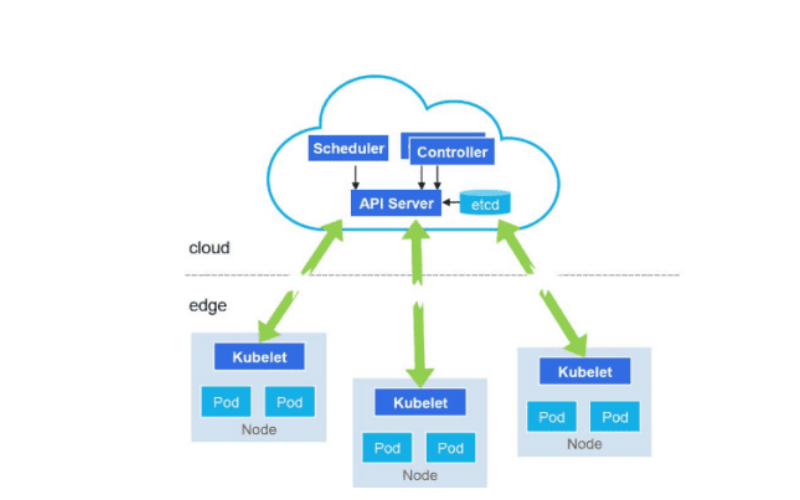
20. Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC)
Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) extends edge computing abilities by providing a standardized platform for deploying applications and services at the network edge. It permits service providers and application developers to deploy software features towards end-users, lowering latency and improving user experience.