There is a desire for most to live in a green and clean world. It is becoming a new norm as there is intent to strategize the use of natural resources. Green computing, also called eco-friendly computing or sustainable computing, is the way of designing, using, and removing computing resources in an environmentally responsible manner. Green computing intends to decrease the negative impact of information technology on the environment whilst optimizing performance and resource usage. When it comes to sustainability, concerns like raw material resourcing, and pollution reduction are major issues to be addressed. Here are a few green computing practices:
1. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a fundamental principle of green computing, aiming to lessen the power consumption of computing systems whilst maintaining or improving performance. It optimises hardware parts and software applications to minimize energy wastage throughout operation. Techniques such as dynamic voltage scaling, power gating, and efficient algorithms contribute to green computing, ensuring in cost savings and a smaller carbon footprint.

2. Virtualization
Virtualization includes developing virtual instances of computing resources, inclusive of servers, storage, or networks, on a single physical system. This enables efficient resource utilization, as multiple virtual machines can run concurrently on a single server, decreasing the requirement for several physical machines. It reduces energy consumption, hardware cost, and space requirements in data centres, promoting a greater sustainable IT environment.
3. Power Management
Power management encompasses strategies and technologies to control the power consumption of devices and systems. It includes techniques like sleep mode, hibernation, and shutting down idle devices when not in use. It guarantees that devices function at optimal energy levels, minimizing energy waste without compromising in functionality.

4. Renewable Energy Sources
Utilising renewable resources like sun, wind, and hydropower to power IT infrastructure reduces the dependence on fossil fuels and minimises greenhouse gas emissions. Data centres can be integrated into renewable energy systems for their operations, powering servers, cooling systems, and networking equipment sustainability.

5. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers scalable and shared resources through virtualization, allowing customers to access computing power and storage on demand. Cloud vendors optimize data centres for performance, consolidating sources and reducing power consumption through efficient cooling and server utilization. It assists in workload migration to regions with cleaner energy resources, contributing to greener operations.
6. Energy-Efficient Cooling
Data centres generate heat from server operation, requiring cooling systems to maintain optimal temperatures. Energy-efficient cooling techniques encompass hot and cold aisle containment, economizers, and liquid cooling. By handling heat effectively, data centres reduce power consumption and limit the environmental impact of cooling infrastructure.

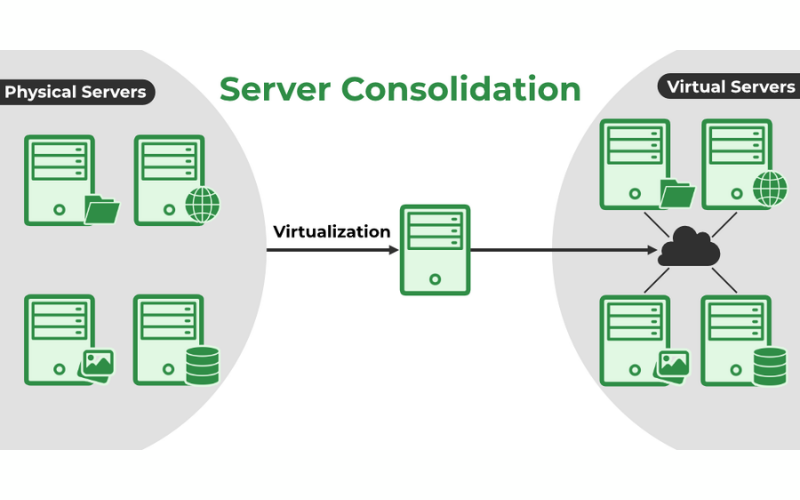
7. Server Consolidation
Server consolidation includes the process of merging physical servers into fewer, more effective servers by virtualization. This practice optimizes resource usage by decreasing the underutilized servers. Fewer servers cause minimal power consumption, reduced cooling needs, and decreased space requirements in data centres. It improves overall performance, reduces costs, and minimizes the environmental impact of IT operations.
8. Green Data Centers
Green data facilities are designed with a focus on energy efficiency and sustainability. They contain technology such as energy-efficient hardware, advanced cooling systems, and renewable resources to minimize electricity consumption and carbon emissions. These data centres prioritize proper airflow management, waste reduction, and eco-friendly materials. They contribute to reduced environmental effects while maintaining high-performance computing capabilities.

9. Energy Star Compliance
Energy Star is an international standard for energy-efficient customer products and goods. In the context of green computing, Energy Star compliance indicates that IT devices, including servers, computers, and data storage devices, meet energy efficiency suggestions. These devices consume minimum energy during operation and standby, leading to cost savings and reduced power consumption.

10. E-waste Management
E-waste management includes handling, recycling, and disposal of electronic waste, which includes old computers, monitors, and other gadgets. Green computing emphasizes lowering e-waste by extending the lifecycle of IT systems, refurbishing devices, and recycling components. Proper e-waste management prevents hazardous substances from coming into landfills and contributes to a more sustainable IT ecosystem.

11. Energy-Efficient Networking
Energy-efficient networking technologies focus on minimizing energy consumption in network infrastructure components. This includes optimizing routers, switches, and networking protocols to reduce energy utilization without sacrificing overall performance. Methodologies like Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) and smart power management contribute to minimising power consumption in networking equipment.

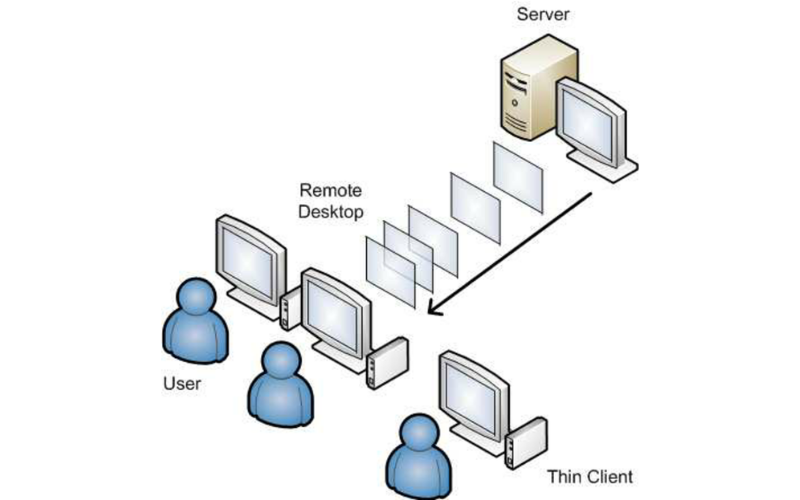
12. Thin Client Computing
Thin client computing uses lightweight, energy-efficient devices to access applications and data hosted on central servers. These devices require much less power than conventional computer systems because most processing occurs at the server level. It lessens power consumption, extends hardware lifespan, and simplifies IT management.
13. Dynamic Voltage Scaling
Dynamic Voltage Scaling (DVS) is a method used in green computing to adjust the voltage supplied to a processor or different hardware components based on the workload. By dynamically scaling voltage and frequency, the hardware can operate at lower power levels for minimum usage, lowering energy consumption. It allows optimal performance while minimizing power utilization, making it a critical element in energy-efficient computing.
14. Energy Monitoring
Energy monitoring includes tracking and analysing energy consumption patterns within IT systems and data centres. By tracking power utilisation in real-time, businesses can detect areas of inefficiency, identify anomalies, and implement techniques to optimize energy consumption. Energy monitoring tools and technology permit informed decision-making for energy-saving.
15. Green Software Development
Green software development emphasises the creation of energy-efficient and resource-conscious software applications. Developers consider efficient code design, minimised resource utilisation, and reduced processing necessities. It offers objectives to create applications that devour fewer computational resources, resulting in low power consumption during operation.

16. Paperless Initiatives
Paperless initiatives include reducing or eliminating paper usage in office and business processes. Digital signatures, digital documentation, and online collaboration tools replace traditional paper-based workflows. They are the most effective way to reduce paper waste but also contribute to decreased resource consumption and carbon emissions associated with paper production.

17. Remote Work
Remote work, or telecommuting, allows employees to work from locations other than conventional office environments. It reduces the requirement of daily commutes, leading to decreased transportation-associated emissions and energy consumption. They aid in the effective use of workplace spaces, contributing to lower power usage in traditional workspaces.

18. Green Procurement
Green procurement includes resourcing products and services which have a reduced environmental effect. In the context of green computing, it refers to buying energy-efficient hardware, applications, and devices. Green procurement considers factors like energy consumption, recyclability, and eco-friendliness within IT assets.

19. Eco-friendly Packaging
Eco-friendly packaging uses sustainable materials and techniques for product packaging. Eco-friendly practices in businesses are the key selling point. Sustainability reduces business waste, helping the company to financially self-sustain. It lessens the environmental impact associated with transportation, manufacturing, and disposal of packaging materials.

20. Green Awareness
Green awareness encompasses instructing people and corporations about the significance of sustainable practices in computing. It involves raising attention to electricity conservation, e-waste reduction, paperless projects, and other eco-friendly practices. It promotes responsible IT practices and encourages advantageous environmental behaviours across industries.





















